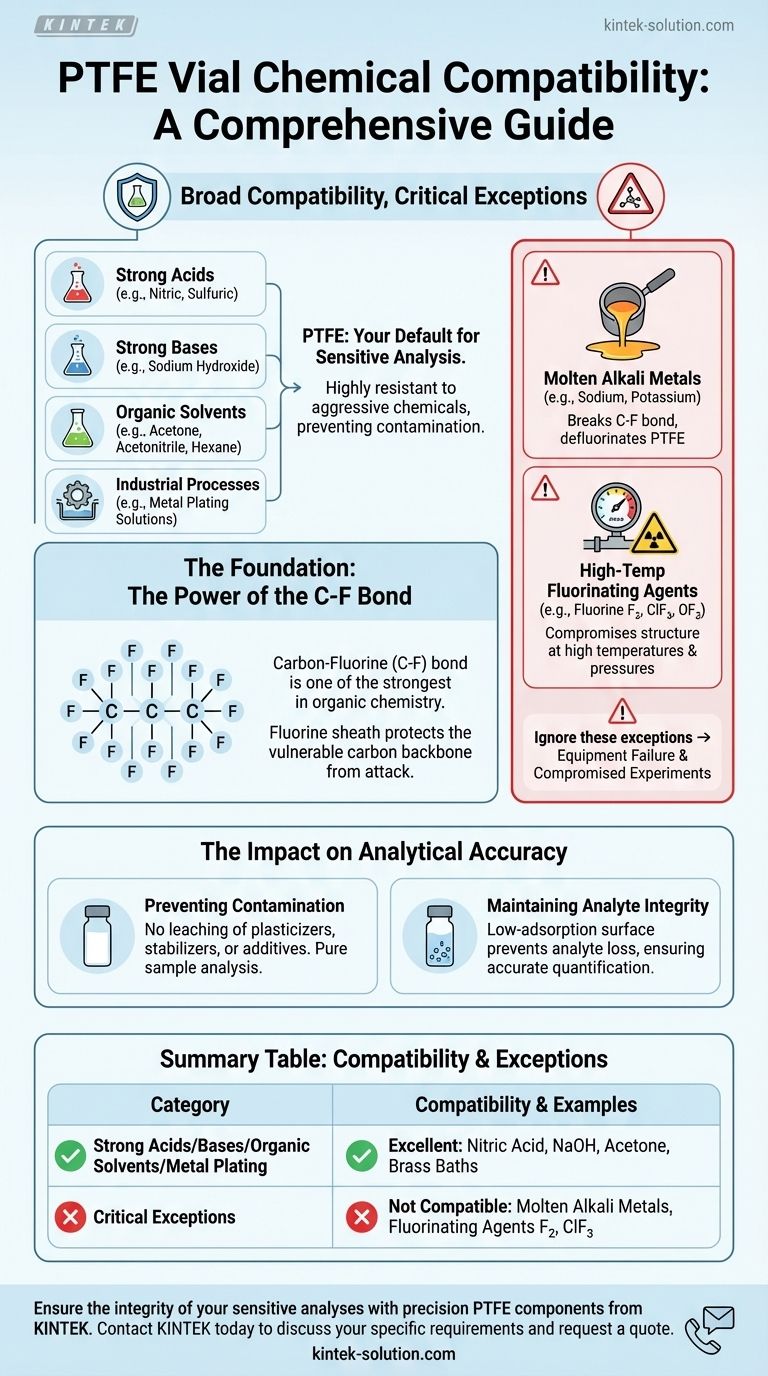
In virtually all common laboratory applications, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) vials are compatible with an exceptionally wide range of chemicals. They are highly resistant to aggressive solvents, strong acids, bases, and most organic compounds, making them a default choice for sensitive analysis where sample purity is critical.
The core takeaway is not simply that PTFE is compatible with most chemicals, but why. Its extreme inertness stems from its unique molecular structure, making it a superior choice for preventing sample contamination in high-stakes analysis like HPLC or GC. However, its few, specific chemical vulnerabilities are absolute and must be respected.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
Polytetrafluoroethylene's reputation for chemical inertness is not an exaggeration; it is a direct result of its molecular architecture. This makes it a uniquely reliable material for storing and handling sensitive samples.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by a sheath of fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This powerful bond and the tight fluorine sheath protect the vulnerable carbon backbone from chemical attack, rendering the material non-reactive to the vast majority of substances.
Broad Compatibility in Analytical Chemistry
Due to its inert nature, PTFE is an ideal material for vials used in sensitive analytical techniques like gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
It reliably contains nearly all common laboratory chemicals, including:
- Strong acids (e.g., nitric acid, sulfuric acid)
- Strong bases (e.g., sodium hydroxide)
- Organic solvents (e.g., acetone, acetonitrile, hexane)
- Aqueous solutions and buffers
Proven Performance in Industrial Processes
PTFE's robustness is not limited to the lab. It demonstrates excellent compatibility in harsh industrial environments, such as with various metal plating solutions.
This includes baths for antimony, arsenic, brass, bronze, and cadmium plating, proving its resilience against complex and reactive chemical mixtures even at elevated temperatures.
Understanding the Critical Exceptions
While its resistance is broad, it is not absolute. PTFE has a few, very specific vulnerabilities to highly reactive and uncommon substances. Ignoring these exceptions can lead to equipment failure and compromised experiments.
Molten Alkali Metals
PTFE will be attacked and degraded by molten alkali metals, such as sodium or potassium. These potent reducing agents are capable of breaking the C-F bond and defluorinating the polymer.
High-Temperature Fluorinating Agents
Certain powerful fluorinating agents can also compromise PTFE's structure, particularly at high temperatures and pressures.
These are not common lab solvents but rather highly specialized and dangerous chemicals, including elemental fluorine (F₂), chlorine trifluoride (ClF₃), and oxygen difluoride (OF₂).
The Impact on Analytical Accuracy
Choosing PTFE is often a strategic decision to protect the integrity of your results. The material's properties directly address common sources of error in chemical analysis.
Preventing Sample Contamination
Unlike many other plastics, PTFE does not contain plasticizers, stabilizers, or other additives that can leach into a sample. This ensures that what you analyze is the sample itself, free from container-derived impurities.
Maintaining Analyte Integrity
PTFE's non-reactive and low-adsorption surface prevents the vial from interacting with or binding to the analytes in your sample. This is critical for accurate quantification, as it ensures the measured concentration reflects the true concentration without loss to the container walls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your choice of vial material should be dictated by the specific demands of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis with common solvents (HPLC, GC): PTFE is an exceptionally safe and reliable choice that guarantees minimal interference with your results.
- If your primary focus is storing or analyzing aggressive reagents: PTFE provides superior chemical resistance to nearly all acids, bases, and reactive organic compounds.
- If your primary focus involves niche, highly reactive fluorine chemistry or molten alkali metals: You must select a different material, as PTFE will fail under these specific and extreme conditions.
Ultimately, understanding both PTFE's remarkable inertness and its precise limitations allows you to select your labware with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Category | Compatibility | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Acids | Excellent | Nitric Acid, Sulfuric Acid |
| Strong Bases | Excellent | Sodium Hydroxide |
| Organic Solvents | Excellent | Acetone, Acetonitrile, Hexane |
| Metal Plating Solutions | Excellent | Brass, Bronze, Cadmium Baths |
| Critical Exceptions | Not Compatible | Molten Alkali Metals, Fluorinating Agents (F₂, ClF₃) |
Ensure the integrity of your sensitive analyses with precision PTFE components from KINTEK.
Our PTFE vials, seals, liners, and custom labware are manufactured to the highest standards of purity and chemical resistance, specifically for demanding applications in semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Whether you need reliable prototypes or high-volume production, our custom fabrication services deliver the precision you need to prevent contamination and achieve accurate results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE ferromagnetic support discs composed of? A Dual-Material Design for Superior Grinding & Polishing
- What are the advantages of PTFE lids for jacketed and process vessels? Achieve Superior Durability & Chemical Resistance
- Which sensitive techniques are compatible with PTFE lined vials? Ensure Accurate Trace-Level Analysis
- What are the primary uses of PTFE silicone septa? Ensure Sample Integrity in GC/LC Analysis
- How does applying a fluoropolymer film improve pharmaceutical stoppers? Enhance Drug Safety and Stability
- Why should PTFE plugs not be used for long-term storage of liquids that attack glass? Avoid Dangerous Seal Failure
- What are the benefits of silicone/PTFE liners? Ensure Unmatched Sample Purity and Integrity
- Why are PTFE/silicone septums considered essential in chromatographic analysis? Ensure Data Integrity and Purity



















