In its most famous role, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is the non-stick coating on cookware, but its primary industrial value comes from a unique combination of other properties. It is a critical material in the chemical processing, electrical, and manufacturing sectors for its extreme chemical resistance, exceptionally low friction, and excellent performance as an electrical insulator.
The true value of PTFE lies not in any single application, but in four key properties that make it uniquely versatile: its extreme chemical inertness, one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, high-temperature stability, and excellent dielectric strength. Understanding these properties is the key to seeing why it appears in everything from aerospace wiring to chemical tank linings.
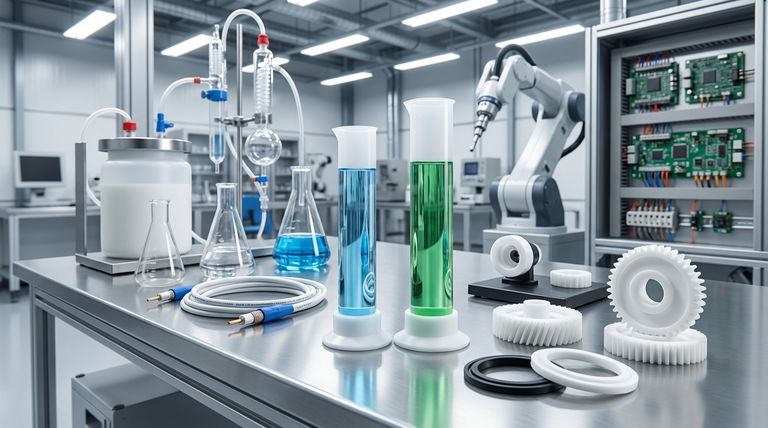

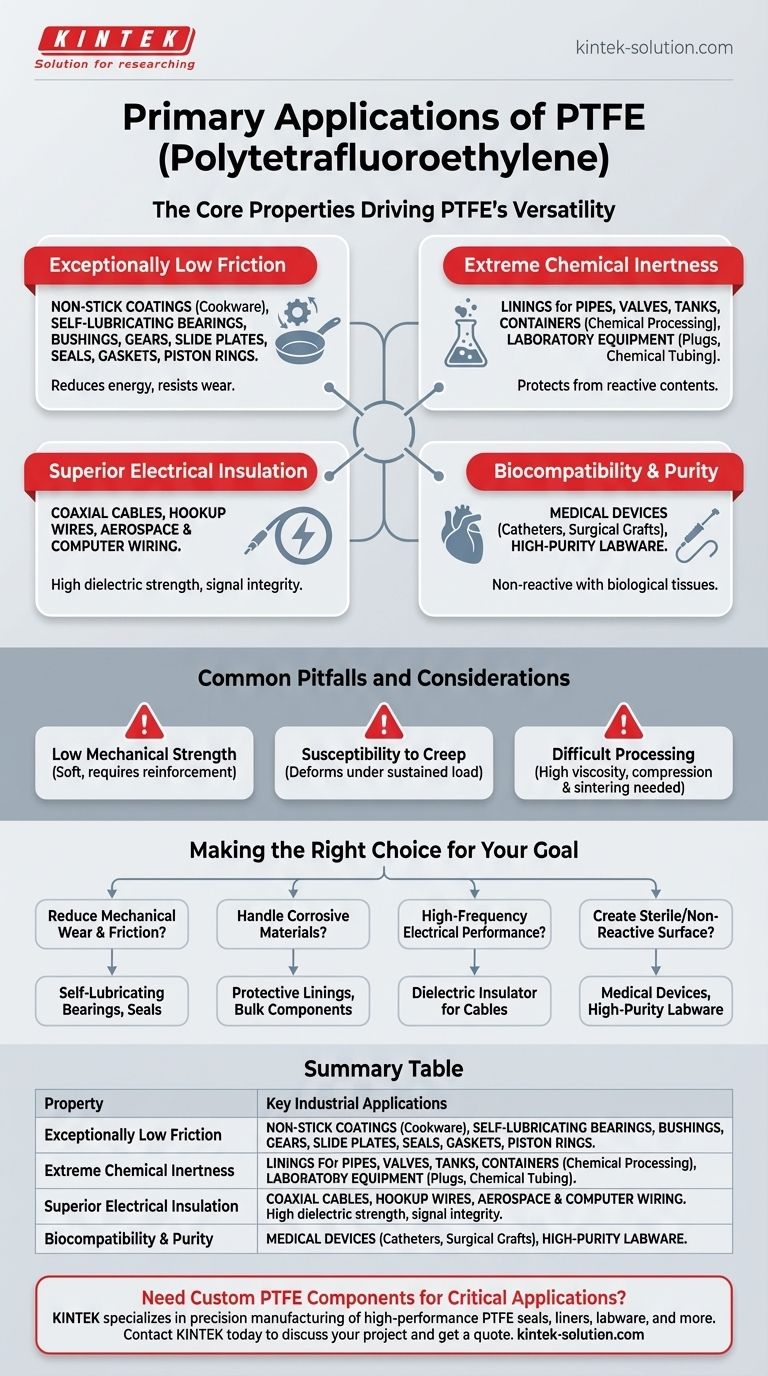
The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Versatility
While most people know PTFE by its brand name, Teflon, its applications extend far beyond the kitchen. Its use in demanding industrial environments is driven by a set of distinct characteristics that solve critical engineering challenges.
Exceptionally Low Friction (Non-Stick Surface)
The most well-known property of PTFE is its extremely low friction, making surfaces slippery and easy to clean.
This is the principle behind its use as a non-stick coating on pans, baking trays, and other cookware.
In industrial settings, this same property is vital for mechanical applications. PTFE is used to create bearings, bushings, gears, and slide plates that require minimal lubrication, reduce energy consumption, and resist wear over time. It is also used for high-performance seals, gaskets, and piston rings.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is highly non-reactive and can withstand a wide range of corrosive and aggressive chemicals, even at high temperatures.
This makes it an ideal material for linings in pipes, valves, tanks, and containers used in the chemical processing industry. It protects standard structural materials from being degraded by reactive contents.
It is also used for laboratory equipment, such as plugs for glassware and chemical tubing, where purity and resistance to chemical attack are essential.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, meaning it does not conduct electricity. This is known as having a high dielectric strength.
This property makes it indispensable in the aerospace and computer industries for insulating high-performance wiring. It is commonly found in coaxial cables and hookup wires where signal integrity is critical.
Biocompatibility and Purity
Because PTFE is so inert, it is also biocompatible, meaning it does not react with biological tissues.
This allows it to be used in demanding medical applications. It can serve as a coating on catheters to prevent bacteria from adhering and is also used as a graft material in certain surgical procedures.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its unique properties come with trade-offs that are critical to understand for proper application.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has low tensile strength and is susceptible to abrasion from sharp particles, which is why it is often reinforced with other materials like glass fiber or carbon in demanding mechanical applications.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as "creep," must be accounted for when designing long-term structural components like seals or gaskets.
Difficult Processing
PTFE has a very high melting point and viscosity, which makes it difficult to process using conventional polymer methods like injection molding. It is typically formed through compression and sintering, which can be more complex and costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE requires matching its unique strengths to your specific engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is reducing mechanical wear and friction: Leverage PTFE for self-lubricating bearings, seals, gears, and slide plates.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive materials: Use PTFE as a protective lining or as the bulk material for components in chemical processing systems.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical performance: Specify PTFE as the dielectric insulator for critical cables and electronic components.
- If your primary focus is creating a sterile or non-reactive surface: Consider PTFE for medical devices or high-purity laboratory equipment.
Understanding these core principles allows you to deploy PTFE not just as a non-stick coating, but as a high-performance engineering material.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Industrial Applications |
|---|---|
| Low Friction | Self-lubricating bearings, seals, gaskets, gears, slide plates |
| Chemical Inertness | Tank linings, pipe liners, valves, labware for corrosive environments |
| Electrical Insulation | Coaxial cables, hookup wires, aerospace and electronics components |
| Biocompatibility | Medical catheters, surgical grafts, sterile lab equipment |
Need a custom PTFE component for your critical application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and more—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We deliver custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, low friction, and electrical performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance



















