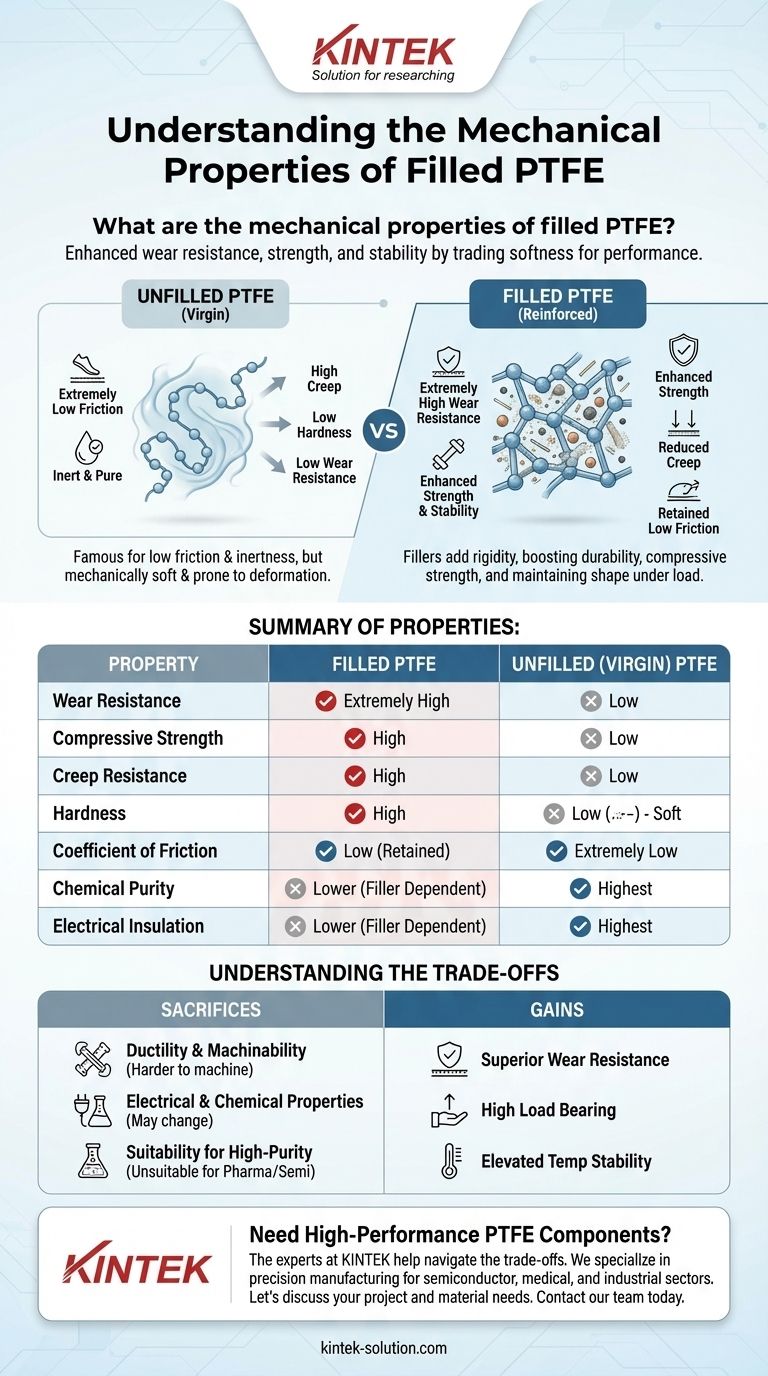
The primary mechanical properties of filled PTFE are significantly enhanced wear resistance, greater strength under load, and improved stability at high temperatures compared to its unfilled counterpart. Fillers are added specifically to overcome the inherent mechanical weaknesses of virgin PTFE, such as its tendency to deform under pressure, while retaining its signature low friction.
The core principle is straightforward: adding fillers to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a deliberate engineering choice to trade some of the material's softness and ductility for a major boost in hardness, wear resistance, and structural integrity.

The Baseline: Understanding Unfilled PTFE
To appreciate the role of fillers, one must first understand the properties of pure, or "virgin," PTFE. It is a material of extremes, defined as much by its weaknesses as its strengths.
### Exceptional Low Friction and Inertness
Unfilled PTFE is famous for its extremely low coefficient of friction, with static and dynamic values being nearly identical. This allows for exceptionally smooth, stick-slip-free motion.
It is also one of the most chemically inert polymers available and possesses excellent electrical insulation properties.
### Key Mechanical Weaknesses
Despite its strengths, virgin PTFE is mechanically soft and not very stiff. It has a relatively low hardness value (Shore D50-55).
This softness contributes to two significant issues in mechanical applications: low wear resistance and a high susceptibility to creep—the tendency to permanently deform over time when subjected to a constant load.
How Fillers Transform PTFE's Mechanical Behavior
Adding filler materials like glass, carbon, or bronze into the PTFE matrix directly counteracts its mechanical limitations.
### Drastically Improved Wear Resistance
This is the most significant improvement. The references note that filled PTFE is extremely hard-wearing. The abrasive fillers increase the material's surface hardness, making it far more durable in dynamic applications like seals, bearings, and guides.
### Enhanced Strength and Stability
Filled PTFE exhibits superior compressive strength and stability, especially under heavy loads and at elevated temperatures. The fillers act as a reinforcing skeleton within the polymer, preventing it from yielding easily.
### Reduced Creep (Deformation Under Load)
The added rigidity from fillers is crucial for combating creep. In applications where a component is under constant pressure, such as a valve seat or a structural seal, filled PTFE maintains its shape and sealing force far better than unfilled grades.
### Retained Core Advantages
Critically, these mechanical enhancements are achieved while retaining PTFE's famously low coefficient of friction. While the exact value may change slightly depending on the filler, the excellent sliding properties remain a key feature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Introducing fillers is not without consequences. Choosing the right material requires acknowledging what is sacrificed to gain mechanical performance.
### Impact on Ductility and Machinability
Unfilled PTFE is soft and ductile, allowing for high cutting speeds and minimal tool wear during machining.
Filled PTFE is significantly harder and more abrasive. Machining it requires lower speeds, specialized tooling, and careful thermal management to prevent damage to both the part and the cutting tool.
### Altered Electrical and Chemical Properties
Virgin PTFE has the highest electrical insulation properties. The addition of certain fillers, particularly carbon, can make the material more conductive, rendering it unsuitable for high-voltage insulation.
While generally still highly resistant, the chemical compatibility of the filler material itself must be considered, as it may not match the near-universal inertness of pure PTFE.
### Suitability for High-Purity Applications
For industries like semiconductor or pharmaceuticals, the purity of the material is paramount. Unfilled, virgin PTFE is the standard choice. Mechanical grade PTFE, made from reground material, and other filled versions are not suitable for these high-purity environments.
Selecting the Right PTFE for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the primary demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance, load-bearing, or high temperatures: Filled PTFE is the definitive choice for its superior strength and durability.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or chemical purity: Unfilled (virgin) PTFE is the only suitable option.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, low-stress applications where cost is a major factor: Mechanical grade PTFE (reprocessed) can offer a good balance of properties.
Ultimately, choosing between filled and unfilled PTFE is a deliberate engineering decision based on a clear understanding of your performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Property | Filled PTFE | Unfilled (Virgin) PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Extremely High | Low |
| Compressive Strength | High | Low |
| Creep Resistance | High | Low |
| Hardness | High | Low (Soft) |
| Coefficient of Friction | Low (Retained) | Extremely Low |
| Chemical Purity | Lower (Filler Dependent) | Highest |
| Electrical Insulation | Lower (Filler Dependent) | Highest |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Choosing the right PTFE material is critical for your application's success. The experts at KINTEK are here to help you navigate the trade-offs between wear resistance, strength, and purity.
We specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, we deliver solutions that meet your exact mechanical and environmental requirements.
Let's discuss your project and material needs. Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















