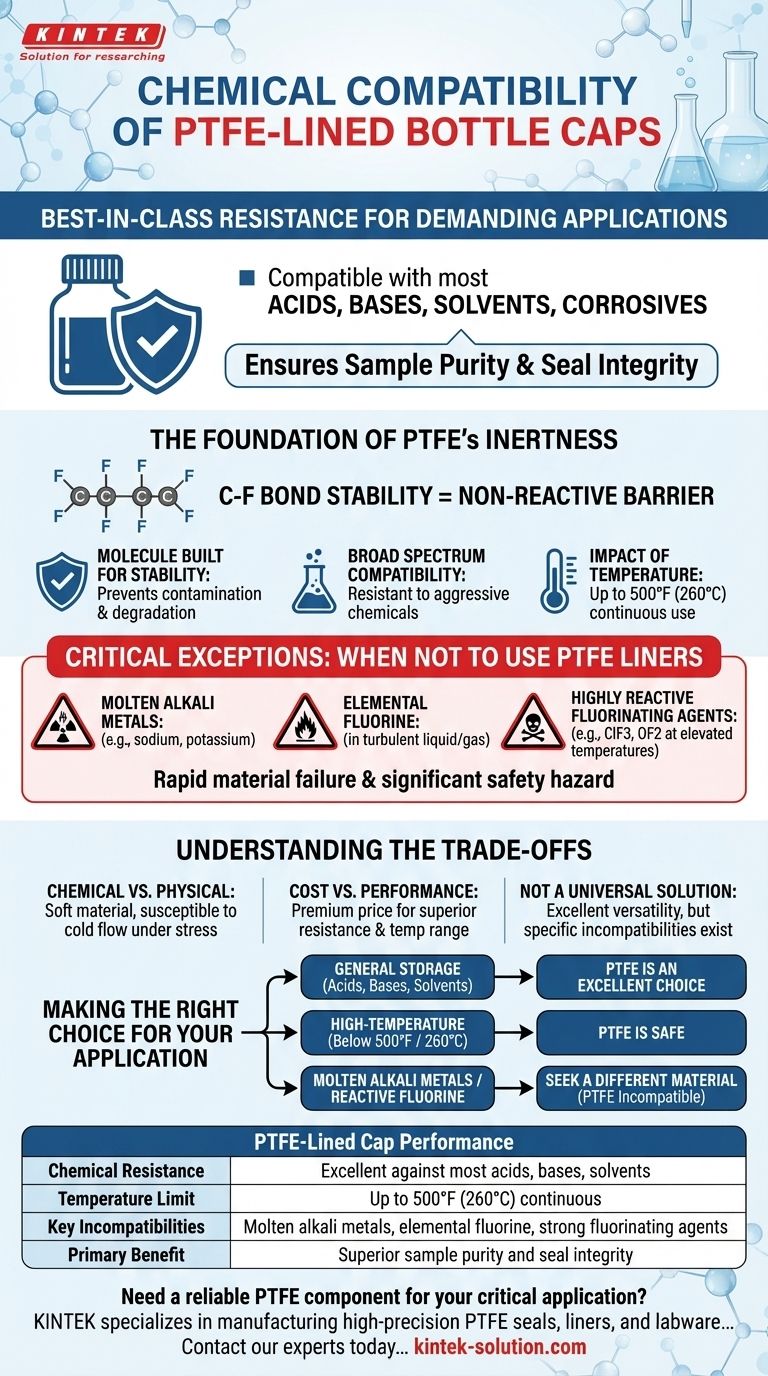
In short, PTFE-lined bottle caps offer best-in-class chemical resistance. They are compatible with a vast range of aggressive chemicals, including most acids, bases, solvents, and other corrosive substances. This makes them a default choice for demanding laboratory and industrial applications where sample purity and seal integrity are paramount.
While PTFE is a nearly universal solution for chemical storage, its reputation rests on understanding its few, but critical, exceptions. True safety and reliability come from knowing not just where it excels, but also where it will fail.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Inertness
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer with unique properties that make it exceptionally non-reactive. Its performance is rooted in its molecular structure, which provides a reliable barrier between your container's contents and the outside environment.
A Molecule Built for Stability
The strength of the carbon-fluorine bond is one of the most powerful in organic chemistry. This molecular structure makes PTFE essentially inert, meaning it will not react with the substances it contains, preventing both contamination of the sample and degradation of the cap liner.
Broad Spectrum Compatibility
Due to its inert nature, PTFE is resistant to the vast majority of common and aggressive chemicals used in professional settings. This includes strong acids, alkalis, alcohols, and complex organic solvents that would degrade lesser materials.
The Impact of Temperature
PTFE maintains its chemical resistance up to its maximum continuous operating temperature of 500°F (260°C). Beyond this point, its structural integrity and chemical inertness can become compromised, especially in the presence of certain aggressive compounds.
Critical Exceptions: When Not to Use PTFE Liners
While its compatibility list is long, the list of exceptions is absolute. Using a PTFE-lined cap with these specific substances can lead to rapid material failure and a significant safety hazard.
Molten Alkali Metals
PTFE will react with molten alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium. This is a highly specific industrial application but represents a critical incompatibility.
Elemental Fluorine
Pure elemental fluorine, particularly in turbulent liquid or gaseous states, is one of the few substances that will chemically attack PTFE.
Highly Reactive Fluorinating Agents
Certain powerful fluorochemicals can also attack PTFE, especially at elevated temperatures. Key examples include chlorine trifluoride (ClF3) and oxygen difluoride (OF2), which can liberate free fluorine and cause liner degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a cap liner involves more than just chemical compatibility. While PTFE is a top performer in this regard, it's essential to consider its complete profile.
Chemical vs. Physical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft material. While this helps create a tight seal, it can be susceptible to deformation or "cold flow" under high mechanical stress or repeated tightening, which could potentially compromise the seal over long-term storage.
Cost vs. Performance
PTFE is a premium performance polymer. Liners made from PTFE are typically more expensive than those made from more common materials like polyethylene or polypropylene. The added cost is justified by its superior chemical resistance and temperature range.
Not a Universal Solution
The inertness of PTFE makes it an excellent choice for versatility across laboratory, industrial, and medical applications. However, the severity of its few incompatibilities means it cannot be treated as a universally perfect solution without first confirming your specific application does not involve its known exceptions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct cap liner is a critical step in ensuring safety, preventing leaks, and maintaining the purity of the stored substance.
- If your primary focus is general storage of acids, bases, or organic solvents: PTFE is an excellent and highly reliable default choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature applications: Ensure your operating temperature remains safely below the 500°F (260°C) continuous limit.
- If your primary focus is working with molten alkali metals or reactive fluorine chemistry: You must seek a different material, as PTFE is incompatible and unsafe for this use.
By understanding both its broad resistance and its specific limitations, you can confidently specify PTFE liners for maximum safety and sample integrity.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE-Lined Cap Performance |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against most acids, bases, solvents |
| Temperature Limit | Up to 500°F (260°C) continuous |
| Key Incompatibilities | Molten alkali metals, elemental fluorine, strong fluorinating agents |
| Primary Benefit | Superior sample purity and seal integrity |
Need a reliable PTFE component for your critical application? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure your materials are protected with components that offer superior chemical resistance and durability. From custom prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver the precision you need. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure the integrity of your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















