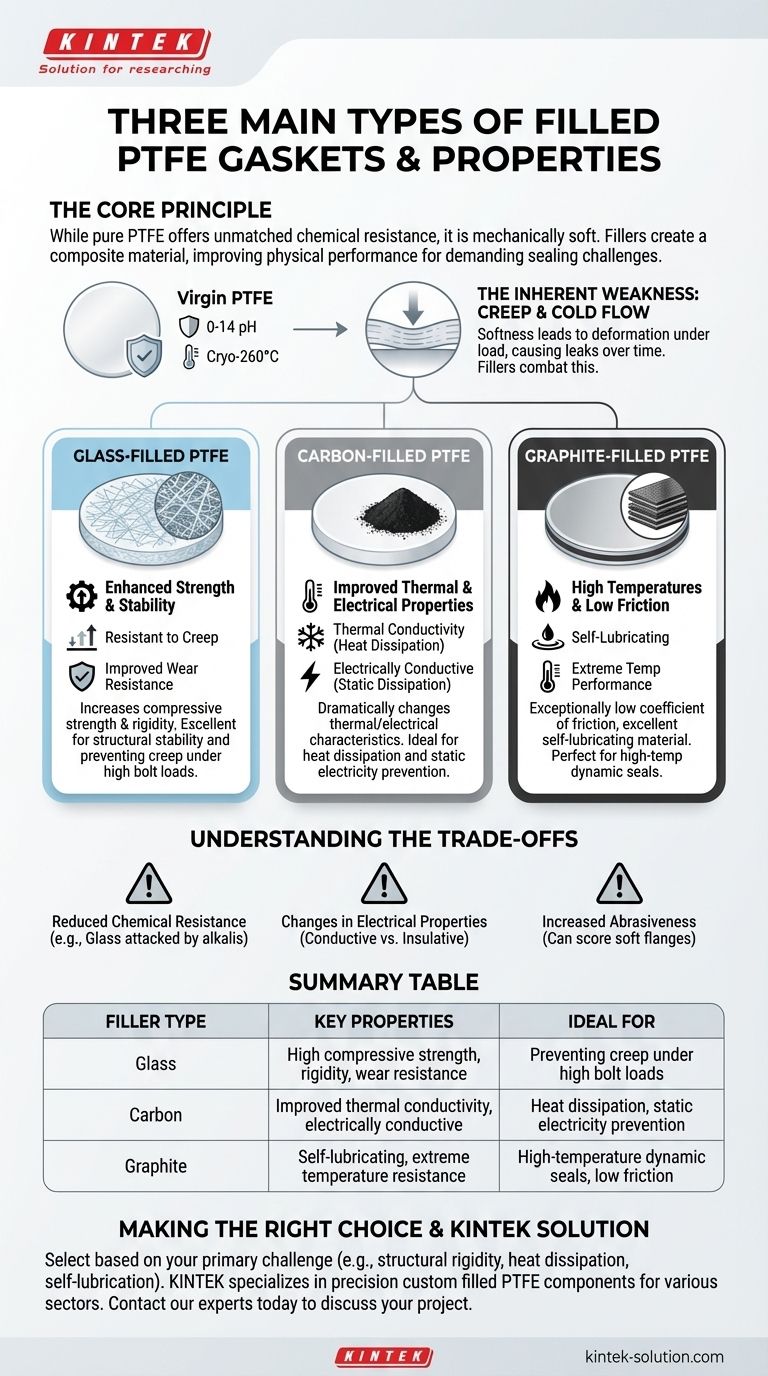
To answer your question directly, the three most common types of filled PTFE gaskets are Glass-Filled, Carbon-Filled, and Graphite-Filled. Each type uses a specific filler material to enhance the natural properties of PTFE, tailoring it for distinct industrial applications by improving its mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, or temperature resistance.
The core principle is simple: while pure PTFE offers unmatched chemical resistance, it is mechanically soft and prone to deforming under load. Fillers are added to create a composite material that retains PTFE's chemical inertness while drastically improving its physical performance for demanding sealing challenges.

The Foundation: Understanding Virgin PTFE
Before analyzing fillers, it's essential to understand the material they are enhancing. Virgin PTFE is a remarkable polymer, but its benefits come with a key limitation.
### Exceptional Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its near-universal chemical resistance, remaining stable across the entire 0-14 pH range.
It also performs reliably across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic levels up to approximately 260°C (500°F). These properties, combined with its low-friction surface, make it a default choice for many sealing applications.
### The Inherent Weakness: Creep and Cold Flow
The primary drawback of virgin PTFE is its softness. When subjected to pressure and temperature, especially over time, it can "creep" or cold flow.
This deformation can lead to a loss of the initial sealing pressure, potentially causing leaks in critical flange connections. This single weakness is the primary reason filled PTFE variants were developed.
The Three Primary Filled PTFE Gaskets
Fillers are added to the PTFE matrix to combat creep and enhance specific properties. Each filler offers a unique profile of benefits.
### Glass-Filled PTFE: For Enhanced Strength and Stability
This is one of the most common filled PTFE types. Microscopic glass fibers or spheres are blended with the PTFE resin.
The primary benefit is a significant increase in compressive strength and rigidity. This makes glass-filled PTFE gaskets far more resistant to creep and cold flow than virgin PTFE.
It also improves wear resistance and dimensional stability, ensuring the gasket holds its shape under mechanical stress.
### Carbon-Filled PTFE: For Improved Thermal and Electrical Properties
In this variant, carbon powder is added to the PTFE base. This dramatically changes the material's thermal and electrical characteristics.
Carbon provides excellent thermal conductivity, allowing the gasket to dissipate heat away from the seal, which is critical in high-temperature dynamic applications.
It also makes the PTFE electrically conductive, which is useful for applications requiring static dissipation. Carbon also improves compressive strength, though typically not as much as glass.
### Graphite-Filled PTFE: For High Temperatures and Low Friction
Graphite, a form of carbon, is used to create a gasket with an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, even when compared to virgin PTFE.
This makes it an excellent self-lubricating material, ideal for dynamic seals with moving parts.
Graphite-filled PTFE also offers outstanding performance at extreme temperatures and further enhances the material's already excellent chemical resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is not a free upgrade. Enhancing one property often means compromising on another. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for proper material selection.
### Reduced Chemical Resistance in Specific Cases
While filled PTFE is still highly resistant, the filler itself can be vulnerable to chemicals that virgin PTFE would easily handle.
For example, the glass fibers in glass-filled PTFE can be attacked by strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid. The core PTFE remains unaffected, but the degradation of the filler can compromise the gasket's integrity.
### Changes in Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. Adding carbon or graphite, however, makes the material electrically conductive.
This completely changes its suitability for applications, making it ideal for anti-static use but entirely unsuitable where electrical insulation is required.
### Increased Abrasiveness
Fillers like glass are inherently more abrasive than pure PTFE. In applications with soft flange surfaces (like plastic or certain alloys), a glass-filled gasket could potentially score or damage the sealing face over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the primary challenge of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is structural rigidity and preventing creep under high bolt loads: Glass-filled PTFE is almost always the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation or static electricity prevention: Carbon-filled PTFE provides the necessary thermal and electrical conductivity.
- If your primary focus is self-lubrication in a high-temperature dynamic seal: Graphite-filled PTFE offers the lowest friction and best temperature resistance.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical purity and electrical insulation with moderate loads: Virgin PTFE remains the best option.
Ultimately, choosing the right filled PTFE is about transforming a chemically superior material into a robust engineering solution for your specific problem.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Properties | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | High compressive strength, rigidity, wear resistance | Preventing creep under high bolt loads |
| Carbon | Improved thermal conductivity, electrically conductive | Heat dissipation, static electricity prevention |
| Graphite | Self-lubricating, extreme temperature resistance | High-temperature dynamic seals, low friction |
Need a high-performance PTFE gasket solution tailored to your specific requirements?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including seals, gaskets, liners, and labware. Whether your application is in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we can help you select the right filled PTFE material—be it glass, carbon, or graphite—to solve your toughest sealing challenges, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















