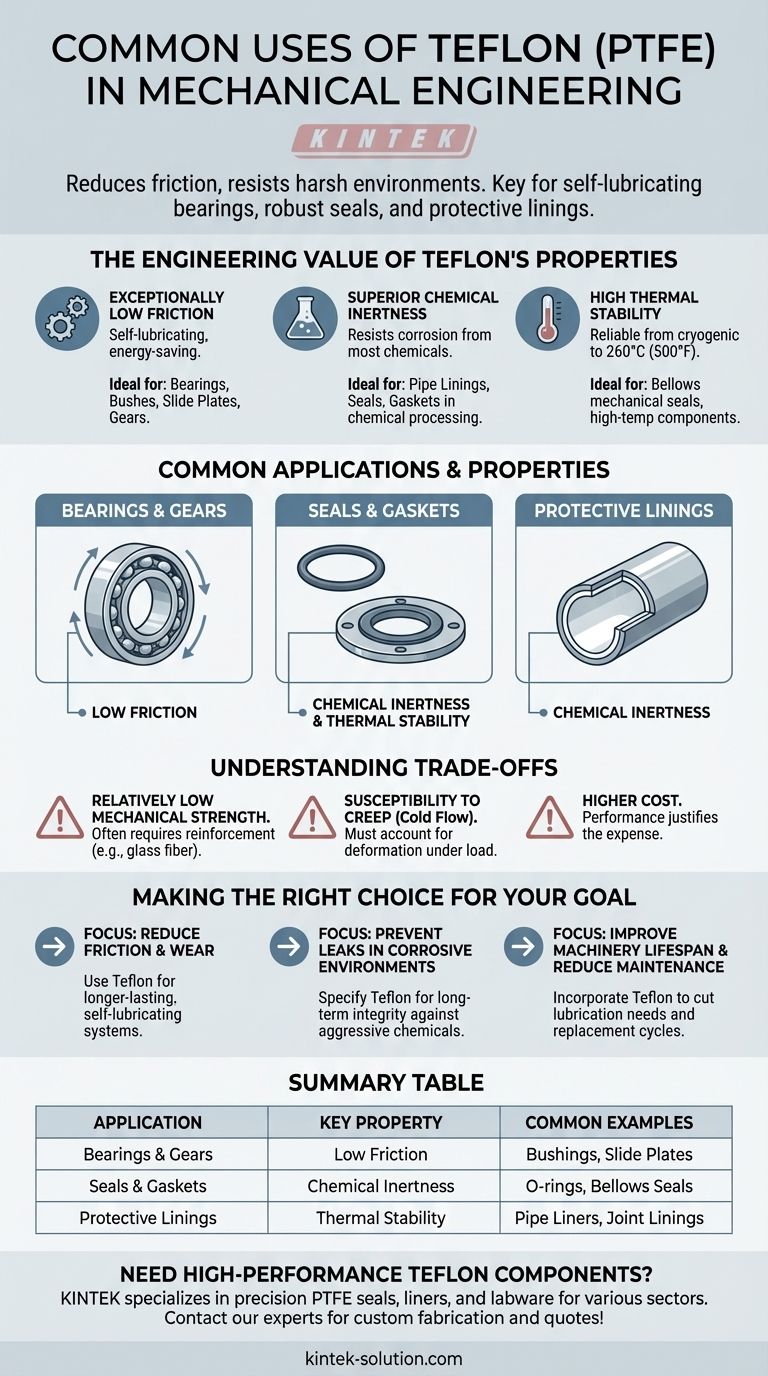
In mechanical engineering, Teflon is most commonly used for components where reducing friction and resisting harsh environments are critical. Its primary applications include self-lubricating bearings and gears, robust seals and gaskets like O-rings, and protective linings for pipes and joints that handle corrosive chemicals.
The core reason Teflon (PTFE) is so prevalent in mechanical design is not just its famous non-stick quality, but its unique combination of extremely low friction, chemical inertness, and thermal stability. This allows engineers to solve persistent problems of wear, corrosion, and sealing in a single material.

The Engineering Value of Teflon's Properties
Teflon, the brand name for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a high-performance fluoropolymer. Its value comes from a set of properties that directly address common mechanical challenges.
Exceptionally Low Friction
Teflon possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This self-lubricating quality is fundamental to its use.
This property drastically reduces the energy required to overcome friction in moving parts, which improves overall system efficiency.
It is ideal for bearings, bushes, slide plates, and gears, where it allows for smooth rotational or sliding movement with minimal wear and without the need for external lubricants.
Superior Chemical Inertness
Teflon is virtually inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and bases.
This makes it an essential material for components exposed to corrosive substances, preventing degradation and extending the equipment's service life.
Applications like pipe linings, seals, and gaskets in chemical processing or pulp and paper manufacturing rely on this property to maintain process integrity and prevent leaks.
High Thermal Stability
This material maintains its key properties across a wide temperature range, from cryogenic lows to highs of around 260°C (500°F).
This thermal resistance allows it to function reliably in high-temperature engines, pumps, and industrial machinery where other polymers would fail.
Bellow mechanical seals and other critical sealing components often use Teflon to ensure they do not become brittle or deform under extreme operational heat.
Effective Sealing and Gasketing
Because Teflon is a stable and conformable material, it is highly effective for creating tight, durable seals.
It prevents leaks of fluids and gases in demanding applications, from simple O-rings to complex custom gaskets. This reliability is crucial for safety and efficiency, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Understanding the Engineering Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, Teflon is not a universal solution. An effective design requires acknowledging its limitations.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals and even other engineering plastics, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has lower tensile strength and is more susceptible to abrasion from sharp particles.
This means it is not suitable for high-load structural components unless it is reinforced with fillers like glass fiber or carbon.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a constant compressive load, Teflon can slowly deform over time in a process known as "creep" or "cold flow."
Engineers must account for this phenomenon in their designs, especially when using Teflon for gaskets and seals, to ensure that sealing pressure is maintained throughout the component's life.
Higher Cost
As a high-performance polymer, Teflon is more expensive than many common plastics and commodity materials.
Its use must be justified by the performance demands of the application, such as extreme temperatures, chemical exposure, or the absolute need for low friction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting Teflon is about matching its unique strengths to your primary engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Use Teflon for bearings, bushings, slide plates, and low-friction coatings to create self-lubricating systems that last longer.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks in corrosive environments: Specify Teflon for seals, gaskets, and pipe linings to ensure long-term integrity against aggressive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is improving machinery lifespan and reducing maintenance: Incorporating Teflon components can significantly cut down on lubrication needs and component replacement cycles.
Ultimately, leveraging Teflon correctly allows you to design more efficient, durable, and reliable mechanical systems.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Teflon Property Utilized | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Bearings & Gears | Exceptionally Low Friction | Bushings, Slide Plates |
| Seals & Gaskets | Superior Chemical Inertness | O-rings, Bellows Seals |
| Protective Linings | High Thermal Stability | Pipe Liners, Joint Linings |
Need high-performance Teflon components for your project? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components like seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to solve your toughest friction, sealing, and corrosion challenges. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















