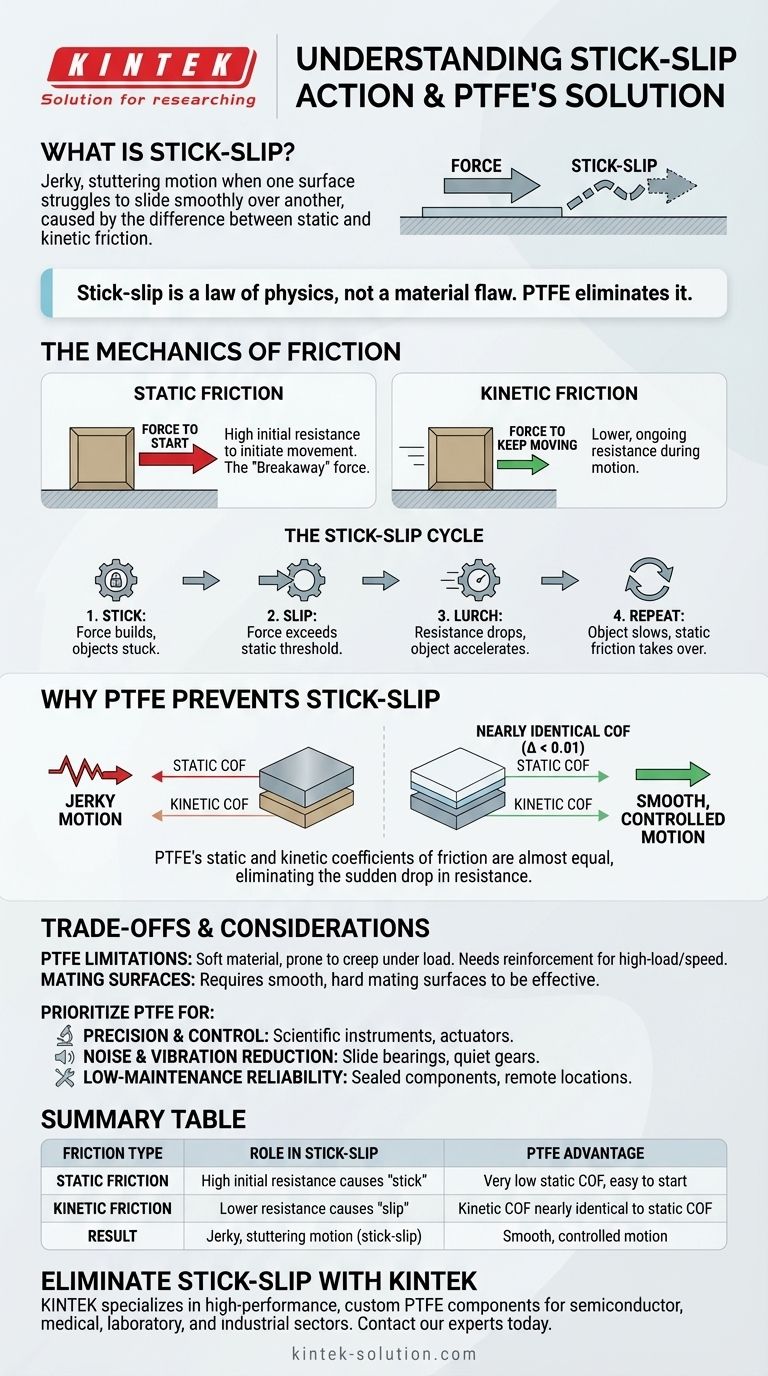
At its core, stick-slip action is the jerky, stuttering motion that occurs when one surface struggles to slide smoothly over another. This phenomenon arises because the force required to start an object moving (static friction) is typically higher than the force needed to keep it in motion (kinetic friction). Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is exceptionally effective at preventing this because its static and kinetic friction values are nearly identical, eliminating the sudden "slip" that causes the jarring motion.
The essential insight is that stick-slip isn't a material flaw, but a law of physics based on the difference between starting friction and sliding friction. PTFE's unique molecular structure nearly eliminates this difference, making it the benchmark material for applications demanding perfectly smooth motion.

The Mechanics of Friction: Static vs. Kinetic
To understand stick-slip, we must first distinguish between the two states of friction that every sliding system contends with.
Understanding Static Friction
Static friction is the force you must overcome to initiate movement between two stationary objects. Think of it as the initial "breakaway" force. When you first push a heavy box across the floor, that initial resistance you feel is static friction.
Understanding Kinetic Friction
Once the box is moving, the force required to keep it sliding at a constant speed decreases. This lower, ongoing resistance is kinetic friction, also known as dynamic friction.
The Root Cause of Stick-Slip
The "stick-slip" cycle is a direct result of the transition between these two forces.
- The "Stick": An external force is applied, but it is not yet strong enough to overcome static friction. The objects remain stuck together as the applied force builds, like energy being stored in a spring.
- The "Slip": The applied force finally exceeds the static friction threshold. The object lurches forward.
- The Lurch: As soon as motion begins, the resistance instantly drops to the lower kinetic friction value. This sudden decrease in resistance causes the object to accelerate, often overshooting its intended position.
- The Repeat: The object may slow down or stop completely, at which point static friction takes over again. The cycle then repeats, creating a characteristic stuttering, vibration, and often, noise.
Why PTFE Delivers Uniquely Smooth Motion
PTFE's effectiveness comes from its ability to nearly erase the difference between the starting and sliding forces.
The Critical Friction Coefficient
The amount of friction is quantified by the Coefficient of Friction (COF). Most materials have a static COF that is significantly higher than their kinetic COF, which is the direct cause of stick-slip.
PTFE's Near-Identical Coefficients
PTFE is a major exception to this rule. Its static and kinetic coefficients of friction differ by an incredibly small margin—often 0.01 or less.
This means the force required to start a PTFE surface moving is almost exactly the same as the force required to keep it moving. There is no sudden drop in resistance, resulting in an exceptionally smooth and controlled transition from stationary to sliding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is superior for anti-stick-slip performance, it is not a universal solution. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging its limitations.
Not a High-Strength Material
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep" (slow deformation under load) and can wear quickly in high-load, high-speed applications unless it is reinforced with fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze.
Impact of Surface Finish and Mating Materials
The low-friction benefits of PTFE are most pronounced when paired with a very smooth, hard mating surface. A rough or abrasive counter-surface can damage the PTFE and negate its anti-stick-slip properties.
When to Prioritize Anti-Stick-Slip Properties
Choosing a material like PTFE is a decision based on your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is precision and control: PTFE is essential for applications like scientific instruments, control valve seals, and actuators where jerky motion would compromise accuracy.
- If your primary focus is reducing noise and vibration: Use PTFE for components like architectural slide bearings, chassis squeak-pads, or quiet gear systems to ensure silent, fluid operation.
- If your primary focus is low-maintenance reliability: The self-lubricating nature of PTFE makes it ideal for sealed components or equipment in remote locations where maintenance is impractical.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a strategic choice for applications where smooth, predictable motion is more critical than raw structural strength.
Summary Table:
| Friction Type | Role in Stick-Slip | PTFE's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Static Friction | High initial resistance causes 'stick' | Very low static COF, easy to start moving |
| Kinetic Friction | Lower resistance during motion causes 'slip' | Kinetic COF nearly identical to static COF |
| Result | Jerky, stuttering motion (stick-slip) | Smooth, controlled motion from start to finish |
Eliminate stick-slip and ensure precision in your critical applications. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production ensures your equipment operates with the smooth, reliable motion you require, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















