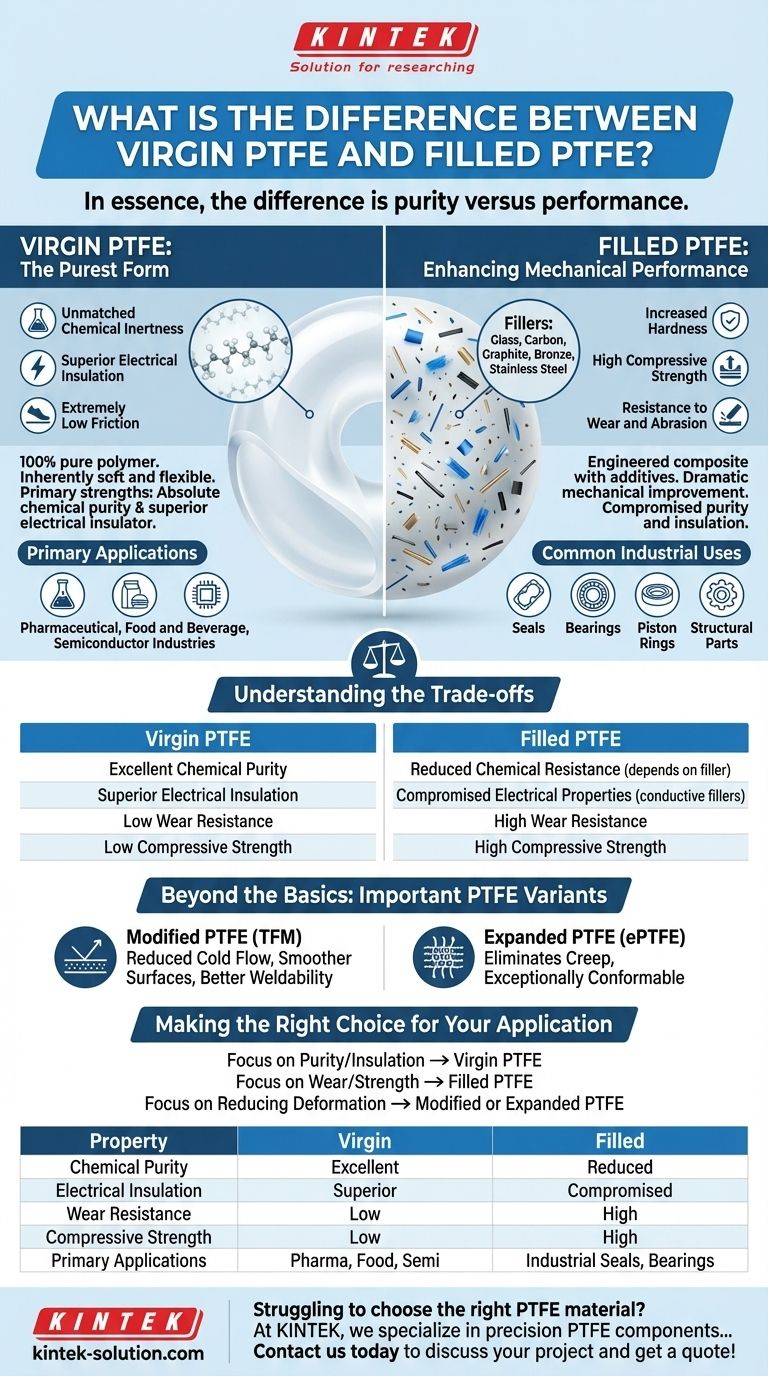
In essence, the difference is purity versus performance. Virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the pure, unadulterated polymer, prized for its exceptional chemical inertness and electrical insulation. Filled PTFE, by contrast, is a composite material where additives like glass, carbon, or bronze are blended into the base PTFE to enhance specific mechanical properties like hardness, wear resistance, and strength.
Choosing between virgin and filled PTFE is a fundamental trade-off. Virgin PTFE offers unmatched chemical purity and electrical insulation, while filled PTFE sacrifices some of these pristine qualities to gain superior mechanical durability for demanding industrial applications.

The Foundation: Core Properties of All PTFE
Before comparing variants, it's crucial to understand the baseline characteristics that make PTFE a unique and valuable material. All forms of PTFE share these foundational traits.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents. This makes it an ideal material for handling corrosive substances.
Extremely Low Friction
Often cited as the most slippery solid material known, PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This non-stick quality is critical for bearings, seals, and low-friction coatings.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE has outstanding dielectric properties, meaning it is an excellent electrical insulator. This makes it indispensable in high-frequency electronics and cable insulation.
Wide Temperature Range
The material maintains its properties across a vast range of temperatures, performing reliably in both cryogenic conditions and high-heat environments.
Virgin PTFE: The Purest Form
Virgin PTFE is 100% pure polymer without any filler materials. Its identity is defined by the core properties of PTFE in their most uncompromised state.
Defining Characteristics
Being unfilled, virgin PTFE is inherently soft and flexible. Its primary strengths are its absolute chemical purity and its status as a superior electrical insulator.
Primary Applications
Because of these traits, virgin PTFE is the standard for applications where contamination is unacceptable or electrical performance is paramount. This includes the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and semiconductor industries.
Filled PTFE: Enhancing Mechanical Performance
Filled PTFE grades are engineered composites designed to overcome the mechanical limitations of the virgin material, such as its softness and tendency to deform under load (creep).
The Role of Fillers
Additives are blended with the PTFE resin before it is processed. Common fillers include glass fibers, carbon, graphite, bronze, and stainless steel, each imparting different characteristics.
Key Improvements
Adding fillers dramatically increases hardness, compressive strength, and resistance to wear and abrasion. For example, carbon and graphite significantly improve wear resistance, while glass improves both wear and compressive strength.
Common Industrial Uses
Filled PTFE is used for components that face significant mechanical stress, such as seals, bearings, piston rings, and structural parts in industrial machinery.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a filled PTFE grade is an engineering decision that involves clear compromises. The benefits of mechanical enhancement come at a cost.
Reduced Chemical Resistance
While still highly resistant, the fillers themselves may not share PTFE's near-total chemical inertness. Aggressive chemicals can attack the filler material, compromising the component.
Compromised Electrical Properties
Fillers like carbon and metallic powders are conductive, completely negating PTFE's natural insulating properties. This makes most filled grades unsuitable for electrical applications.
The Problem of Creep (Cold Flow)
One of virgin PTFE's primary weaknesses is "creep" or "cold flow"—its tendency to slowly deform under sustained pressure. While fillers are excellent at reducing creep, they are not the only solution.
Beyond the Basics: Important PTFE Variants
The choice isn't limited to just virgin versus filled. Other advanced processing methods create materials with unique property profiles.
Modified PTFE (TFM)
This material incorporates a second chemical modifier into the polymer chain. The result is a denser molecular structure that provides significantly reduced cold flow, smoother machined surfaces, and better weldability compared to virgin PTFE, all while maintaining chemical purity.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE is also 100% pure, but it has been physically stretched in multiple directions. This process creates a strong, microporous material that eliminates creep entirely. It is exceptionally conformable, making it a superior material for gaskets and seals, especially on imperfect flange surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision depends entirely on the primary demands of your environment. By identifying your most critical requirement, you can select the appropriate material.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is the definitive and often only choice.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and mechanical strength under load: A filled PTFE grade is necessary to ensure durability and a long service life.
- If your primary focus is reducing deformation (creep) without sacrificing purity: Investigate Modified PTFE (TFM) for solid components or Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for gasketing.
Understanding this core distinction empowers you to select a material precisely engineered for your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Purity | Excellent | Reduced (depends on filler) |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior | Compromised (conductive fillers) |
| Wear Resistance | Low | High |
| Compressive Strength | Low | High |
| Primary Applications | Pharmaceutical, Food & Beverage, Semiconductor | Industrial Seals, Bearings, Piston Rings |
Struggling to choose the right PTFE material for your components? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need the chemical purity of virgin PTFE or the mechanical strength of filled PTFE, our experts can guide you to the optimal solution. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your parts meet exact specifications. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















