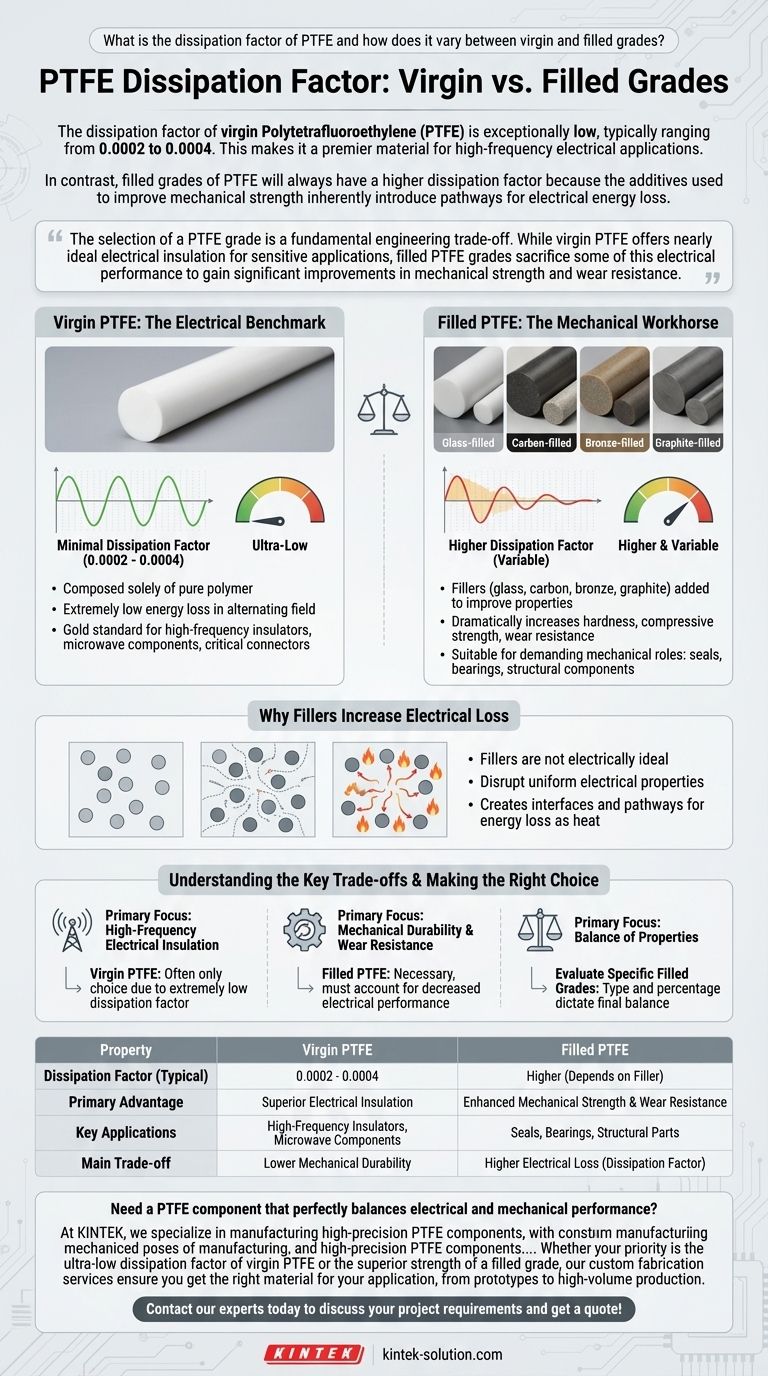
The dissipation factor of virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is exceptionally low, typically ranging from 0.0002 to 0.0004. This makes it a premier material for high-frequency electrical applications. In contrast, filled grades of PTFE will always have a higher dissipation factor because the additives used to improve mechanical strength inherently introduce pathways for electrical energy loss.
The selection of a PTFE grade is a fundamental engineering trade-off. While virgin PTFE offers nearly ideal electrical insulation for sensitive applications, filled PTFE grades sacrifice some of this electrical performance to gain significant improvements in mechanical strength and wear resistance.

Deconstructing Performance: Electrical vs. Mechanical Properties
The choice between virgin and filled PTFE hinges entirely on the most critical requirement for your application. The two variants are optimized for fundamentally different performance goals.
Virgin PTFE: The Electrical Benchmark
Virgin PTFE is composed solely of the pure polymer. Its chemical inertness and the strength of its carbon-fluorine bonds result in extremely low energy loss when exposed to an alternating electric field.
This translates to a minimal dissipation factor (also known as loss tangent), making it the gold standard for high-frequency insulators, microwave components, and critical electronic connectors.
Filled PTFE: The Mechanical Workhorse
Virgin PTFE is relatively soft and can be prone to deformation under load. To counteract this, fillers such as glass, carbon, bronze, or graphite are added to the polymer matrix.
These additives dramatically increase hardness, compressive strength, and resistance to wear and creep. This makes filled PTFE suitable for demanding mechanical roles like seals, bearings, and structural components.
Why Fillers Increase Electrical Loss
The fillers themselves are not as electrically ideal as the pure PTFE matrix. They disrupt the uniform electrical properties of the material.
This creates interfaces and pathways that allow more electrical energy to be converted into heat, thereby increasing the dissipation factor. The specific type and percentage of filler will determine the extent of this electrical performance degradation.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong grade of PTFE can lead to either mechanical failure or poor electrical performance. It is crucial to understand the compromises inherent in each choice.
The Limitation of Purity
While electrically superior, virgin PTFE lacks mechanical robustness. In applications involving high pressure or abrasive contact, it will wear quickly and may fail structurally. Its softness makes it unsuitable for components that must maintain tight tolerances under load.
The Cost of Strength
Using a filled PTFE grade in a high-frequency application can lead to unacceptable signal loss and heat generation. The energy that dissipates due to the higher loss tangent can degrade signal integrity and, in high-power scenarios, potentially damage the component.
Beyond the Datasheet
It is critical to recognize that the final properties of any PTFE product are influenced by the processing method and specific compound. The values on a datasheet are a starting point; you are ultimately responsible for testing the material to confirm its suitability for your specific application environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your selection on the single most important performance characteristic your design demands.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is the definitive and often only choice due to its extremely low dissipation factor.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and wear resistance: A filled PTFE grade (such as glass or carbon-filled) is necessary, but you must account for the corresponding decrease in electrical performance.
- If you require a balance of properties: You must carefully evaluate specific filled grades, as the type and percentage of filler directly dictate the final balance between electrical and mechanical characteristics.
Understanding this fundamental trade-off empowers you to select the precise material that meets your design's most critical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Dissipation Factor (Typical) | 0.0002 - 0.0004 | Higher (Depends on Filler) |
| Primary Advantage | Superior Electrical Insulation | Enhanced Mechanical Strength & Wear Resistance |
| Key Applications | High-Frequency Insulators, Microwave Components | Seals, Bearings, Structural Parts |
| Main Trade-off | Lower Mechanical Durability | Higher Electrical Loss (Dissipation Factor) |
Need a PTFE component that perfectly balances electrical and mechanical performance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Whether your priority is the ultra-low dissipation factor of virgin PTFE or the superior strength of a filled grade, our custom fabrication services ensure you get the right material for your application, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















