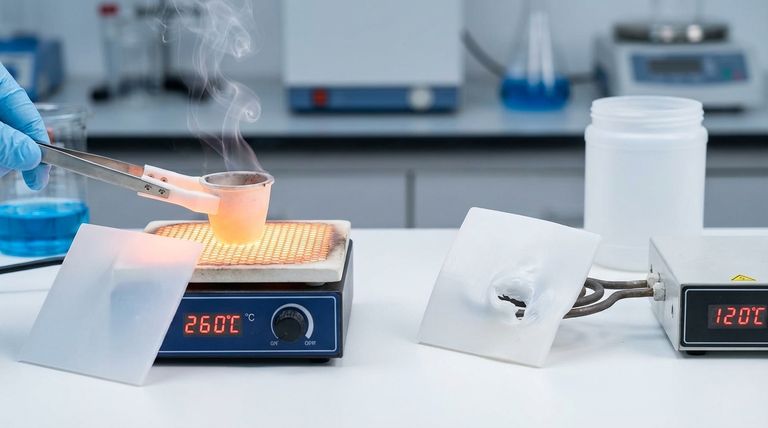
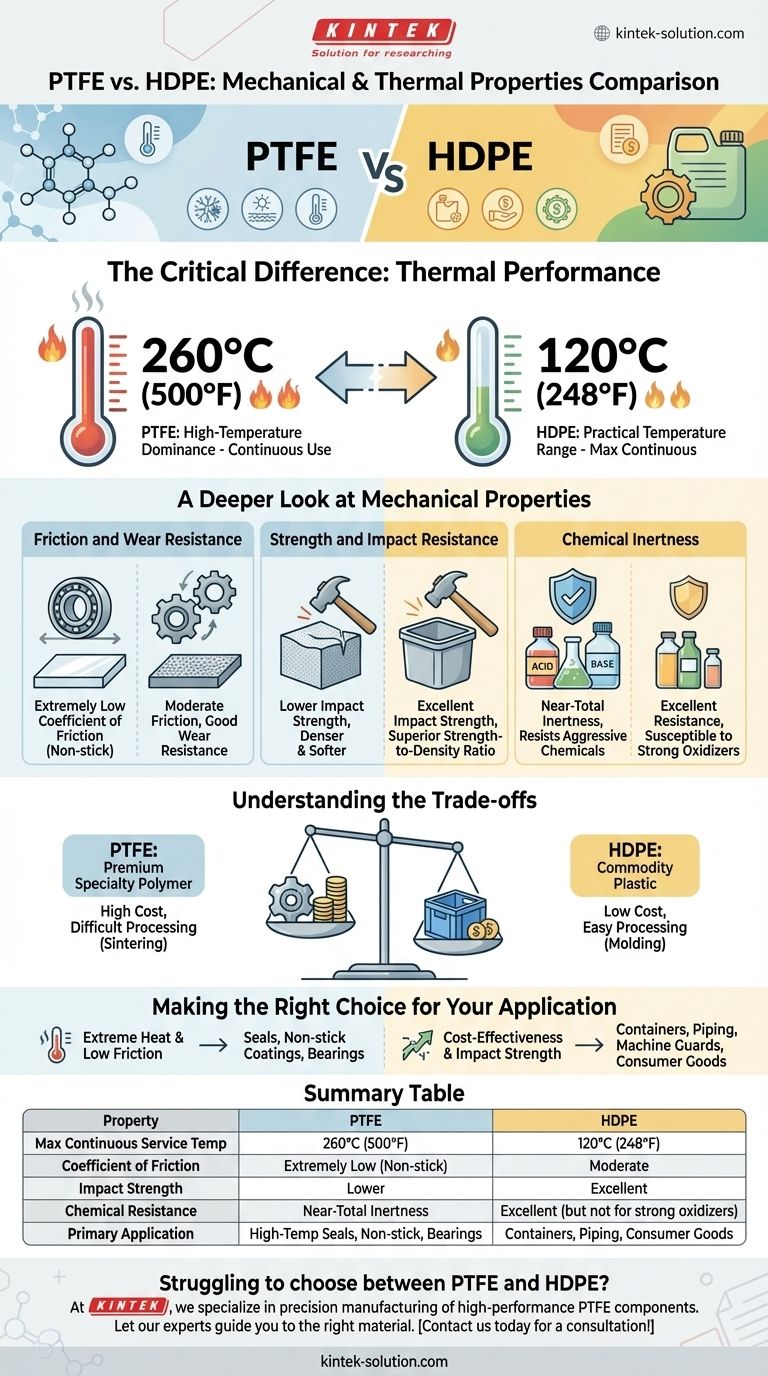
In a direct comparison, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance fluoropolymer designed for extreme conditions, while HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is a versatile and cost-effective workhorse plastic. PTFE far surpasses HDPE in thermal stability, maintaining its properties at temperatures up to 260°C, whereas HDPE's performance significantly degrades above 120°C.
The choice between PTFE and HDPE is fundamentally a trade-off between performance and cost. PTFE is the clear choice for high-temperature, low-friction, and extreme chemical applications, while HDPE provides excellent durability and impact resistance for a fraction of the price in less demanding environments.

The Critical Difference: Thermal Performance
The most significant distinction between these two materials is their ability to withstand heat. This single factor often dictates which material is suitable for a given application.
PTFE's High-Temperature Dominance
PTFE is engineered for thermal stability. It can be used continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) without significant degradation of its mechanical properties.
This makes it an essential material for high-temperature seals, gaskets, and components used in aerospace, chemical processing, and advanced manufacturing.
HDPE's Practical Temperature Range
HDPE offers good performance in a more common range of temperatures. Its maximum continuous service temperature is approximately 120°C (248°F).
Beyond this point, HDPE will begin to soften and lose its structural integrity. While unsuitable for high-heat applications, this range is more than sufficient for a vast array of consumer and industrial products.
A Deeper Look at Mechanical Properties
While temperature is a primary differentiator, the mechanical behaviors of PTFE and HDPE are fundamentally different and suited for distinct purposes.
Friction and Wear Resistance
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it its famous non-stick quality. This property, combined with good wear resistance, makes it ideal for high-performance bearings, bushings, and sliding plates where low friction is critical.
Strength and Impact Resistance
HDPE exhibits a superior strength-to-density ratio and excellent impact resistance. It is a tough, durable material that can withstand significant physical abuse without fracturing.
This is why HDPE is commonly used for products like chemical drums, cutting boards, and piping systems that require high durability at ambient temperatures. In contrast, PTFE is much denser and softer, making it less suitable for high-load, high-impact structural applications.
Chemical Inertness
Both materials have excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals. However, PTFE is almost completely chemically inert, able to resist even the most aggressive acids and bases.
HDPE is resistant to many common chemicals but can be susceptible to strong oxidizing agents and certain hydrocarbons over long-term exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct material requires a clear-eyed assessment of performance needs versus budget constraints. The differences here are stark.
Cost vs. Performance
This is the most practical trade-off. PTFE is a premium specialty polymer, and its cost can be many times higher than that of HDPE.
HDPE is a commodity plastic, produced in massive volumes at a very low cost. Its combination of good performance and low price makes it one of the most widely used plastics in the world.
Processing and Fabrication
HDPE is easily processed using common high-volume methods like injection molding and blow molding, contributing to its low cost for finished goods.
PTFE is more difficult to process. It cannot be melt-processed in the same way and is typically shaped through compression and sintering, which is a slower and more expensive manufacturing cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided entirely by the demands of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat and low friction: Choose PTFE for applications like high-temperature seals, non-stick coatings, and self-lubricating bearings.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and impact strength: Choose HDPE for products like containers, piping, machine guards, and consumer goods.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical resistance: PTFE is the safest choice for handling the most aggressive solvents and acids.
Choosing the right material begins with a clear understanding of your application's specific operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Continuous Service Temp | 260°C (500°F) | 120°C (248°F) |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely Low (Non-stick) | Moderate |
| Impact Strength | Lower | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Near-Total Inertness | Excellent (but not for strong oxidizers) |
| Primary Application | High-Temp Seals, Non-stick, Bearings | Containers, Piping, Consumer Goods |
Struggling to choose between PTFE and HDPE for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components like seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the optimal material solution for your specific thermal, chemical, and mechanical requirements.
Let our experts guide you to the right material. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















