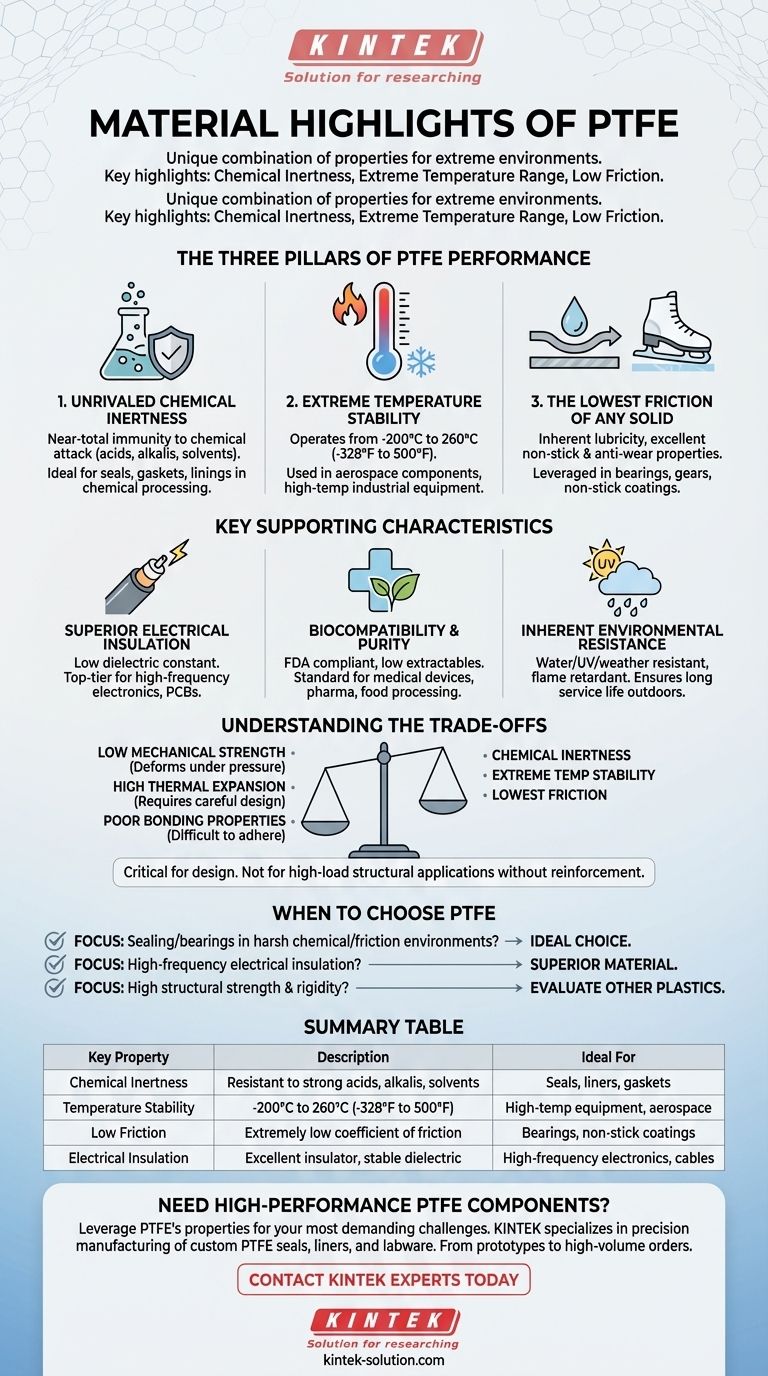
In the world of high-performance polymers, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the brand name Teflon, stands out for a unique combination of properties. Its defining highlights are an almost universal chemical inertness, an extremely wide operating temperature range, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material.
PTFE is fundamentally a problem-solver for extreme environments. Its value lies in its exceptional resistance to chemical attack, heat, and friction, but this performance comes with mechanical trade-offs that are critical to understand for proper application.

The Three Pillars of PTFE Performance
The primary advantages of PTFE can be understood through three core characteristics that make it suitable for applications where other materials would quickly fail.
Pillar 1: Unrivaled Chemical Inertness
PTFE exhibits near-total immunity to chemical attack. It is highly resistant to a vast range of substances, including strong acids, alkalis, and aggressive organic solvents.
This remarkable inertness means it won't degrade, swell, or corrode when exposed to harsh chemicals, making it an essential material for seals, gaskets, and linings in the chemical processing industry.
Pillar 2: Extreme Temperature Stability
This material maintains its properties across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum. It remains functional and stable from cryogenic temperatures of -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F).
This thermal stability allows PTFE to be used in applications ranging from aerospace components to high-temperature industrial equipment without becoming brittle or melting.
Pillar 3: The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
PTFE has an incredibly low coefficient of friction, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This inherent lubricity results in excellent non-stick and anti-wear properties.
Components like bearings, gears, and non-stick coatings leverage this quality to reduce energy loss, prevent seizing, and ensure smooth, low-maintenance operation.
Key Supporting Characteristics
Beyond its three primary strengths, several other properties broaden PTFE's utility in specialized fields.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with a very low dielectric constant. Its insulating properties remain stable across a wide range of frequencies and temperatures.
This makes it a top-tier choice for high-frequency electronics, such as in coaxial cable insulation and printed circuit boards.
Biocompatibility and Purity
The material is inherently pure, with virtually no extractables that can leach out and contaminate a system. It is also biocompatible and frequently FDA compliant.
These attributes make PTFE a standard material for use in medical devices, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food processing equipment.
Inherent Environmental Resistance
PTFE does not absorb water and is highly resistant to weathering and UV radiation. It is also naturally flame resistant.
This durability ensures a long service life for components that are exposed to the elements or require a high degree of fire safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and PTFE's unique strengths come with corresponding limitations that are critical for design and engineering decisions.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE has relatively low tensile strength, stiffness, and creep resistance. It is not a material suited for high-load, structural applications.
Its softness, while beneficial for creating effective seals, means it can deform under sustained pressure.
High Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes more significantly than most metals and other plastics.
This must be accounted for in designs with tight tolerances to prevent parts from binding or failing when subjected to thermal cycling.
Poor Bonding Properties
The same low surface tension that makes PTFE non-stick also makes it extremely difficult to bond to other materials.
Using adhesives with PTFE requires aggressive chemical etching or other specialized surface preparation techniques, adding complexity and cost to fabrication.
When to Choose PTFE
Your decision to use PTFE should be based on a clear understanding of its strengths and weaknesses relative to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is sealing or bearings in harsh chemical environments: PTFE is an ideal choice due to its chemical inertness and exceptionally low friction.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its low and stable dielectric constant makes it a superior material for demanding electronics.
- If your primary focus is high structural strength and rigidity: You should evaluate other engineering plastics, as this is a known limitation of PTFE.
By understanding both its exceptional resilience and its inherent mechanical limitations, you can leverage PTFE to solve some of the most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Description | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to strong acids, alkalis, and solvents | Seals, liners, gaskets in chemical processing |
| Temperature Stability | Operates from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | High-temp industrial equipment, aerospace components |
| Low Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction | Bearings, non-stick coatings, low-wear parts |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulator with stable dielectric constant | High-frequency electronics, coaxial cables |
| Biocompatibility | Inherently pure, FDA compliant, non-contaminating | Medical devices, pharmaceutical, and food processing equipment |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Leverage PTFE's unique properties to solve your most demanding engineering challenges. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver the chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction your application requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance



















