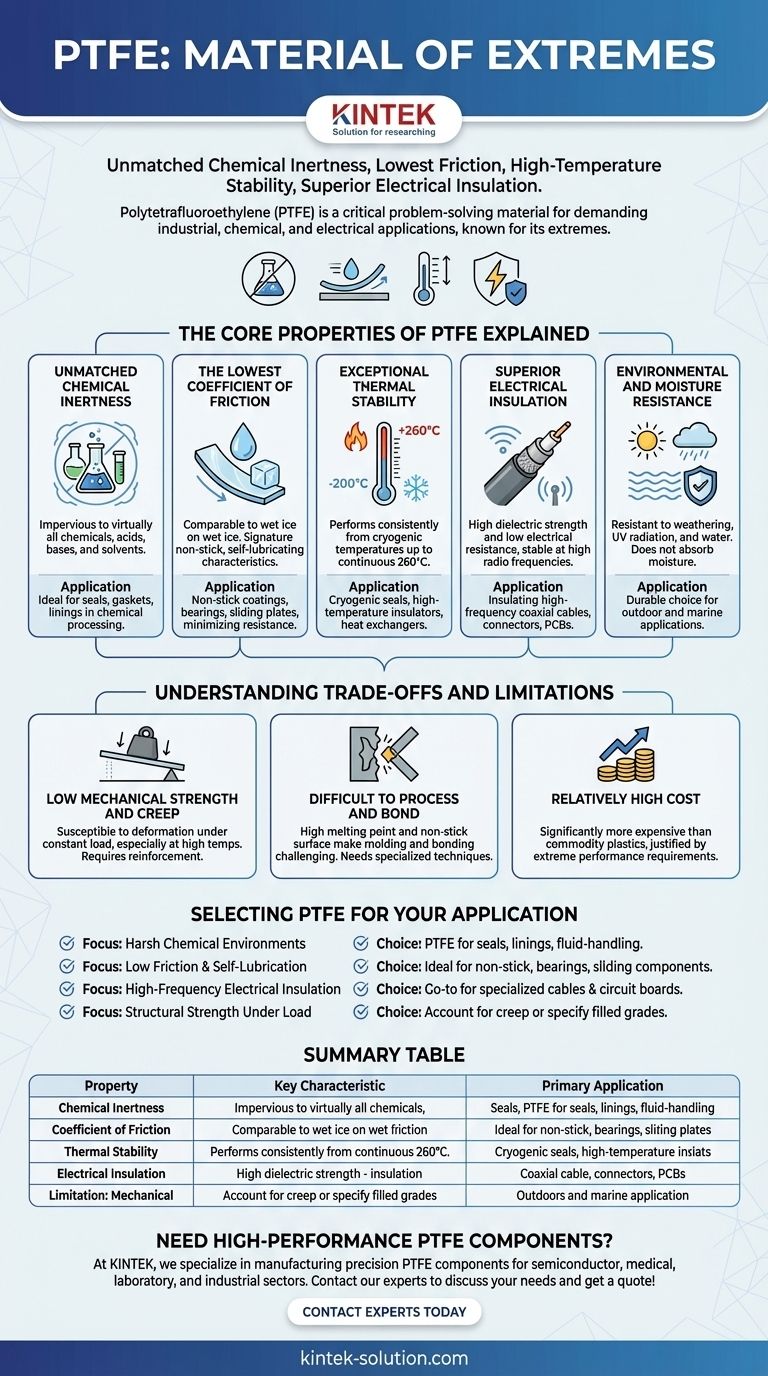
Fundamentally, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of extremes. Its defining properties include near-universal chemical inertness, an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, excellent high-temperature stability, and outstanding electrical insulation. This unique combination makes it a critical problem-solving material in demanding industrial, chemical, and electrical applications.
PTFE is the material of choice when a component must survive harsh chemical environments, operate across a wide temperature range, or provide a non-stick, low-friction surface. Its value is not as a general-purpose plastic, but as a specialty polymer that performs reliably where conventional materials fail.

The Core Properties of PTFE Explained
To select PTFE, you must understand how its unique characteristics translate into real-world performance. Each property serves a distinct engineering purpose.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually impervious to chemical attack. It shows remarkable resistance to a vast range of mineral and organic acids, bases, solvents, and other corrosive agents.
This property makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, linings, and components used in chemical processing and fluid handling systems where material degradation is a primary concern.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, comparable to wet ice on wet ice. This gives it its signature non-stick and self-lubricating characteristics.
This is the principle behind non-stick coatings on cookware, but it is also critical for industrial applications like low-friction bearings, sliding plates, and any component where minimizing resistance and preventing material adhesion is essential.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE performs consistently across an exceptionally broad temperature range. It maintains its properties and flexibility from cryogenic temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F).
This allows it to be used in applications ranging from cryogenic seals to high-temperature insulators and components in heat exchangers, where other polymers would become brittle or melt.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength and very low electrical resistance. Crucially, these properties remain stable even at high radio frequencies.
This makes it a premier choice for insulating high-frequency coaxial cables, connectors, and as a substrate for printed circuit boards (PCBs) used in microwave and radio frequency applications.
Environmental and Moisture Resistance
PTFE is highly resistant to weathering, UV radiation, and water. It does not absorb moisture, which ensures its mechanical and electrical properties remain stable even in damp environments. This makes it a durable choice for outdoor and marine applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. While PTFE's properties are extraordinary, its limitations are equally important to consider during the design phase.
Low Mechanical Strength and Creep
Compared to engineering metals or even other high-performance plastics, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to "creep," meaning it can slowly deform over time when under a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures.
This is a critical design consideration. For structural applications, PTFE's load-bearing capacity is limited unless it is reinforced with fillers like glass fiber or carbon.
Difficult to Process and Bond
The very properties that make PTFE useful also make it challenging to work with. Its high melting point and melt viscosity make it unsuitable for conventional injection molding.
Furthermore, its non-stick surface makes it extremely difficult to bond to other materials using adhesives. Joining PTFE parts often requires specialized surface treatments or mechanical fastening.
Relatively High Cost
As a high-performance fluoropolymer, PTFE is significantly more expensive than common commodity plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its use is typically justified by performance requirements that other, cheaper materials cannot meet.
Selecting PTFE for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is performance in harsh chemical environments: PTFE is an almost unmatched choice for seals, linings, and fluid-handling components.
- If your primary focus is low friction and self-lubrication: It is ideal for non-stick surfaces, bearings, and sliding components where external lubricants are not viable.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its excellent dielectric properties make it a go-to material for specialized cables and circuit boards.
- If your primary focus is structural strength under load: You must account for its tendency to creep or specify a filled grade of PTFE to improve mechanical properties.
Ultimately, PTFE's value lies in its ability to provide long-term reliability in operating conditions that are simply too extreme for most other materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Near-universal resistance to acids, bases, solvents | Seals, gaskets, linings in chemical processing |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely low, self-lubricating | Non-stick surfaces, bearings, sliding components |
| Thermal Stability | Stable from -200°C to +260°C | Cryogenic seals, high-temperature insulators |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, stable at high frequencies | High-frequency cables, connectors, PCBs |
| Limitation: Mechanical | Low strength, susceptible to creep under load | Requires filled grades for structural applications |
Need high-performance PTFE components that leverage these extreme properties?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand how to design and fabricate with PTFE to overcome its limitations and maximize its unique benefits for your specific application.
Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get reliable, high-quality parts that perform in your most demanding environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss your PTFE component needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and how was it first manufactured? The Accidental Discovery of Teflon
- What certifications does the manufacturer of PTFE products hold? The ISO 9001 Assurance for Quality
- How is Teflon utilized in the automotive industry? Enhance Vehicle Efficiency and Durability
- What are the applications of PTFE in the food and beverage industry? Ensure Purity, Safety, and Efficiency
- How chemically resistant is PTFE? Discover its near-total inertness to most chemicals
- What are some consumer product applications of PTFE? Discover its Versatility Beyond Non-Stick Pans
- What are the key takeaways about PTFE and expanded PTFE? Choosing the Right High-Performance Polymer
- What are common uses of PTFE? Unlock Versatility for Your Industry



















