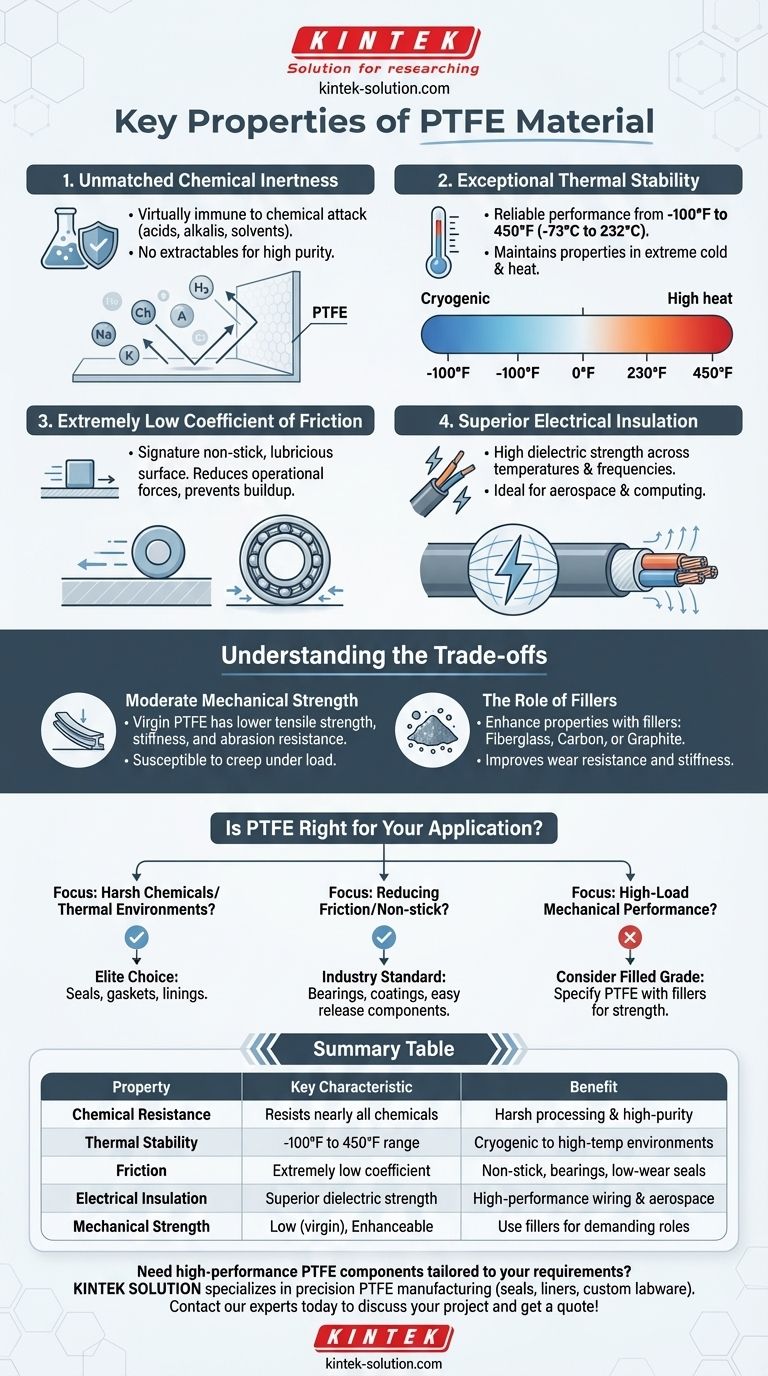
The key properties of PTFE are its exceptional chemical resistance, a very wide operating temperature range, an extremely low coefficient of friction (making it non-stick), and excellent electrical insulation. These characteristics make Polytetrafluoroethylene, often known by the brand name Teflon, one of the most versatile and high-performing engineering plastics available.
PTFE is fundamentally a material of extremes. Its value comes from its profound inertness—resisting nearly all chemicals and temperatures—and its uniquely slippery surface, but this performance profile requires careful consideration of its moderate mechanical strength.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE
To understand if PTFE is the right material for your project, it's essential to look at each of its core properties in the context of real-world performance.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually immune to chemical attack. It shows extreme resistance to strong acids, alkalis, and nearly all organic solvents.
This inertness means it will not degrade or swell when exposed to aggressive substances, ensuring reliability in demanding environments like chemical processing.
Furthermore, it has virtually no extractables, meaning it doesn't leach chemicals, which is critical for high-purity applications in the medical or semiconductor industries.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE performs reliably across a remarkably broad temperature range, typically from -100°F to 450°F (-73°C to 232°C).
Unlike many plastics that become brittle in extreme cold or deform under heat, PTFE maintains its key properties, providing stability in applications from cryogenic systems to high-temperature processing equipment.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This gives it its signature non-stick, or "lubricious," quality.
This property is invaluable for applications requiring smooth, low-wear movement, such as in bearings, bushings, and seals. It reduces operational forces and prevents material buildup on surfaces.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator that maintains its high dielectric strength across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
This makes it a preferred material for high-performance applications, including insulation for wiring and cables, especially in demanding aerospace and computing contexts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its primary properties are exceptional, PTFE is not without limitations. Acknowledging its trade-offs is crucial for successful material selection.
Moderate Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, virgin (unfilled) PTFE has relatively low tensile strength, stiffness, and abrasion resistance.
It is a softer material, which can make it susceptible to deformation under high loads, a phenomenon known as "creep" or cold flow.
The Role of Fillers
To counteract its mechanical limitations, PTFE is often enhanced with fillers.
Adding substances like fiberglass, carbon, or graphite can significantly improve wear resistance, increase stiffness, and reduce creep, tailoring the material for more demanding structural or high-wear roles.
Cost and Machinability
While often described as cost-effective for its performance level, it is more expensive than common commodity plastics.
It is highly machinable, but its softness requires sharp tools and specific techniques to achieve tight tolerances without causing deformation.
Is PTFE the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is survival in harsh chemical or thermal environments: PTFE is an elite choice for seals, gaskets, and linings where material integrity is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction or creating a non-stick surface: PTFE is the industry standard for low-wear bearings, non-stick coatings, and components that require easy release.
- If your primary focus is high-load mechanical performance or abrasion resistance: Virgin PTFE is likely unsuitable; you should specify a filled grade of PTFE designed for enhanced mechanical strength.
Understanding this balance between extreme inertness and moderate strength is the key to leveraging PTFE effectively.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resists nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents. | Ideal for harsh chemical processing and high-purity applications. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from -100°F to 450°F (-73°C to 232°C). | Reliable in cryogenic to high-temperature environments. |
| Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction. | Excellent for non-stick surfaces, bearings, and low-wear seals. |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior dielectric strength across temperatures. | Perfect for high-performance wiring and aerospace components. |
| Mechanical Strength | Low tensile strength and stiffness (virgin PTFE). | Can be enhanced with fillers (glass, carbon) for demanding roles. |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components deliver the extreme chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction that PTFE is famous for.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the dissipation factor of PTFE? A Guide to Virgin vs. Filled Grades
- What is the reactivity of PTFE and why is it inert? Discover the Science Behind Its Unmatched Chemical Resistance
- What are some common uses of PTFE laminated fabrics? Essential for Waterproof, Breathable Performance Gear
- What are the notable physical and chemical properties of PTFE? Master Its Unique Strengths and Limitations
- What is PTFE and what is its commercial name? A Guide to Teflon and ePTFE
- What are the key advantages of PTFE with fillers over pure PTFE? Unlock Superior Mechanical Performance
- How is PTFE used in the beauty industry? Enhance Product Performance and Safety
- Which industries benefit from Teflon's chemical resistance? Ensure Purity and Safety in Harsh Environments



















