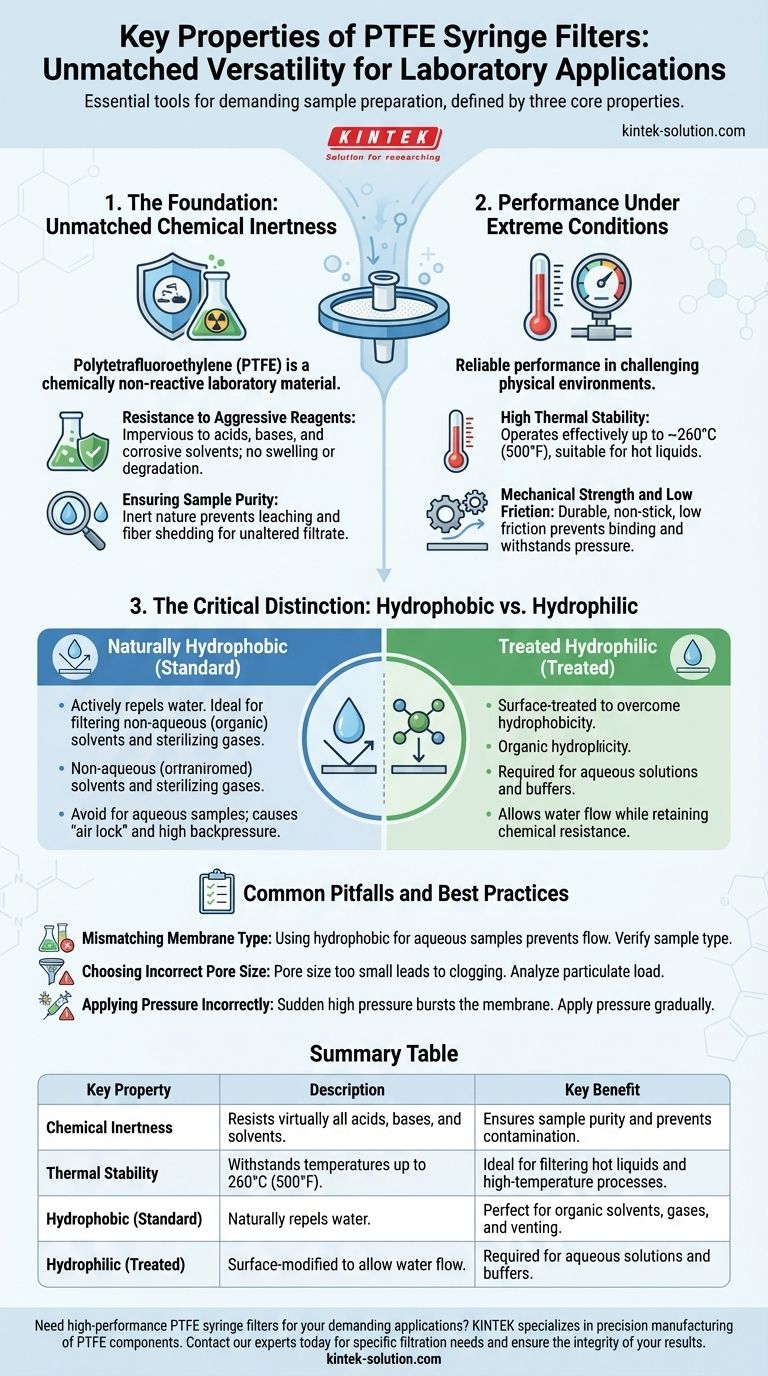
In essence, PTFE syringe filters are defined by three core properties: exceptional chemical resistance to nearly all acids, bases, and solvents; high thermal stability for use in high-temperature applications; and a naturally water-repelling (hydrophobic) surface that can be modified to be water-attracting (hydrophilic). These characteristics make them a uniquely versatile tool for sample preparation in demanding laboratory environments.
The central decision when choosing a PTFE filter is not just about its superior resistance, but about its interaction with water. Understanding whether your sample requires a standard hydrophobic filter (for organic solvents and gases) or a treated hydrophilic filter (for aqueous solutions) is the key to preventing membrane blockage and ensuring successful filtration.

The Foundation: Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most chemically non-reactive materials used in laboratory settings. This inertness is its most significant advantage.
Resistance to Aggressive Reagents
PTFE is virtually impervious to chemical attack. It can handle corrosive solvents, strong acids, and aggressive bases without degrading, swelling, or breaking down.
This ensures the filter itself does not become a variable in your experiment.
Ensuring Sample Purity
Because PTFE is so inert, it will not react with or leach contaminants into the filtrate. This is critical for sensitive analytical techniques where sample composition must remain unaltered.
Furthermore, the material does not shed fibers, preventing particulate contamination of your final sample.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Beyond its chemical resilience, PTFE performs reliably in challenging physical environments, particularly those involving high heat.
High Thermal Stability
PTFE syringe filters can operate effectively across a wide temperature range, withstanding temperatures up to approximately 260°C (500°F).
This makes them suitable for filtering hot liquids or for processes that involve heat, where materials like nylon or cellulose might fail.
Mechanical Strength and Low Friction
PTFE is a durable, pliable material with a very low coefficient of friction, making it exceptionally non-stick. This helps prevent binding and ensures a smooth filtration process.
Its physical integrity ensures it can withstand the pressures of syringe-based filtration without tearing.
The Critical Distinction: Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic
The most important practical property of a PTFE filter is its relationship with water. Choosing the wrong type is a common source of failure.
Naturally Hydrophobic PTFE
In its standard form, PTFE is hydrophobic—it actively repels water. This makes it the ideal choice for filtering non-aqueous (organic) solvents and for venting applications or sterilizing gases.
Attempting to filter a water-based solution through a standard PTFE membrane will result in extremely high backpressure and little to no flow, an effect known as "air lock."
Treated Hydrophilic PTFE
To filter aqueous solutions, a hydrophilic PTFE filter is required. This is a PTFE membrane that has been surface-treated to overcome its natural hydrophobicity.
This modification allows water and water-based solutions to pass through easily while retaining the material's broad chemical resistance and low protein-binding characteristics.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of PTFE filters, it is crucial to use them correctly. Simple mistakes can lead to membrane failure or poor results.
Mismatching the Membrane Type
The most common error is using a hydrophobic PTFE filter for an aqueous sample. This will prevent the liquid from passing through the membrane pores. Always verify your sample type and choose the appropriate membrane.
Choosing the Correct Pore Size
Selecting a pore size that is too small for your sample can lead to rapid clogging and high backpressure. Analyze the particulate load of your sample to choose an appropriate pore size and filter diameter for efficient filtration.
Applying Pressure Incorrectly
Applying sudden, high pressure from the syringe can burst the filter membrane. Always apply pressure gradually and evenly to avoid rupturing the membrane and compromising your sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal determines which type of PTFE filter is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive organic solvents: A standard, untreated hydrophobic PTFE filter is the correct and most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is clarifying aqueous solutions or buffers: You must use a surface-treated hydrophilic PTFE filter to ensure proper flow.
- If your primary focus is high-purity analysis (e.g., HPLC prep): PTFE's inertness and non-shedding nature are ideal, but you must match the membrane type (hydrophobic/hydrophilic) to your mobile phase.
- If you are working with high-temperature liquids: PTFE's exceptional thermal stability makes it a superior choice over most other common filter materials.
By understanding these core properties, you can confidently leverage PTFE filters to protect your equipment and ensure the integrity of your results.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all acids, bases, and solvents. | Ensures sample purity and prevents contamination. |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). | Ideal for filtering hot liquids and high-temperature processes. |
| Hydrophobic (Standard) | Naturally repels water. | Perfect for organic solvents, gases, and venting. |
| Hydrophilic (Treated) | Surface-modified to allow water flow. | Required for aqueous solutions and buffers. |
Need high-performance PTFE syringe filters for your demanding applications?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including seals, liners, labware, and custom parts for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the chemical resistance, thermal stability, and membrane type (hydrophobic or hydrophilic) your application requires—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific filtration needs and ensure the integrity of your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE ensure seal integrity in chromatography vials? Achieve Leak-Free, Contaminant-Free Results
- How do PTFE/silicone septa reduce sample carryover in HPLC analysis? Achieve Accurate, Contamination-Free Results
- What are the advantages of using PTFE lined caps? Superior Sealing for Volatile Liquids & High-Temp Storage
- What are the main advantages of PTFE/silicone septa in laboratory applications? Ensure Sample Integrity and Accuracy
- What makes Teflon membranes versatile for use in various laboratory environments? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What are the sealing and barrier properties of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Sample Integrity with Superior Protection
- What makes PTFE vials effective in preventing sample contamination or evaporation? Superior Chemical Inertness & Airtight Seals
- What types of samples are compatible with PTFE lined vials? Ensure Sample Integrity for Demanding Applications



















