In the world of precision analytics, the smallest components can have the largest impact on your results. The primary advantages of PTFE/silicone septa are their unique combination of exceptional chemical inertness from the PTFE layer and the reliable, resealable seal provided by the silicone body. This dual-material design provides superior sample protection, prevents evaporation and contamination, and maintains stability across a wide range of temperatures.
The choice of a vial septum is not a minor detail; it is a critical control point for analytical accuracy. PTFE/silicone septa are the industry standard because they solve a core problem: they isolate a sample chemically while maintaining a perfect physical seal, even after being punctured.

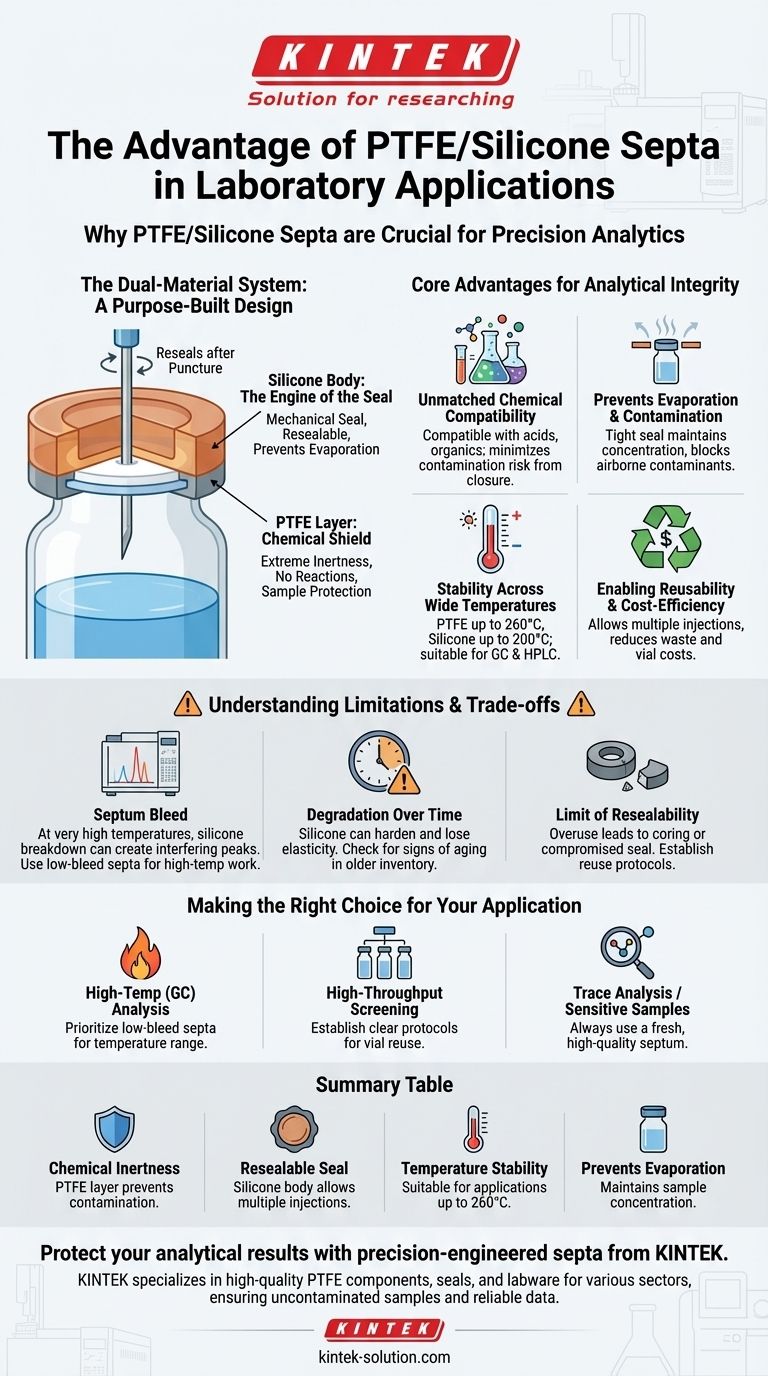
The Two-Material System: A Purpose-Built Design
The effectiveness of these septa comes from leveraging the distinct properties of two different materials in a single, laminated component. Each material plays a specific and crucial role.
The PTFE Layer: Your Sample's Chemical Shield
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the material that directly faces your sample. Its primary job is to be chemically invisible.
Because of its extreme inertness, PTFE does not react with or leach into the solvent or sample, ensuring the analytical integrity of your run. This makes it ideal for sensitive applications in fields like chromatography and pharmaceutical research.
The Silicone Body: The Engine of the Seal
While PTFE provides the chemical barrier, silicone provides the mechanical seal. It is a soft, pliable material that presses firmly against the rim of the vial, creating a leak-proof closure.
The elasticity of the silicone is also what makes the septum resealable. When a needle pierces it, the silicone expands back to close the hole, protecting the sample from the atmosphere and preventing evaporation.
Core Advantages for Analytical Integrity
This two-part design delivers tangible benefits that directly contribute to the reliability and consistency of laboratory results.
Unmatched Chemical Compatibility
The PTFE layer ensures that the septum is compatible with a vast range of solvents and chemicals, from aggressive acids to organic compounds. This versatility minimizes the risk of sample contamination from the closure itself.
Preventing Evaporation and Contamination
The tight, consistent seal from the silicone body is essential for volatile samples. It effectively prevents solvent evaporation, which would alter sample concentration and skew results. It also serves as a physical barrier against airborne contaminants.
Stability Across Wide Temperatures
These septa are suitable for a variety of analytical techniques because they remain stable across a broad temperature range. PTFE can withstand temperatures up to 260°C, while silicone is generally stable up to 200°C, accommodating most GC and HPLC methods.
Enabling Reusability and Cost-Efficiency
The self-sealing nature of the silicone allows for multiple injections from the same vial. For many routine applications, this durability allows for the reuse of autosampler vials, reducing waste and contributing to significant cost savings.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While PTFE/silicone septa are highly effective, they are not infallible. Understanding their limitations is key to preventing failed analyses.
The Reality of Septum Bleed
At very high temperatures, especially in gas chromatography, components from the silicone can sometimes break down and enter the analytical stream. This phenomenon, known as septum bleed, can create interfering peaks in your chromatogram. For this reason, specialized low-bleed septa are recommended for sensitive, high-temperature work.
Degradation Over Time
Septa have a finite shelf life. Over time, the silicone can harden and lose its elasticity, compromising its ability to form a tight seal. Always check for signs of degradation, especially with older inventory.
The Limit of "Resealability"
While a septum can handle multiple punctures, it cannot be reused indefinitely. Each injection creates a potential failure point. Overuse can lead to coring (where pieces of the septum fall into the sample) or a compromised seal that allows for evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct septum is about matching its capabilities to your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature analysis (like GC): Prioritize low-bleed septa specifically rated for your instrument's temperature range to minimize contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening: The resealability is a key advantage, but you must establish a clear protocol for vial reuse to avoid cross-contamination and seal failure.
- If your primary focus is trace analysis or highly sensitive samples: Always use a fresh, high-quality PTFE/silicone septum for each new sample to guarantee the highest level of integrity.
By understanding how these critical components work, you move from simply using them to strategically deploying them to protect your data.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | PTFE layer prevents sample contamination and reactions. |
| Resealable Seal | Silicone body allows for multiple injections and reusability. |
| Temperature Stability | Suitable for a wide range of applications (up to 260°C). |
| Prevents Evaporation | Maintains sample concentration and integrity. |
Protect your analytical results with precision-engineered septa from KINTEK.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-quality PTFE components, including septa, seals, and custom labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our commitment to precision production ensures your samples remain uncontaminated and your data is reliable.
Whether you need standard components or custom-fabricated solutions—from prototypes to high-volume orders—we deliver the performance your applications demand.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















