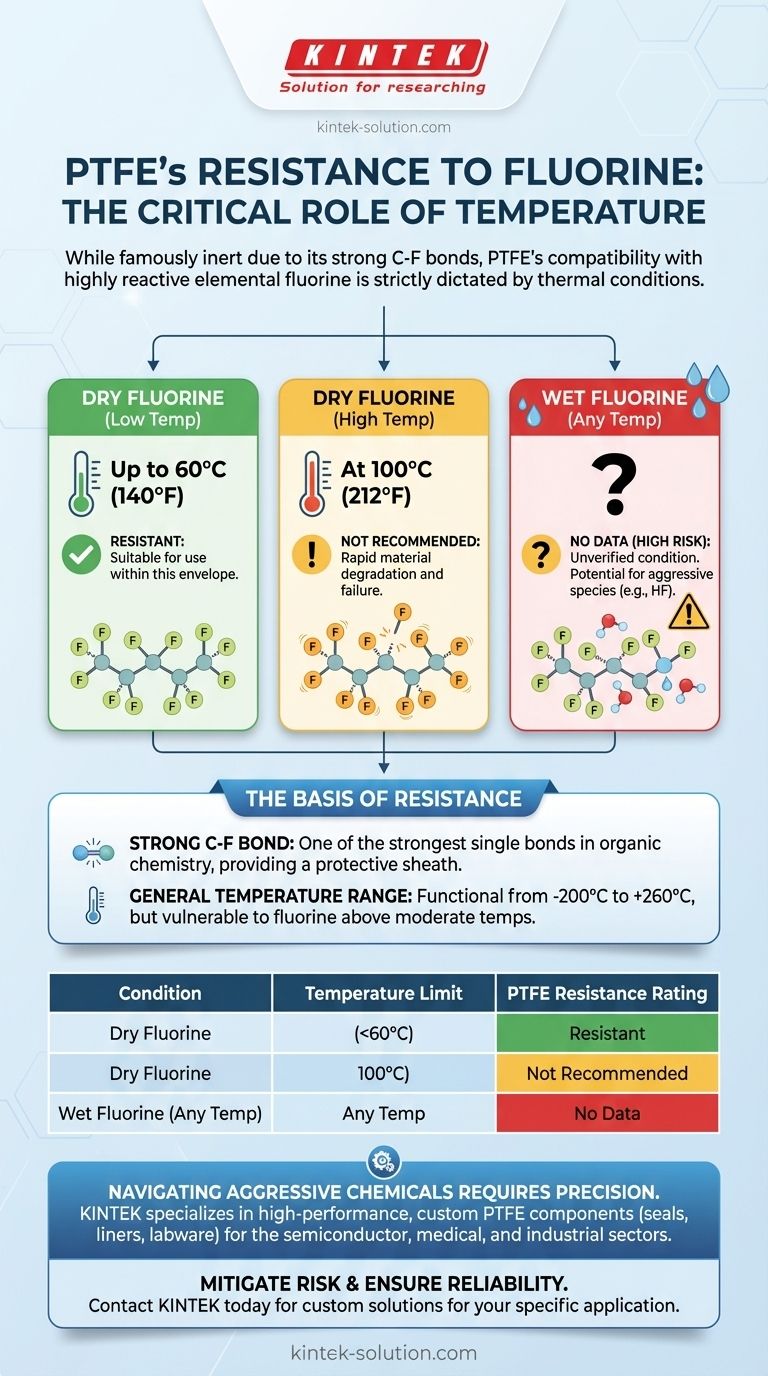
Under specific conditions, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) shows excellent resistance to dry fluorine gas at moderate temperatures but fails rapidly as the temperature rises. For dry fluorine, it is considered resistant up to 60°C (140°F) but is not recommended for use at 100°C (212°F). Crucially, there is no available data on its resistance to wet fluorine, making that an unverified and high-risk condition.
The core takeaway is that while PTFE is famously inert, its compatibility with elemental fluorine is dictated entirely by temperature. Heat provides the necessary energy for highly reactive fluorine to break down the polymer, making temperature the single most critical factor in determining system safety and material survival.

The Basis of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE's legendary chemical inertness stems from the strength of the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond. This bond is one of the strongest known single bonds in organic chemistry.
The polymer consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by a protective sheath of fluorine atoms. This stable, non-reactive structure is what makes PTFE resistant to a vast range of acids, bases, and solvents.
General Performance Envelope
Beyond chemical resistance, PTFE operates effectively across an exceptionally wide temperature range. It remains functional from cryogenic conditions as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to high-temperature applications at 260°C (500°F).
The Unique Challenge of Elemental Fluorine
Why Fluorine is an Exception
Fluorine is the most electronegative and reactive of all elements. It is one of the very few chemicals capable of attacking PTFE's robust structure under the right conditions.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The interaction between PTFE and fluorine is highly dependent on thermal energy. At lower temperatures, there isn't enough energy to initiate a reaction.
As the temperature increases, fluorine atoms become energized enough to break the C-F bonds, causing the PTFE polymer to degrade and fail. This is why the material's rating changes so drastically over a relatively small temperature increase.
Understanding the Resistance Data and Its Limits
The 100°C (212°F) Failure Point
The rating of "Not Recommended" (NR) at 100°C for dry fluorine is an explicit warning. At this temperature, a chemical reaction is expected, leading to the rapid degradation of the material and certain system failure.
The Hazard of "No Data" for Wet Fluorine
The "No Data" (ND) rating for wet fluorine is not an invitation for testing; it is a critical red flag. The presence of water can introduce other reactive species, like hydrofluoric acid (HF), creating an unpredictable and potentially more aggressive chemical environment.
Without verified data, using PTFE with wet fluorine at any temperature introduces an unknown and unacceptable level of risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
When evaluating PTFE for use with fluorine, your operating conditions are the only thing that matters.
- If your primary focus is a system with dry fluorine below 60°C (140°F): PTFE is considered a resistant and suitable material based on standard chemical compatibility data.
- If your primary focus is a system with temperatures approaching or exceeding 100°C (212°F): You must select an alternative material, as PTFE is expected to fail in this environment.
- If your primary focus is a system that may contain wet fluorine: You must avoid using PTFE entirely, as this represents an unvalidated and potentially dangerous combination.
Ultimately, successful material selection requires strict adherence to documented limits, especially when handling highly reactive chemicals.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Temperature Limit | PTFE Resistance Rating | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Fluorine | Up to 60°C (140°F) | Resistant | Suitable for use within this temperature envelope. |
| Dry Fluorine | At 100°C (212°F) | Not Recommended (NR) | Material will rapidly degrade and fail. |
| Wet Fluorine | Any Temperature | No Data (ND) | High-risk, unverified condition. Avoid entirely. |
Navigating aggressive chemicals like fluorine requires precision-engineered components.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. We understand that material selection is critical to your system's safety and longevity.
Let us help you mitigate risk and ensure reliability. Our experts can guide you in selecting or fabricating the right components for your specific temperature and chemical environment.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application requirements and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PTFE in terms of shelf life and service intervals? Maximize Reliability and Minimize Downtime
- What are the recommended PTFE formulations for the chemical processing industry and why? Optimize for Durability and Chemical Resistance
- What are the benefits of using PTFE? Achieve Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What makes PTFE chemically resistant and why is this advantageous? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in Harsh Environments
- How does PTFE resist chemical attacks? The Science Behind Its Unmatched Chemical Inertness
- What are the different grades of PTFE and their uses? A Guide to Selecting the Right Material
- What is the electrical insulation capability of PTFE? Unmatched Reliability for Demanding Applications
- Which industries commonly use PTFE due to its special properties? Solve Critical Engineering Challenges



















