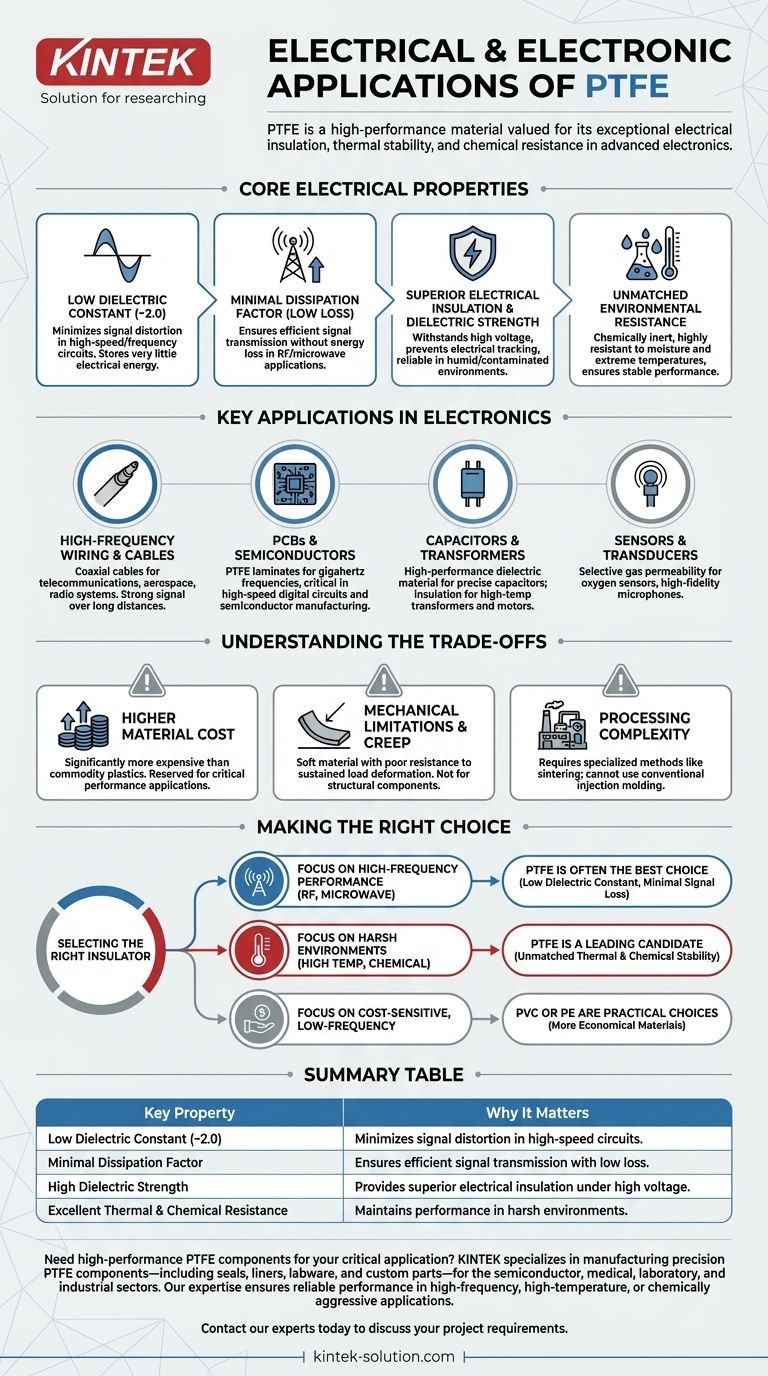
In the electrical and electronics industry, PTFE is prized for its use in high-performance applications like wire and cable insulation, printed circuit boards (PCBs), capacitors, and connectors. Its selection is driven by a unique combination of exceptional electrical insulation, thermal stability, and chemical resistance that commodity plastics cannot match.
The core reason PTFE is indispensable in advanced electronics is not simply that it's a good insulator. Its true value lies in its remarkably low dielectric constant and minimal signal loss, which are critical for maintaining signal integrity in high-frequency and high-speed applications.

The Core Electrical Properties That Define PTFE
To understand PTFE's role, you must first understand the properties that set it apart. These characteristics are a direct result of its stable and symmetric molecular structure.
Exceptionally Low Dielectric Constant
PTFE has a dielectric constant of around 2.0, one of the lowest of any solid material. This means it stores very little electrical energy in an electric field.
For high-speed circuits and high-frequency cables, this property is crucial as it minimizes capacitance between conductors, preventing signal distortion and interference.
Minimal Dissipation Factor (Low Loss)
The material has an extremely low dissipation factor, meaning it absorbs very little energy from alternating electrical signals that pass through it.
This "low loss" characteristic is vital for radio frequency (RF) and microwave applications, ensuring that the signal's power is transmitted efficiently without being wasted as heat.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand a very high voltage before it breaks down and allows current to flow.
It is also highly resistant to electrical tracking, which is the formation of a conductive path along the surface of an insulator, a common failure point in contaminated or high-humidity environments.
Unmatched Environmental Resistance
Beyond its electrical properties, PTFE is almost completely chemically inert and highly resistant to moisture.
This durability ensures its electrical performance remains stable and reliable even when exposed to harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures, or humidity.
Key Applications in Electronics and Electrical Systems
These fundamental properties translate directly into specific, high-value applications where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
High-Frequency Wiring and Cables
PTFE is the insulator of choice for coaxial cables used in telecommunications, aerospace, and radio systems. Its low loss properties ensure the signal remains strong and clear over long distances.
Its high-temperature resistance also makes it ideal for wiring inside electronic enclosures where heat can build up.
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) and Semiconductors
In high-speed digital and RF circuits, the PCB substrate material is critical. PTFE-based laminates are used to create circuits that can handle gigahertz frequencies with minimal signal degradation.
Its purity and chemical resistance also make it a valuable material in semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Capacitors and Transformers
PTFE film is used as a high-performance dielectric material in capacitors. Its stability across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies allows for the creation of precise and reliable electronic components.
Similarly, its excellent insulation and high-temperature tolerance make it ideal for insulating windings in high-performance transformers and motors.
Sensors and Transducers
Specialized applications leverage PTFE's other unique qualities. For example, its selective gas permeability makes PTFE film a key component in oxygen sensors and high-fidelity microphones.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its performance is exceptional, PTFE is not the default choice for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE is significantly more expensive than common insulators like Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) or Polyethylene (PE). Its use is typically reserved for applications where its unique performance characteristics justify the cost.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material with poor resistance to "creep," meaning it can slowly deform under a sustained mechanical load. It is not suitable for structural components.
Processing Complexity
Due to its high melt viscosity, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding. It requires specialized methods like sintering, which adds to manufacturing complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right insulator requires matching the material's properties to the technical and commercial demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency performance (RF, microwave, high-speed data): PTFE is often the best technical choice due to its low dielectric constant and minimal signal loss.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments (high temp, chemical exposure): PTFE's unmatched thermal and chemical stability makes it a leading candidate for wire insulation and component protection.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, low-frequency applications (e.g., standard building wire): More economical materials like PVC or polyethylene are the practical and appropriate choice.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental electrical properties of PTFE empowers you to specify it precisely where its unique advantages are most needed.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for Electronics |
|---|---|
| Low Dielectric Constant (~2.0) | Minimizes signal distortion in high-speed/high-frequency circuits. |
| Minimal Dissipation Factor | Ensures efficient signal transmission with low loss in RF/microwave applications. |
| High Dielectric Strength | Provides superior electrical insulation, even under high voltage. |
| Excellent Thermal & Chemical Resistance | Maintains performance and reliability in harsh operating environments. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom parts—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures your high-frequency, high-temperature, or chemically aggressive applications perform reliably.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















