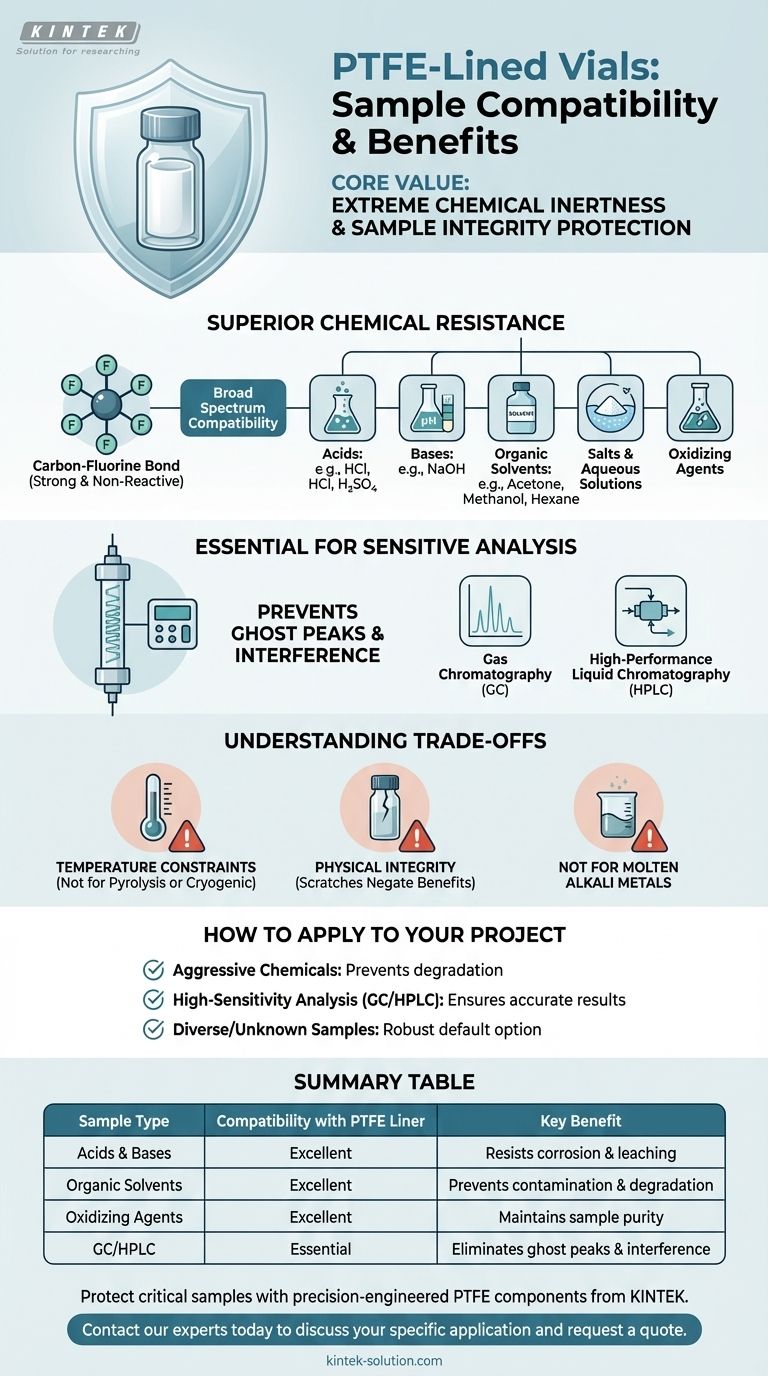
At its core, the value of a PTFE liner is its extreme chemical inertness. This property makes PTFE-lined vials compatible with a vast range of samples, including most acids, bases, organic solvents, salts, and oxidants. They are specifically engineered for laboratories that handle diverse and often aggressive chemical matrices where sample purity is non-negotiable.
The decision to use a PTFE-lined vial is fundamentally about safeguarding sample integrity. Its non-reactive surface prevents chemical leaching and contamination, which is absolutely critical when storing corrosive substances or preparing samples for highly sensitive analytical techniques like GC and HPLC.
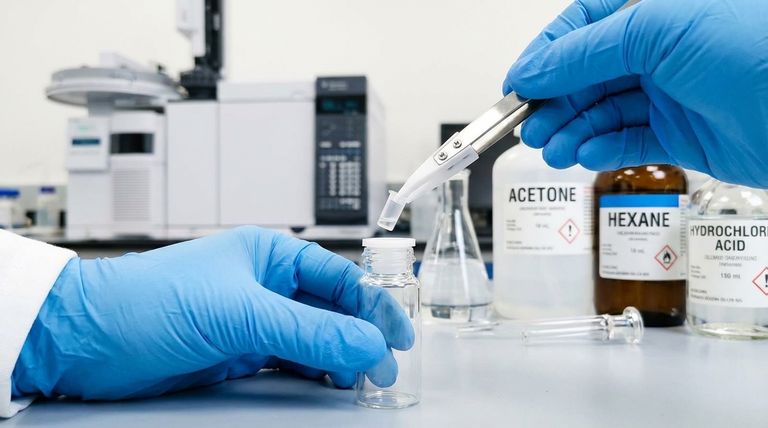

Why PTFE Liners Offer Superior Chemical Resistance
The compatibility of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is not accidental; it stems directly from its unique molecular structure. Understanding this helps clarify why it is a trusted material for demanding applications.
The Chemical Inertness of PTFE
PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry.
This powerful bond makes the material exceptionally non-reactive. It will not react with your sample, nor will it leach contaminants into your sample, preserving its original composition.
Broad Spectrum Compatibility
Because of this inertness, PTFE is resistant to a wide array of chemicals that would degrade lesser materials.
This includes:
- Acids (e.g., hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid)
- Bases (e.g., sodium hydroxide)
- Organic Solvents (e.g., acetone, methanol, hexane)
- Salts and other aqueous solutions
- Oxidizing Agents
This makes PTFE-lined vials a highly versatile and reliable choice for general-purpose and specialized laboratory work.
Essential for Sensitive Analysis
The inertness of PTFE is paramount for trace analysis techniques where even minuscule contamination can invalidate results.
In methods like gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), a non-reactive vial liner ensures that the only compounds detected are from the sample itself, not from the container. This prevents the appearance of "ghost peaks" or other analytical interference.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE offers exceptional chemical compatibility, no single material is a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its practical limitations.
Temperature Constraints
PTFE has a defined operational temperature range. It is not suitable for extremely high-temperature applications (pyrolysis) or cryogenic storage where material properties might change. Always verify the manufacturer's specifications for your specific vial.
Physical Integrity is Key
The PTFE liner is a physical barrier. If it is scratched or compromised, the underlying vial material (typically glass) will be exposed to your sample. This would negate the benefits of the liner entirely.
Not for Molten Alkali Metals
While its resistance is broad, PTFE is known to react with a few rare and highly reactive substances, such as molten alkali metals and certain exotic fluorine compounds at high temperatures and pressures. For the vast majority of laboratory applications, however, this is not a practical concern.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of vial should directly support your analytical goals. Use these guidelines to make a confident decision.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE's broad resistance to acids, bases, solvents, and oxidants makes it one of the safest and most reliable choices to prevent container degradation.
- If your primary focus is high-sensitivity analysis (GC/HPLC): The inertness of a PTFE liner is essential to prevent sample contamination and ensure you obtain accurate, reproducible results.
- If your primary focus is storing diverse or unknown samples: A PTFE-lined vial provides a robust default option, minimizing the risk of unpredictable and unwanted vial-sample interactions.
Ultimately, choosing a vial with a PTFE liner is a proactive measure to protect the integrity of your most critical samples.
Summary Table:
| Sample Type | Compatibility with PTFE Liner | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Acids & Bases | Excellent | Resists corrosion and leaching |
| Organic Solvents | Excellent | Prevents contamination and degradation |
| Oxidizing Agents | Excellent | Maintains sample purity |
| High-Sensitivity Analysis (GC/HPLC) | Essential | Eliminates ghost peaks and interference |
Protect your most critical samples with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Our PTFE-lined vials, seals, liners, and custom labware are manufactured to the highest standards of chemical inertness and precision, ensuring your sample integrity from prototype to high-volume production. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide the reliable containment solutions you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is chemical resistance important in chromatography vials? Ensure Accurate and Reliable Results
- What are the safety features of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Chemical Inertness and Sample Integrity
- How does applying a fluoropolymer film improve pharmaceutical stoppers? Enhance Drug Safety and Stability
- In what ways are PTFE silicone septas versatile for pharmaceutical applications? Ensuring Sample Integrity from Discovery to QC
- Why is temperature stability important for PTFE silicone septas in pharmaceutical processes? Ensure Data Integrity & Sample Safety
- What material is used to mold PTFE labware? The Critical Role of Pure PTFE Resin
- What materials are used in PTFE-lined bottle caps? A Guide to PP Caps and PTFE Liners
- What types of equipment are PTFE ferromagnetic support discs compatible with? Boost Your Lab's Efficiency



















