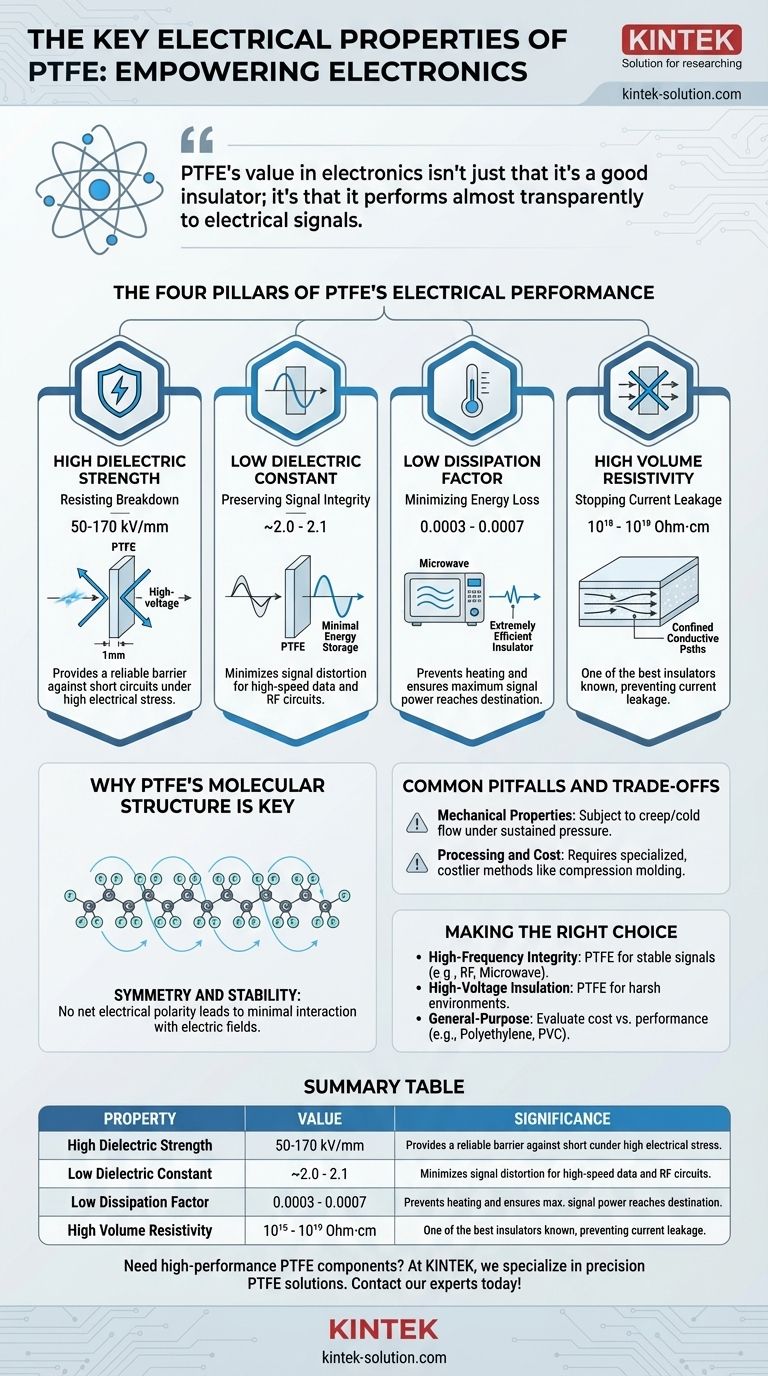
The defining electrical properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are its high dielectric strength, exceptionally low dielectric constant and dissipation factor, and tremendous volume resistivity. These characteristics are not independent; they work together to make PTFE one of the most effective and reliable insulators available, particularly for demanding high-frequency and high-voltage applications where signal integrity and safety are paramount.
PTFE's value in electronics isn't just that it's a good insulator; it's that it performs almost transparently to electrical signals. Its unique molecular structure allows it to block current flow effectively while storing minimal energy and losing almost none to heat, making it essential for high-performance components.
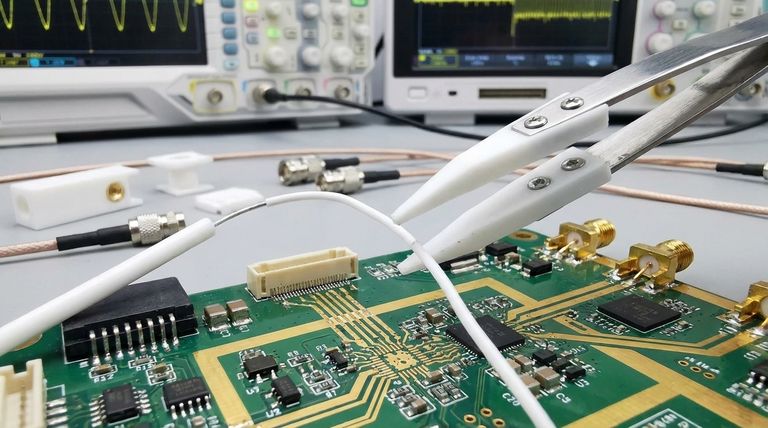

The Four Pillars of PTFE's Electrical Performance
To understand why PTFE is so widely used, we must examine its core electrical properties individually. Each one solves a specific problem for engineers and designers.
High Dielectric Strength: Resisting Breakdown
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a high voltage before it fails and a current punches through.
PTFE exhibits a very high dielectric strength, typically in the range of 50-170 kV/mm. This means a 1mm thick sheet of PTFE can withstand up to 170,000 volts before breaking down.
This property is critical for insulation in wiring, cables, and connectors, where it provides a reliable barrier to prevent short circuits and ensure operational safety under high electrical stress.
Low Dielectric Constant: Preserving Signal Integrity
The dielectric constant indicates how much electrical energy a material can store when placed in an electric field. For high-frequency signals, a lower value is better.
PTFE has an exceptionally low dielectric constant of around 2.0 to 2.1. This is very close to a perfect vacuum (1.0).
Because it stores very little energy from a passing electrical signal, PTFE helps maintain the signal's speed and shape. This minimizes distortion, making it an ideal material for high-speed data cables and radio frequency (RF) circuits.
Low Dissipation Factor: Minimizing Energy Loss
The dissipation factor (or loss tangent) quantifies how much of a signal's energy is absorbed by the insulating material and lost as heat.
PTFE's dissipation factor is incredibly low, around 0.0003 to 0.0007. This means it is extremely efficient as an insulator.
In high-frequency applications, such as microwave circuits and coaxial cables, this minimal energy loss prevents the insulator from heating up and ensures that maximum signal power reaches its destination.
High Volume Resistivity: Stopping Current Leakage
Volume resistivity measures a material's fundamental resistance to the flow of electrical current through its bulk.
With a volume resistivity of 10¹⁸ to 10¹⁹ Ohm·cm, PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators known.
This property guarantees that virtually no current leaks through the material itself, ensuring that electricity is confined strictly to the intended conductive paths.
Why PTFE's Molecular Structure is Key
These exceptional properties are not accidental; they are a direct result of PTFE's unique molecular structure.
A Matter of Symmetry and Stability
The PTFE molecule consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by a helix of larger fluorine atoms.
This highly symmetric arrangement results in a molecule with no net electrical polarity. Consequently, it interacts very little with passing electric fields, which is the underlying reason for its low dielectric constant and dissipation factor.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While its electrical properties are outstanding, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Its selection requires an understanding of its limitations.
Mechanical Properties
PTFE is a relatively soft material and is subject to "creep" or "cold flow," where it can deform over time under sustained pressure. This must be accounted for in mechanical designs.
Processing and Cost
PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt techniques like injection molding. It requires specialized methods like compression molding and sintering, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
For these reasons, PTFE is typically reserved for applications where its superior electrical or chemical performance justifies the higher cost and design considerations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right insulator depends entirely on the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity (e.g., RF, microwave): PTFE is often the best choice due to its exceptionally low and stable dielectric constant and dissipation factor.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation in harsh environments: PTFE's combination of high dielectric strength and chemical inertness makes it a highly reliable material for preventing electrical breakdown.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose, low-cost application: You should evaluate whether the premium performance of PTFE is necessary, as materials like Polyethylene or PVC may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a decision to prioritize unparalleled electrical performance and stability where other materials would fail.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Range | Significance for Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | 50 - 170 kV/mm | Withstands high voltages, prevents electrical breakdown |
| Dielectric Constant | ~2.0 - 2.1 | Preserves signal integrity and speed in high-frequency applications |
| Dissipation Factor | 0.0003 - 0.0007 | Minimizes signal energy loss as heat |
| Volume Resistivity | 10¹⁸ - 10¹⁹ Ohm·cm | Provides superior insulation, prevents current leakage |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical electronics, medical, or industrial applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Our expertise ensures your designs benefit from PTFE's superior electrical properties, chemical resistance, and reliability—from initial prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is ePTFE and how is it produced? Unlock the Power of Microporous PTFE
- What makes PTFE resistant to UV and weathering? The Science Behind its Inherent, Lasting Durability
- How does the friction of Teflon compare to other materials? Discover the Benchmark for Low Friction
- How does PTFE compare to High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)? A Guide to Extreme Performance vs. Cost-Effectiveness
- How does Teflon demonstrate superior chemical resistance? Unlocking Its Molecular Fortress
- What are the key aspects of the CNC machining process for PTFE? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What is PTFE's resistance to fluorine under different conditions? Avoid Costly Failures with Temperature-Specific Data
- How is Teflon coating used in the food and kitchenware industry? Enhancing Efficiency and Product Quality



















