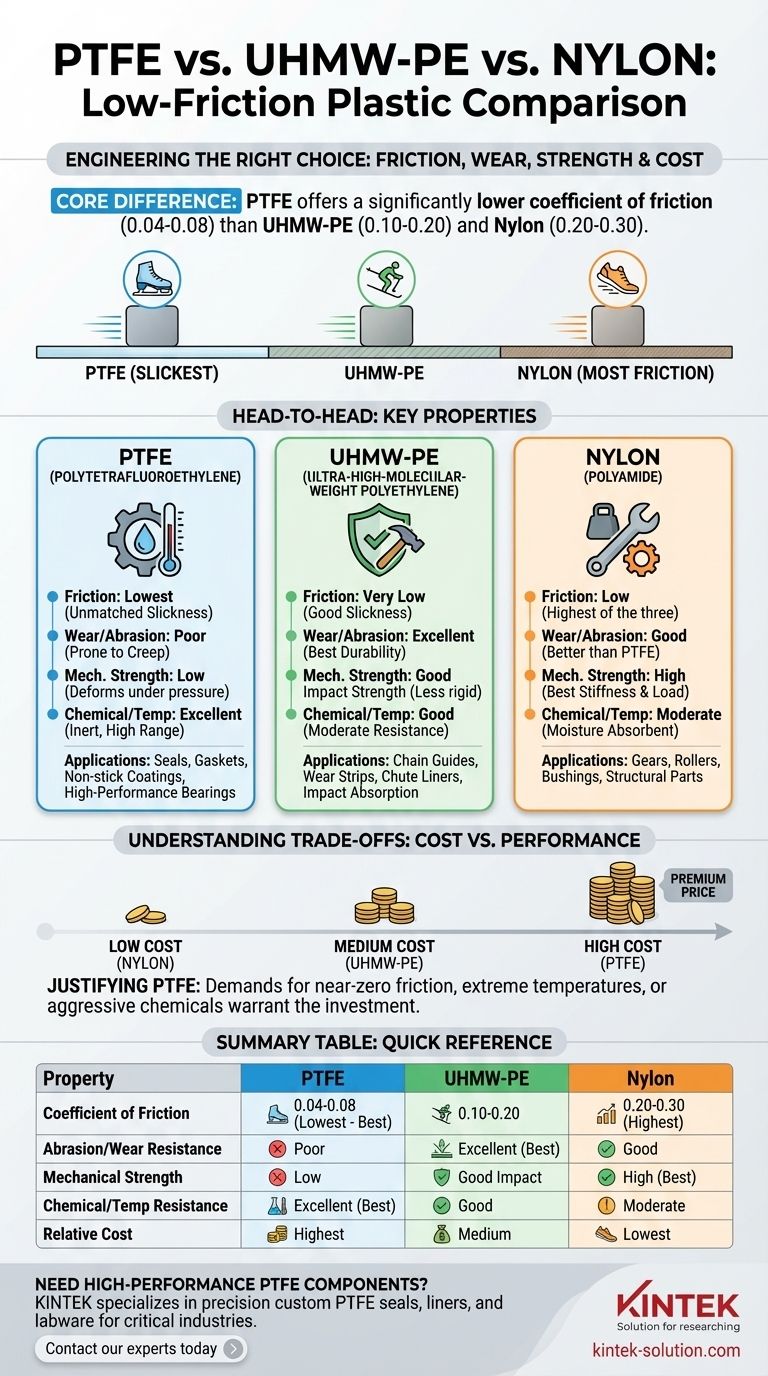
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers a significantly lower coefficient of friction than both Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMW-PE) and Nylon. With a coefficient of friction ranging from 0.04 to 0.08, PTFE is one of the "slickest" materials available, compared to UHMW-PE (0.10–0.20) and Nylon (0.20–0.30). However, this single metric does not tell the full story.
The decision between PTFE, UHMW-PE, and Nylon is a critical engineering trade-off. PTFE provides unmatched low friction and chemical resistance, UHMW-PE excels in abrasion resistance, and Nylon delivers superior mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness.
A Head-to-Head Comparison of Key Properties
Choosing the right low-friction plastic requires looking beyond a single specification. Each material is engineered with a distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses that makes it suitable for different operational demands.
Coefficient of Friction (The "Slickness" Factor)
The coefficient of friction (COF) measures the resistance to motion between two surfaces. In this category, there is a clear hierarchy.
PTFE is the undisputed leader, making it the ideal choice for applications like high-performance sliding bearings, non-stick coatings, and seals where minimizing static and dynamic friction is the primary goal.
UHMW-PE offers a very low COF that is still significantly higher than PTFE's. It provides an excellent low-friction surface for less demanding applications.
Nylon has the highest friction of the three. While still considered a low-friction plastic, it is typically chosen for properties other than pure slickness.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
A low-friction surface is only useful if it can withstand mechanical wear over time. This is where the materials diverge significantly.
UHMW-PE is the standout performer in this category. Its long molecular chains give it exceptional resistance to abrasion, making it a preferred material for chain guides, wear strips, and chute liners.
PTFE, by contrast, is a relatively soft material. It can be prone to "creep" or cold flow under load and has poor abrasion resistance compared to UHMW-PE, limiting its use in high-wear environments unless it is reinforced.
Nylon offers good wear resistance, often superior to PTFE, but it generally does not match the longevity of UHMW-PE in high-abrasion scenarios.
Mechanical Strength and Load Bearing
The ability to withstand physical stress without deforming or breaking is critical for many components.
Nylon is known for its high tensile strength, stiffness, and load-bearing capacity. This makes it an excellent choice for structural parts like gears, rollers, and bushings where mechanical integrity is paramount.
PTFE has low mechanical strength and can deform under sustained pressure. It is not suitable for structural applications without being filled with additives like glass or carbon.
UHMW-PE possesses excellent impact strength but lacks the rigidity and tensile strength of Nylon, making it better for impact absorption than for bearing heavy, static loads.
Temperature and Chemical Stability
The operating environment often dictates the material choice, particularly when extreme temperatures or corrosive chemicals are involved.
PTFE has an outstanding operational temperature range and is almost completely inert to most chemicals. This makes it essential for seals, gaskets, and components used in chemical processing, aerospace, and medical applications.
Nylon has moderate temperature resistance and can be susceptible to moisture absorption, which can alter its dimensional stability and properties. It is not suitable for highly corrosive environments.
UHMW-PE offers good chemical resistance to many acids and bases but does not match the near-universal inertness or high-temperature stability of PTFE.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Performance
A material's technical merits must be weighed against its economic feasibility for a given project.
The Cost Factor
There is a clear cost progression among these three materials.
Nylon is generally the most affordable option, making it a go-to choice for high-volume, cost-sensitive projects that require good mechanical properties.
UHMW-PE typically sits in the middle ground, offering a balanced price point for its unique combination of low friction and high wear resistance.
PTFE is the most expensive of the three due to its complex manufacturing process and superior performance characteristics in temperature and chemical resistance.
When to Justify the Cost of PTFE
The premium price of PTFE is justified in applications where its unique properties are non-negotiable.
If an application demands near-zero friction, must operate in extreme temperatures, or will be exposed to aggressive chemicals, the reliability and performance of PTFE outweigh its higher initial cost.
Common Selection Pitfalls
A frequent mistake is selecting a material based on a single property—most often, the coefficient of friction.
Choosing PTFE for a high-abrasion environment just because of its low COF will likely lead to premature failure. Similarly, using Nylon in a chemical processing line could result in degradation. A holistic view of the entire operational environment is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the optimal material, you must first define your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction: PTFE is the definitive choice, especially for high-precision sliding parts, non-stick surfaces, or chemically exposed seals.
- If your primary focus is durability against abrasive wear: UHMW-PE offers an unmatched combination of high abrasion resistance and low friction, ideal for wear strips and guides.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness: Nylon provides the structural integrity and affordability needed for gears, rollers, and other high-load components.
By evaluating the complete demands of your application against the distinct profile of each material, you can ensure you are making a sound engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE | UHMW-PE | Nylon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.04 - 0.08 (Lowest) | 0.10 - 0.20 | 0.20 - 0.30 (Highest) |
| Abrasion/Wear Resistance | Poor | Excellent (Best) | Good |
| Mechanical Strength | Low | Good Impact Strength | High (Best) |
| Chemical/Temp Resistance | Excellent (Best) | Good | Moderate |
| Relative Cost | Highest | Medium | Lowest |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Selecting the right material is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver the unmatched low friction and chemical resistance of PTFE, with the capability to reinforce it for enhanced strength and wear resistance when your application demands it. From initial prototypes to high-volume production, we ensure your components meet exact specifications.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















