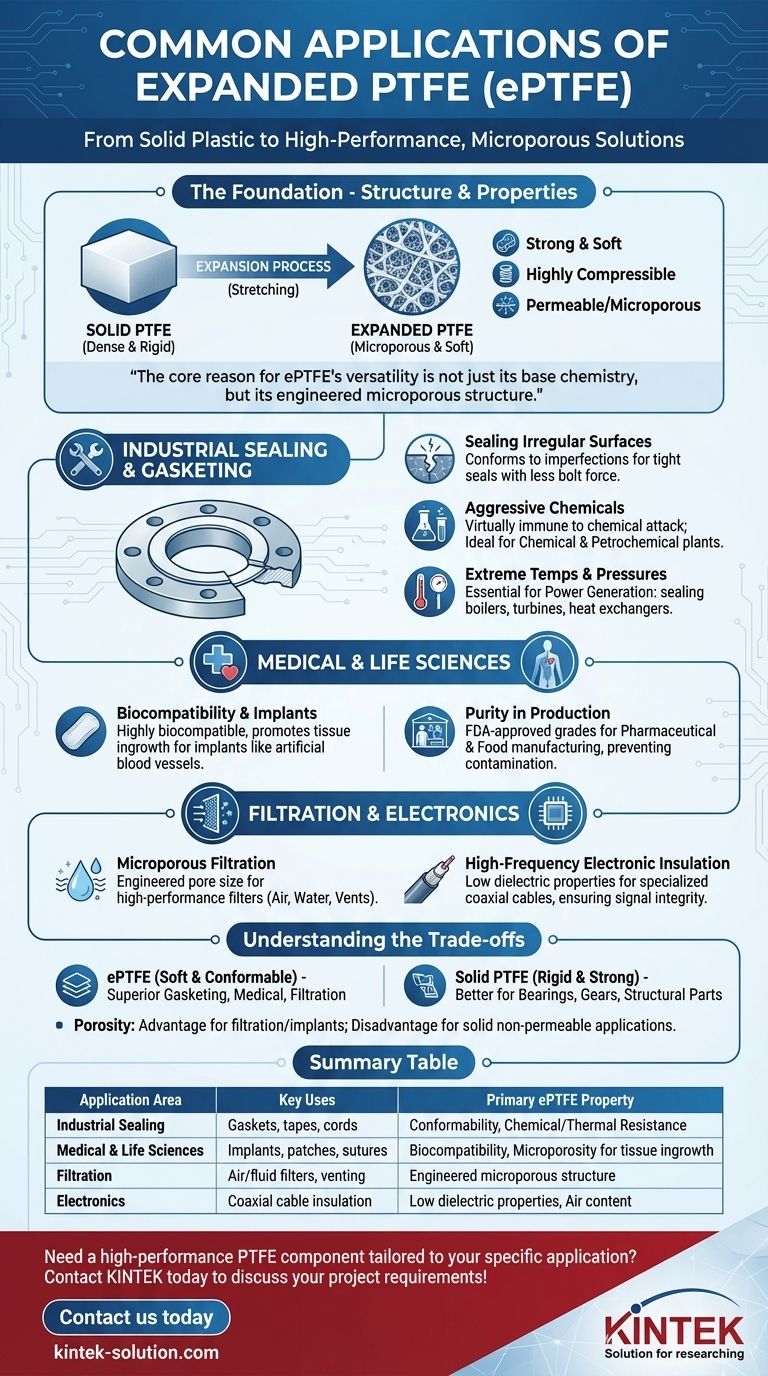
In its most common forms, expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is a premier material for industrial sealing, medical implants, and high-performance filtration. It is most frequently found as gaskets, tapes, or cords used to seal pipe flanges in chemical, power, and pharmaceutical plants, as well as in medical devices like artificial blood vessels and surgical patches due to its unique physical properties.
The core reason for ePTFE's versatility is not just its base chemistry, but its engineered microporous structure. This process of expanding PTFE transforms it from a dense plastic into a strong, soft, and porous material, unlocking a vast range of applications that solid PTFE cannot serve.

The Foundation: Why Expanded PTFE is Different
Before examining its applications, it is critical to understand what makes ePTFE unique. It begins as standard PTFE, a material known for its extreme chemical inertness and low friction.
From Solid Plastic to Microporous Wonder
Standard PTFE is dense and rigid. The expansion process rapidly stretches this material, creating a web-like internal structure of nodes interconnected by fine fibrils.
This microporous structure gives ePTFE a unique combination of properties: it retains PTFE's chemical and thermal resistance while becoming exceptionally soft, compressible, and permeable on a microscopic level.
Core Application Area: Industrial Sealing and Gasketing
The most widespread use of ePTFE is creating highly reliable seals in demanding industrial environments. It is often supplied as a gasket, tape, or pliable cord.
Sealing Irregular and Damaged Surfaces
Unlike rigid gaskets, the soft and conformable nature of ePTFE allows it to compress easily and fill in scratches, pits, and other imperfections on flange faces. This creates a tight, long-lasting seal with less bolt force.
Handling Aggressive Chemicals
Because it is still fundamentally PTFE, ePTFE is virtually immune to attack from aggressive chemicals. This makes it the material of choice for sealing pipelines, vessels, and reactors in the chemical processing and petrochemical industries.
Withstanding Extreme Temperatures and Pressures
ePTFE gaskets and seals maintain their integrity across a wide range of temperatures and high pressures. This makes them essential in power generation plants for sealing boilers, turbines, and heat exchangers.
High-Stakes Applications: Medical and Life Sciences
ePTFE's unique structure and purity make it suitable for applications where material failure is not an option.
Biocompatibility and Medical Implants
The material is highly biocompatible, meaning it does not cause a reaction in the human body. Its microporous structure allows for tissue ingrowth, enabling the body to integrate with the implant.
This property is leveraged in devices such as artificial blood vessels, surgical patches for organ repair, and even specialized sutures.
Purity in Pharmaceutical and Food Production
Due to its inertness and ability to be produced in a pure state, many grades of ePTFE are FDA-approved. This makes it ideal for sealing systems in pharmaceutical and food manufacturing, where preventing contamination is paramount.
Specialized Technical Uses: Filtration and Electronics
The versatility of ePTFE extends to highly technical and specialized roles that depend directly on its unique physical form.
Microporous Filtration
The network of pores in ePTFE can be engineered to a specific size, turning it into a high-performance filter membrane. It is used to filter fine particulates from air, vent sensitive electronics while blocking water, and purify fluids.
A specific example is its use in water purification systems, where ozone gas is diffused through ePTFE tubing to treat water.
High-Frequency Electronic Insulation
Standard PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with low dielectric properties. In its expanded form, ePTFE is used in specialized applications, such as insulators for high-performance coaxial cables, where air content and signal integrity are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing ePTFE requires understanding its specific advantages and limitations compared to its solid counterpart, standard PTFE.
Strength vs. Conformability
ePTFE is exceptionally soft and conformable, making it a superior gasketing material. However, it lacks the rigidity and compressive strength of solid PTFE, making it unsuitable for structural components like bearings or gears.
Porosity as a Deliberate Feature
The microporosity of ePTFE is its key advantage for medical implants and filtration. This same porosity, however, means it cannot be used for applications requiring a completely solid, non-permeable material block, such as a valve seat.
Cost and Complexity
The manufacturing process to create expanded PTFE is more complex than producing solid PTFE stock. This generally results in a higher material cost, which is justified by its unique performance in specialized applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material decision should be guided by the primary demand of your project.
- If your primary focus is sealing imperfect flanges or aggressive chemicals: ePTFE gaskets and tapes offer a superior, conformable seal that standard gaskets cannot match.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility for medical implants: ePTFE's microporous structure is essential for promoting tissue integration and ensuring patient safety.
- If your primary focus is high-purity filtration: ePTFE membranes provide a chemically inert and efficient solution for separating microscopic particles from fluids and gases.
- If your primary focus is a rigid, load-bearing component: Standard, solid PTFE is the correct choice for applications like bearings, gears, or solid valve components.
Ultimately, expanded PTFE is a testament to how engineering a material's physical structure can create a completely new class of high-performance solutions.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Primary ePTFE Property |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Sealing | Gaskets, tapes, cords for chemical, power, and pharmaceutical plants | Conformability, chemical/thermal resistance |
| Medical & Life Sciences | Artificial blood vessels, surgical patches, sutures | Biocompatibility, microporosity for tissue ingrowth |
| Filtration | Air/fluid filters, venting membranes, water purification | Engineered microporous structure |
| Electronics | Insulation for high-frequency coaxial cables | Low dielectric properties, air content |
Need a high-performance PTFE component tailored to your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a custom ePTFE gasket for a challenging chemical seal or a prototype for a new medical device, our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a solution that delivers superior performance, reliability, and value.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our PTFE solutions can meet your exact needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Can PTFE butterfly valves be used for all types of fluids? Maximize Chemical Resistance and Purity
- What is the overall industrial significance of PTFE sheets? Solve Critical Challenges with Versatile Material
- What are some common grades of PTFE used in fabrication? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the key properties of PTFE flange gaskets? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What industries commonly use PTFE bellows and diaphragms, and why? Ensure Purity & Chemical Resistance
- What are the limitations of PTFE gaskets in high-pressure applications? Overcoming Cold Flow & Creep Issues
- What factors should be considered when choosing a PTFE sheet? Select the Right Grade for Your Application
- How does a PTFE lined wafer check valve function? A Guide to Reliable Backflow Prevention



















