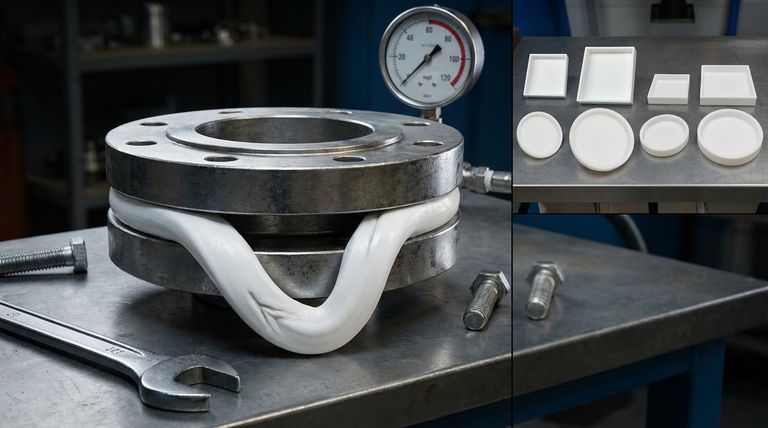
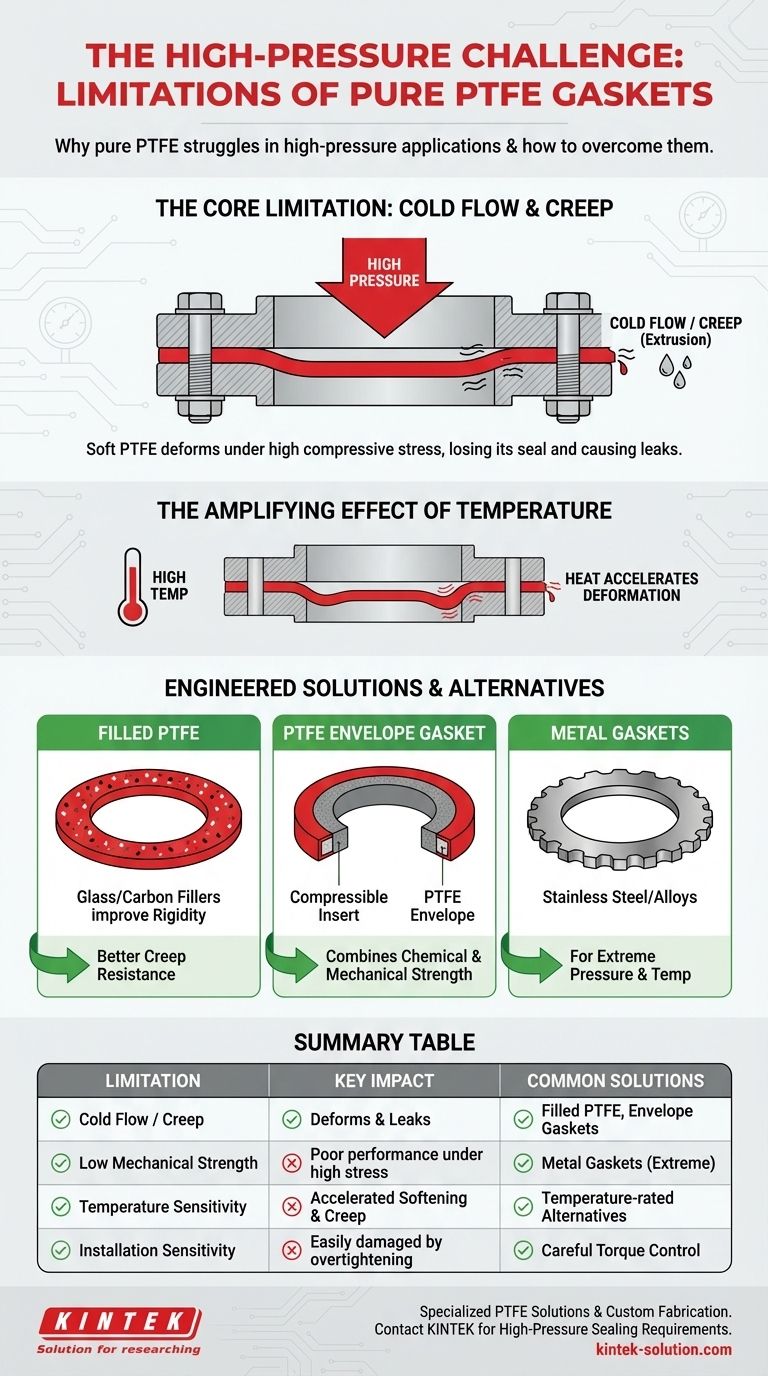
The primary limitation of PTFE gaskets in high-pressure applications is their inherent softness, which makes them prone to deformation and leakage under significant mechanical stress. Unlike metal gaskets, pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) can be squeezed out of a flange connection, a phenomenon known as "cold flow" or creep, which compromises the integrity of the seal over time.
While PTFE offers unmatched chemical resistance, its effectiveness in high-pressure systems is not a given. The core challenge is mechanical, not chemical: the material's tendency to deform under load requires careful engineering considerations or the selection of alternative materials for the most demanding applications.

The Core Limitation: Deformation Under Load
The main reason PTFE gaskets struggle with high pressure is their lack of structural rigidity compared to metals. This softness leads to a specific type of failure.
Understanding "Cold Flow" or Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. When subjected to the high compressive forces required to create a seal in a high-pressure system, the material can slowly deform and "flow" away from the point of pressure.
This process, known as creep or cold flow, is the primary mechanical failure mode. The gasket material essentially extrudes from between the flange faces, leading to a loss of the necessary sealing stress.
The Impact on Sealing Integrity
A gasket works by maintaining a constant sealing force against the flange faces. As PTFE creeps, this stored energy in the compressed gasket dissipates.
The result is a gradual loss of the seal. This may not cause a catastrophic, immediate failure but can lead to slow, persistent leaks that are problematic and potentially dangerous in high-pressure environments.
The Amplifying Effect of Temperature
High temperatures make the problem worse. As PTFE heats up, it becomes even softer and more susceptible to deformation.
Applications involving both high pressure and high temperature significantly accelerate the rate of creep, making pure PTFE gaskets unsuitable for large, hot surface areas where the material can degrade and fail.
Engineered Solutions and Alternatives
While pure PTFE has limitations, the material can be modified or used in specific designs to improve performance. For the most extreme applications, however, other materials are superior.
Specially Designed PTFE Gaskets
Manufacturers have developed solutions to counteract cold flow. These often involve "filled" PTFE, where materials like glass fiber or carbon are added to the polymer matrix to improve rigidity and creep resistance.
Another common solution is the PTFE envelope gasket. This design features a soft, compressible insert material protected by a thin outer layer, or "envelope," of PTFE. This construction combines the chemical resistance of PTFE with the superior mechanical properties of the insert material, allowing it to perform well under higher pressures.
When to Choose Metal Gaskets
For truly high-pressure and high-temperature applications, metal gaskets are often the preferred choice.
Materials like stainless steel or specialized alloys provide superior strength and can maintain a seal under extreme mechanical stress and thermal cycling where a polymer gasket would fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a gasket material always involves balancing competing properties. PTFE is an excellent material, but its advantages come with clear limitations.
Mechanical Strength vs. Chemical Resistance
The decision often comes down to this trade-off. PTFE is chemically inert and can handle a vast range of aggressive media that would destroy other materials.
However, this chemical superiority comes at the cost of lower mechanical strength. You must determine if the primary challenge in your system is chemical attack or mechanical stress.
The Cost Factor
PTFE is a specialized polymer, and its manufacturing process makes it more expensive than traditional rubber gaskets.
While its performance can justify the cost in many applications, it is an important consideration, especially when comparing it to less expensive, lower-performance alternatives.
Installation and Handling
The softness of PTFE means it requires careful handling during installation. Overtightening bolts can easily crush the gasket and initiate cold flow before the system is even pressurized.
Proper torque specifications and installation procedures are critical to ensuring the gasket performs as designed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the appropriate gasket, you must first define the primary challenge of your sealing application.
- If your primary focus is extreme pressure and temperature integrity: Your best choice is likely a metal or composite gasket designed specifically for those conditions.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical media in a low-to-moderate pressure system: A standard, pure PTFE gasket is an excellent and reliable solution.
- If you need a balance of chemical resistance and moderate-to-high pressure: Investigate engineered solutions like filled PTFE or envelope gaskets, and always consult the manufacturer's specifications.
Ultimately, selecting the right gasket requires matching the material's mechanical properties to the specific pressure and temperature demands of your system.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Common Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Flow / Creep | Gasket deforms & extrudes from flange, causing leaks | Filled PTFE, PTFE envelope gaskets |
| Low Mechanical Strength | Poor performance under high compressive stress | Metal gaskets for extreme conditions |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Accelerated creep and softening at high temperatures | Temperature-rated alternatives |
| Installation Sensitivity | Easily damaged by overtightening | Careful torque control during installation |
Struggling with PTFE gasket failure in high-pressure systems? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) and custom solutions for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. We help you overcome cold flow and creep challenges with engineered PTFE formulations and custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific high-pressure sealing requirements and get a solution that delivers both chemical resistance and mechanical reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















