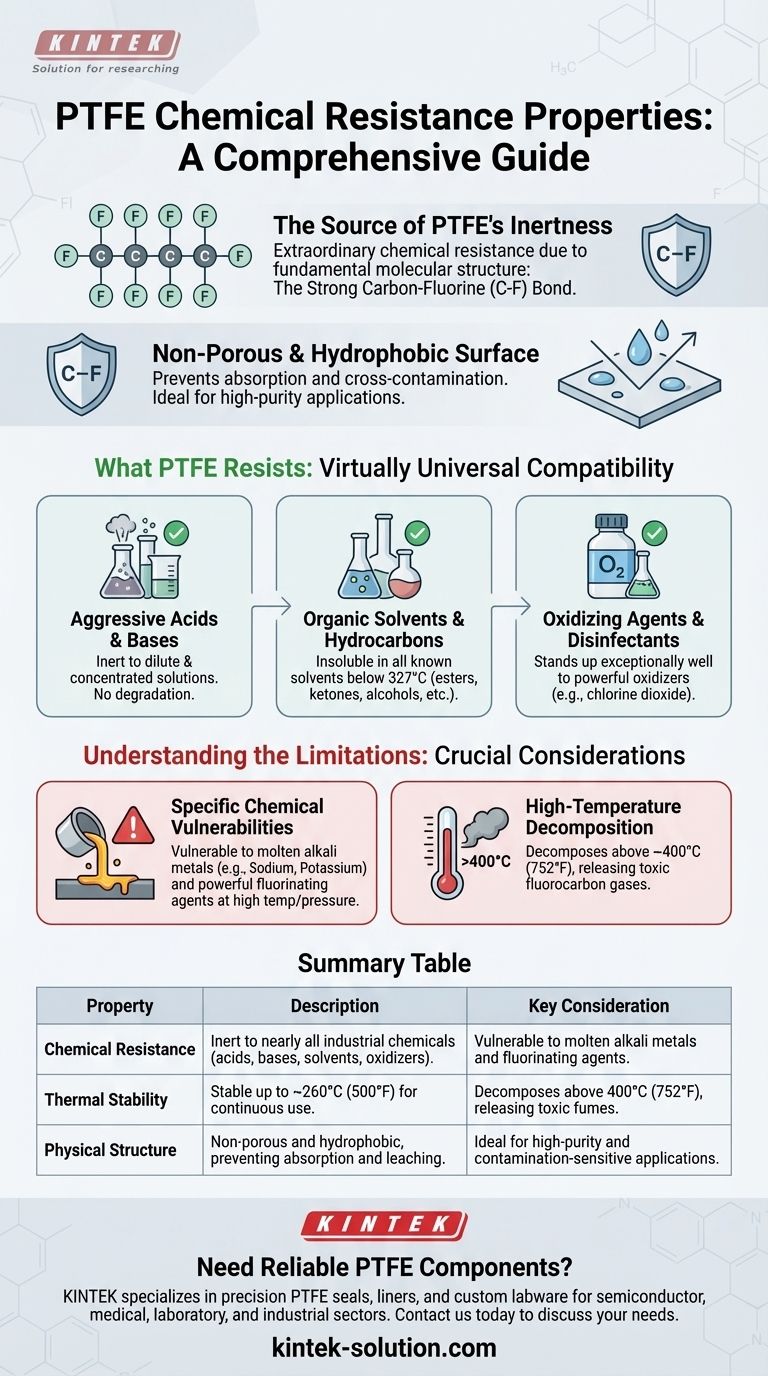
To be direct, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has extraordinary chemical resistance, making it inert to the vast majority of industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizing agents. Its only known vulnerabilities are to a very specific and limited class of substances: molten alkali metals like sodium, and powerful fluorinating agents such as gaseous fluorine and chlorine trifluoride, especially at elevated temperatures and pressures.
The core reason for PTFE's exceptional performance is not a coating or treatment, but its fundamental molecular structure. The incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds create a stable, non-reactive material that functions as a reliable barrier in the most demanding chemical environments.

The Source of PTFE's Chemical Inertness
To properly leverage PTFE, it's essential to understand why it is so resistant. Its properties are not accidental; they are a direct result of its unique molecular architecture.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At the heart of PTFE's resilience is the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond. This is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
The fluorine atoms effectively form a protective, non-reactive sheath around the carbon backbone of the polymer. This "molecular armor" prevents other chemicals from getting close enough to initiate a reaction.
A Non-Porous and Hydrophobic Surface
PTFE's physical structure complements its chemical stability. It is non-porous and does not absorb substances, including water, which means corrosive agents cannot seep into the material to cause degradation from within.
This property is critical for preventing cross-contamination in high-purity applications, as it ensures that residues from one process do not leach out and affect a subsequent one.
What PTFE Resists: A Comprehensive Overview
PTFE is virtually a universal standard for chemical compatibility. Its resistance spans nearly every category of chemical used in industrial and laboratory settings.
Aggressive Acids and Bases
PTFE shows no degradation when exposed to either dilute or concentrated acids and bases. This makes it an ideal material for linings, seals, and gaskets in chemical processing equipment.
Organic Solvents and Hydrocarbons
PTFE is insoluble in all known solvents below its melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F). This includes esters, ketones, alcohols, and all aliphatic, aromatic, and halogenated hydrocarbons.
Oxidizing Agents and Disinfectants
The material stands up exceptionally well to powerful oxidizing agents. This includes substances found in aggressive cleaning and disinfecting solutions, such as chlorine dioxide.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While its resistance is remarkable, no material is perfect. Acknowledging PTFE's specific weaknesses is crucial for safe and effective implementation.
The Few Chemical Exceptions
The primary chemical vulnerabilities of PTFE are few but significant. It can be attacked by molten alkali metals, such as sodium and potassium.
It is also susceptible to attack from highly reactive fluorinating agents. These include elementary fluorine gas, chlorine trifluoride, and oxygen difluoride, particularly when subjected to high temperatures and pressures.
High-Temperature Decomposition
PTFE is thermally stable, but it has a distinct limit. Above approximately 400°C (752°F), it begins to decompose.
This decomposition is critical to understand because it can release toxic and corrosive fluorocarbon gases. Therefore, its use must always be kept well below this temperature threshold.
Applying PTFE for Your Specific Needs
Your choice of material depends entirely on the operational environment. PTFE is often the default choice for chemical resistance, but its suitability hinges on respecting its specific limitations.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive chemicals: PTFE is an industry standard for pipes, vessel linings, and seals precisely because of its near-total inertness to acids, bases, and solvents.
- If your primary focus is purity and preventing contamination: PTFE's non-porous, non-leaching, and hydrophobic surface makes it a premier choice for laboratory, semiconductor, and medical applications.
- If you are working with extreme conditions: You must verify that your application avoids PTFE's specific chemical weaknesses (alkali metals, fluorinating agents) and remains safely below its thermal decomposition temperature.
Ultimately, PTFE's reputation for chemical inertness is well-earned, making it a cornerstone material for modern engineering and science.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all industrial chemicals (acids, bases, solvents, oxidizers). | Vulnerable to molten alkali metals and fluorinating agents. |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to ~260°C (500°F) for continuous use. | Decomposes above 400°C (752°F), releasing toxic fumes. |
| Physical Structure | Non-porous and hydrophobic, preventing absorption and leaching. | Ideal for high-purity and contamination-sensitive applications. |
Need a reliable PTFE component for your corrosive or high-purity application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment has the chemical resistance and purity required for peak performance and safety.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions



















