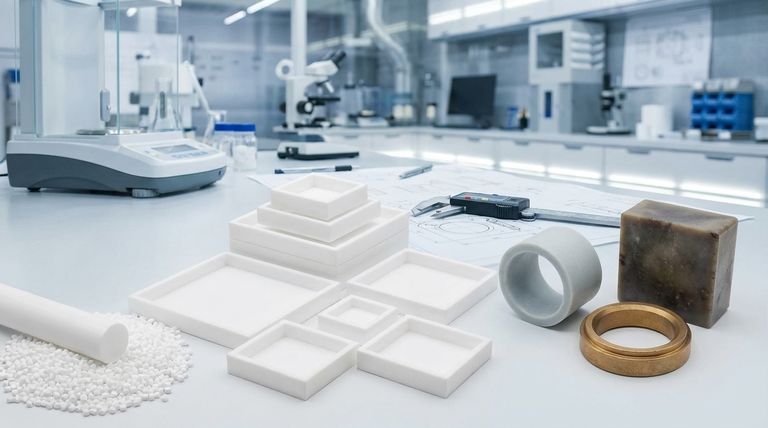
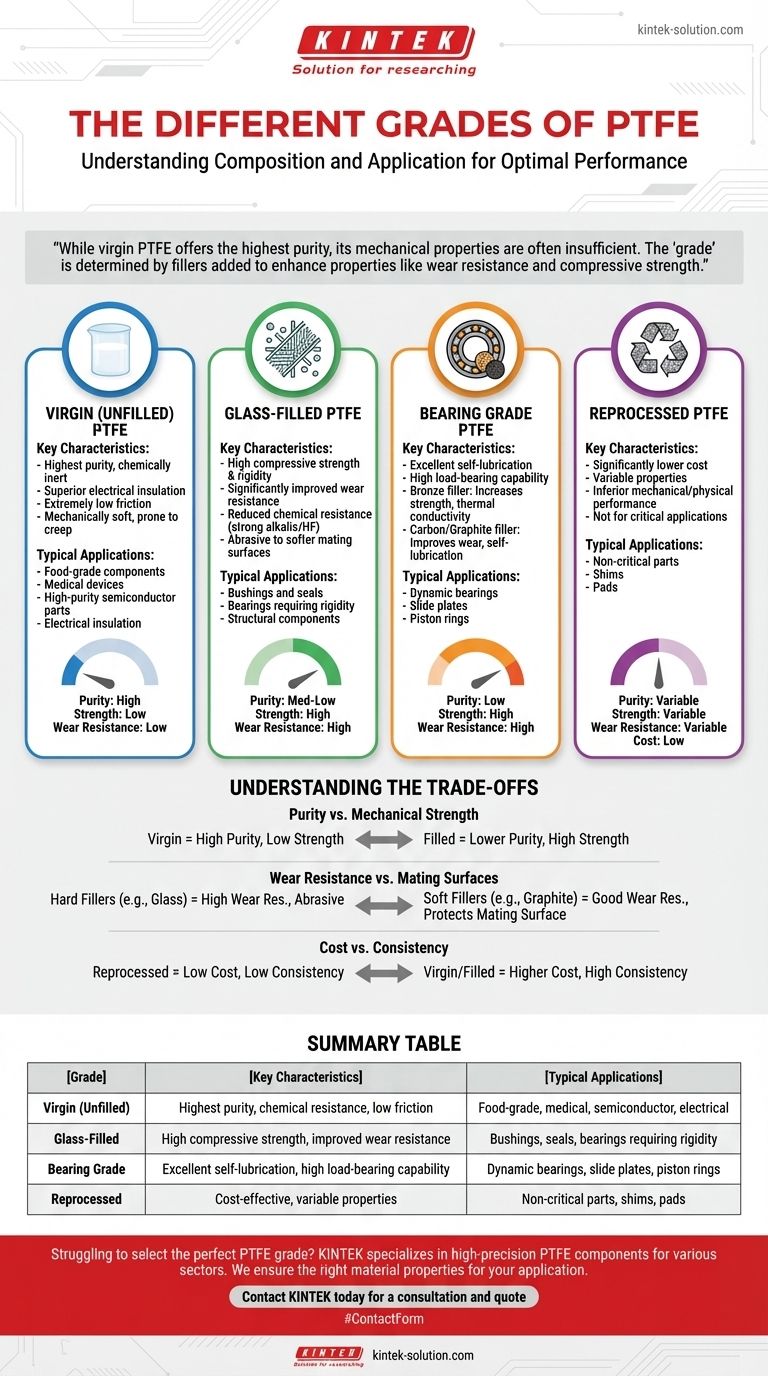
The primary grades of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are categorized by their composition and intended application. The main types include virgin (unfilled) PTFE for purity, various filled grades for enhanced mechanical properties, specialized bearing grades for dynamic applications, and reprocessed PTFE as a cost-effective alternative. Each grade is engineered to solve a different set of technical challenges.
While virgin PTFE offers the highest purity and chemical resistance, its mechanical properties are often insufficient for demanding applications. The "grade" of PTFE is therefore determined by the specific fillers added to enhance properties like wear resistance and compressive strength, creating a trade-off between purity and performance.

A Breakdown of Key PTFE Grades
To select the correct material, it's essential to understand how the composition of each PTFE grade affects its performance characteristics. The choice is rarely about which is "best" overall, but which is best for a specific environment and function.
Virgin (Unfilled) PTFE
Virgin PTFE is the purest form of the material, made directly from resin without any fillers or recycled content.
Its primary characteristics are superior chemical resistance, excellent electrical insulation, and an extremely low coefficient of friction.
However, virgin PTFE is mechanically soft and susceptible to creep (cold flow under load) and has poor wear resistance, making it unsuitable for high-load or abrasive applications. It is the standard for food-grade, medical, or high-purity semiconductor applications.
Glass-Filled PTFE
This is one of the most common filled grades, where glass fibers are blended with the PTFE resin, typically in proportions from 5% to 40%.
The glass filler dramatically increases compressive strength and rigidity. It also significantly improves wear resistance compared to virgin PTFE.
The trade-off is a reduction in chemical resistance against strong alkalis and hydrofluoric acid. The abrasive nature of glass can also cause wear on softer mating surfaces.
Bearing Grade PTFE
This is not a single grade but a category of PTFE compounds specifically engineered for dynamic, low-friction applications like bearings, slide plates, and piston rings.
These grades use fillers that enhance strength while providing self-lubricating properties. Common fillers include:
- Bronze: Increases compressive strength and thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in high-speed applications.
- Carbon/Graphite: Improves wear resistance, load-bearing capability, and provides excellent self-lubrication.
Reprocessed (Recycled) PTFE
Reprocessed PTFE is manufactured from recycled scrap and unused ends from the production of virgin material.
Its main advantage is a significantly lower cost. This makes it a viable option for applications where material performance is not critical.
The downside is that its mechanical and physical properties are less consistent and generally inferior to those of virgin or filled grades. It should not be used in applications requiring tight tolerances or high reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE grade is an exercise in balancing competing requirements. Adding a filler to improve one property will almost always impact another.
Purity vs. Mechanical Strength
Virgin PTFE offers the highest purity and is the most chemically inert. Any filler, by definition, compromises this purity to gain mechanical advantages like wear resistance or strength.
Wear Resistance vs. Mating Surfaces
While hard fillers like glass provide excellent wear resistance for the PTFE part, they can be abrasive to the surfaces they run against, especially softer metals like aluminum.
Bearing grades with softer, self-lubricating fillers like graphite are often chosen to protect the integrity of the mating surface in a dynamic system.
Cost vs. Consistency
Reprocessed PTFE provides a clear cost benefit. However, this comes at the expense of material predictability and performance, making it unsuitable for anything beyond non-critical components like shims or pads.
Selecting the Right PTFE Grade for Your Application
Your final decision should be driven entirely by the primary demands of your project's environment and function.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or electrical insulation: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance against hard surfaces: A glass-filled or bronze-filled grade will provide the necessary durability.
- If your primary focus is low friction in a dynamic system against a sensitive mating surface: A bearing grade with carbon or graphite fillers offers the best self-lubricating properties.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost for non-critical parts: Reprocessed PTFE may be a viable option.
Ultimately, selecting the correct PTFE grade involves aligning the material's specific enhancements with the precise demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin (Unfilled) | Highest purity, chemical resistance, low friction | Food-grade, medical, semiconductor, electrical insulation |
| Glass-Filled | High compressive strength, improved wear resistance | Bushings, seals, bearings requiring rigidity |
| Bearing Grade | Excellent self-lubrication, high load-bearing capability | Dynamic bearings, slide plates, piston rings |
| Reprocessed | Cost-effective, variable properties | Non-critical parts, shims, pads |
Struggling to select the perfect PTFE grade for your component? The choice between virgin, filled, bearing, or reprocessed PTFE is critical to your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the right material properties for your specific application, balancing performance, purity, and cost. Let our team guide you from prototype to high-volume production. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are some industrial applications of expanded PTFE? Solve Critical Sealing, Filtration, and Insulation Challenges
- What are the mechanical properties of filled PTFE? Enhanced Wear Resistance and Strength for Demanding Applications
- What are the disadvantages of PTFE/Teflon? Understanding Its Mechanical and Fabrication Limits
- What PTFE formulations are recommended for automotive and aerospace applications and why? Optimize with Bronze-Filled PTFE
- What alternatives exist for PTFE in consumer products? Discover Safer Options for Cookware, Clothing & Cosmetics
- How is Teflon used in industrial applications? Solve Extreme Heat, Chemical & Friction Challenges
- What medical applications benefit from PTFE? A Guide to Its Critical Role in Healthcare
- What are the non-stick properties of PTFE and their applications? Unlock Clean Release & Low Friction



















