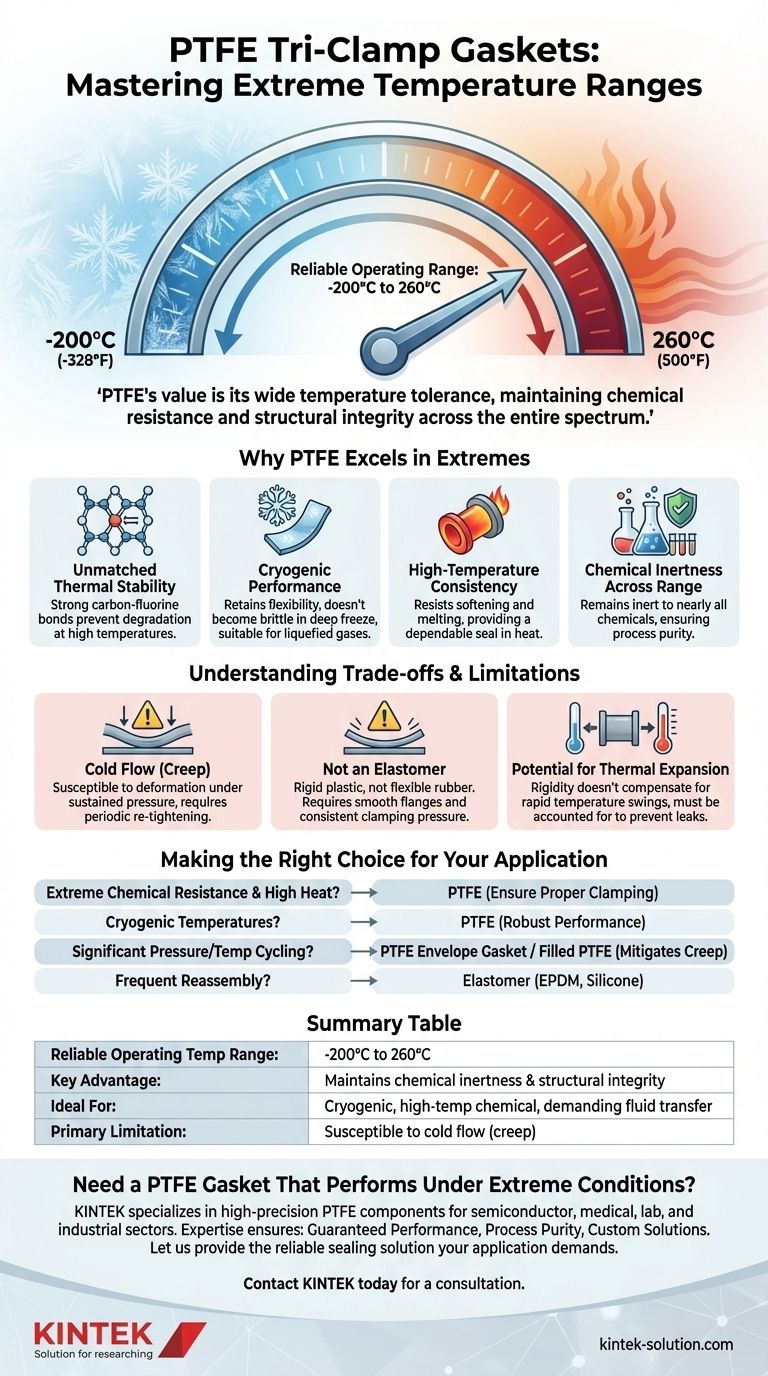
For most industrial applications, the reliable operating temperature range for a standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Tri-Clamp gasket is from approximately -200°C (-328°F) to 260°C (500°F). This remarkable range makes it suitable for everything from cryogenic processes to high-temperature fluid handling, establishing it as a key material in demanding environments.
PTFE's value isn't just its wide temperature tolerance, but its ability to maintain exceptional chemical resistance and structural integrity across that entire spectrum, from deep cryogenic lows to high-heat processing.
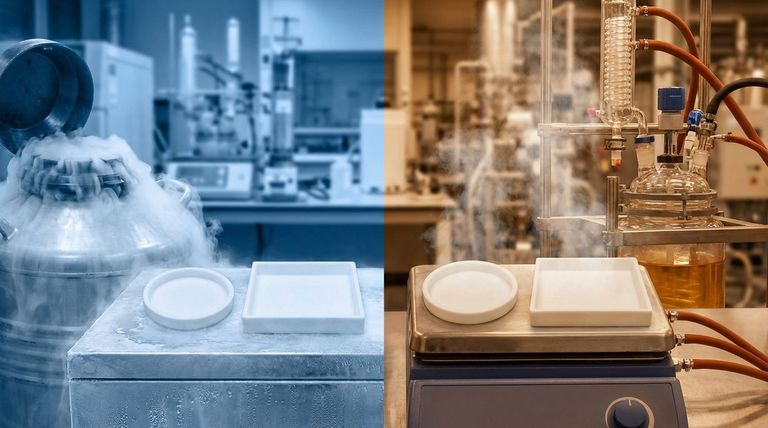

Why PTFE Excels in Extreme Temperatures
The performance of PTFE is rooted in its unique molecular structure. Understanding this provides the context for its wide operating range and helps clarify where it is best applied.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
The bond between carbon and fluorine atoms in PTFE is exceptionally strong. This inherent chemical stability is what prevents the material from degrading or breaking down when exposed to high temperatures, allowing it to maintain its form and function.
Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
Unlike many elastomeric (rubber-like) materials that become hard and brittle at very low temperatures, PTFE retains a useful degree of flexibility. This makes it a reliable choice for sealing applications involving liquefied gases and other cryogenic fluids.
Consistency at High Temperatures
At the upper end of its range, PTFE resists softening and melting. It maintains its solid structure and continues to provide a dependable seal in applications like chemical processing or high-temperature food production, where other materials would fail.
Chemical Inertness Across the Range
Crucially, PTFE’s legendary chemical resistance is not compromised by temperature fluctuations. It remains inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and acids, whether at -200°C or +260°C, ensuring process purity and gasket longevity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its temperature range is impressive, PTFE is not without its limitations. Being aware of these trade-offs is critical for successful implementation.
The Issue of Cold Flow (Creep)
PTFE is a relatively soft material that can deform or "creep" over time when subjected to sustained pressure, a tendency that increases with temperature. This means that clamp connections may require periodic re-tightening to maintain a proper seal.
Not an Elastomer
It is essential to recognize that PTFE is a rigid plastic, not a flexible rubber. It does not compress and rebound like silicone or EPDM. It creates a seal through deformation, which requires a clean, smooth flange surface and consistent clamping pressure.
Potential for Thermal Expansion
Like all materials, PTFE has a coefficient of thermal expansion. In systems that experience wide and rapid temperature swings, this expansion and contraction must be accounted for to prevent leaks. The rigidity of the material means it won't compensate for these changes as readily as a true elastomer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket material requires matching its properties to your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance with moderate to high heat: PTFE is an excellent choice, provided you ensure proper and consistent clamp pressure to prevent leaks.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic temperatures: PTFE is one of the best available options due to its robust performance and resistance to becoming brittle.
- If your system experiences significant pressure and temperature cycling: Consider a PTFE envelope gasket (which has a flexible filler) or a filled PTFE material, as these can help mitigate the effects of creep.
- If you need a gasket that rebounds after compression for frequent reassembly: An elastomeric material like EPDM or Silicone is a more appropriate choice, as rigid PTFE will not meet this need.
By understanding these properties, you can confidently leverage PTFE for its exceptional stability where it matters most.
Summary Table:
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Reliable Operating Temperature Range | -200°C (-328°F) to 260°C (500°F) |
| Key Advantage | Maintains chemical inertness & structural integrity across the entire range |
| Ideal For | Cryogenic processes, high-temperature chemical handling, demanding fluid transfer |
| Primary Limitation | Susceptible to cold flow (creep) under sustained pressure |
Need a PTFE Gasket That Performs Under Extreme Conditions?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including Tri-Clamp gaskets, seals, liners, and custom labware. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, where material integrity is non-negotiable.
Our expertise ensures your gaskets deliver:
- Guaranteed Performance: Consistent sealing from cryogenic lows to high-temperature peaks.
- Process Purity: Unmatched chemical resistance protects your critical applications.
- Custom Solutions: From rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs, tailored to your exact specifications.
Let us provide the reliable sealing solution your application demands. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the chemical resistance properties of PTFE labware? The Ultimate Guide to Inert Labware
- What is the correct placement of the PTFE washer in a stopcock plug assembly? Ensure Smooth, Leak-Free Operation
- What are the main materials considered for laboratory impellers? PTFE vs. Stainless Steel
- What is the significance of thickness in PTFE-coated septums? Maximize Durability and Analytical Reliability
- How does PTFE ensure seal integrity in chromatography vials? Achieve Leak-Free, Contaminant-Free Results
- What are the main advantages of PTFE as a material for laboratory bottles? Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How does the non-stick surface of PTFE shovels benefit laboratory work? Enhance Accuracy & Efficiency
- How is PTFE used in laboratory settings? Essential for Chemical Resistance and Sample Purity



















