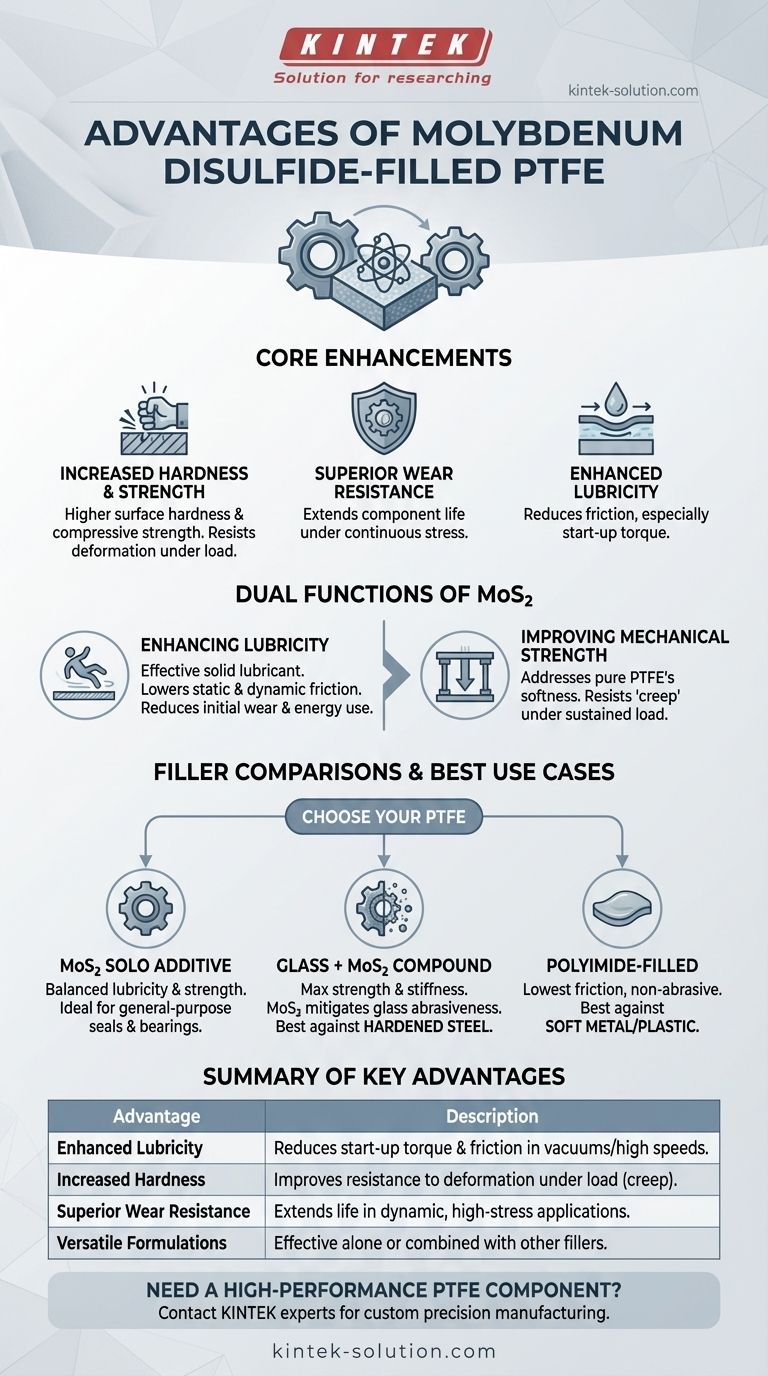
At its core, adding molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) to Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) enhances the material's mechanical properties without compromising its inherent lubricity. This filler increases hardness, compressive strength, and wear resistance while further decreasing the coefficient of friction, particularly during start-up.
Molybdenum disulfide acts as a solid lubricant within the PTFE matrix. It is chosen to improve the material's physical durability and reduce friction, making it a superior choice for dynamic applications involving high speeds, vacuums, or scenarios where reducing initial torque is critical.

The Core Functions of Molybdenum Disulfide in PTFE
Adding MoS₂ transforms standard PTFE into a more robust and efficient material for demanding mechanical roles. Its primary contributions fall into two categories: enhancing lubricity and improving physical strength.
Enhancing Lubricity and Reducing Friction
Molybdenum disulfide is itself a highly effective solid lubricant. When dispersed within the PTFE, it enhances the material's already low-friction surface.
This results in a significant reduction in both static and dynamic friction. The most notable benefit is a decrease in the torque required on start-up, which reduces initial wear and energy consumption in machinery.
Improving Mechanical Strength
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material prone to "creep" or deformation under a sustained load. MoS₂ addresses this weakness directly.
The addition of MoS₂ (typically up to 5%) measurably increases surface hardness, compressive strength, and overall wear resistance. This makes the material better suited for bearings, seals, and components that face continuous mechanical stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
While MoS₂ provides significant benefits, it is often part of a more complex material science calculation. Its effectiveness is best understood when compared to other common PTFE fillers.
MoS₂ as a Solo Additive
When used alone, MoS₂ provides a balanced improvement in both lubricity and strength. It creates a harder, more slippery material ideal for general-purpose seals and bearings where moderate improvements are needed.
MoS₂ in Compound Formulations
MoS₂ is frequently combined with other fillers, most commonly glass or bronze. A typical formulation might be 15% glass and 5% MoS₂.
In this blend, the glass provides the bulk of the added stiffness, tear resistance, and compressive strength. However, glass is abrasive and can wear down softer mating surfaces. The MoS₂ is added specifically to mitigate the abrasiveness of the glass and improve the compound's overall sliding properties.
When to Choose Other Fillers
The choice of filler depends entirely on the application's specific demands, particularly the mating surface material.
- Glass-Filled PTFE: Offers superior wear resistance and stiffness, especially in oxidizing environments. It is best used against very hard metal shafts that can resist its abrasive nature.
- Polyimide-Filled PTFE: Provides the lowest coefficient of friction of any common filler and is non-abrasive. This makes it the superior choice for applications involving soft shafts made of aluminum, brass, or plastic, where a glass-filled material would cause rapid damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material requires aligning the filler's properties with your primary engineering objective.
- If your primary focus is reducing start-up friction and general durability: Standard MoS₂-filled PTFE is an excellent and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength against a hardened steel shaft: A compound of glass and MoS₂ offers the best combination of strength, stiffness, and lubricity.
- If your primary focus is performance against a soft metal or plastic shaft: Polyimide-filled PTFE is the only suitable option to prevent abrasion and ensure component longevity.
Ultimately, understanding these filler interactions empowers you to select a material optimized for performance, durability, and system-wide reliability.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Lubricity | Reduces static/dynamic friction and start-up torque, especially in vacuums or high speeds. |
| Increased Hardness | Improves surface hardness and resistance to deformation under load (creep). |
| Superior Wear Resistance | Extends component life in dynamic applications with continuous stress. |
| Versatile Formulations | Effective as a solo filler or combined with others (e.g., glass) to balance strength and lubricity. |
Need a high-performance PTFE component optimized for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including advanced formulations with molybdenum disulfide and other fillers. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, our expertise ensures you get a solution that delivers superior wear resistance, reduced friction, and long-lasting reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















