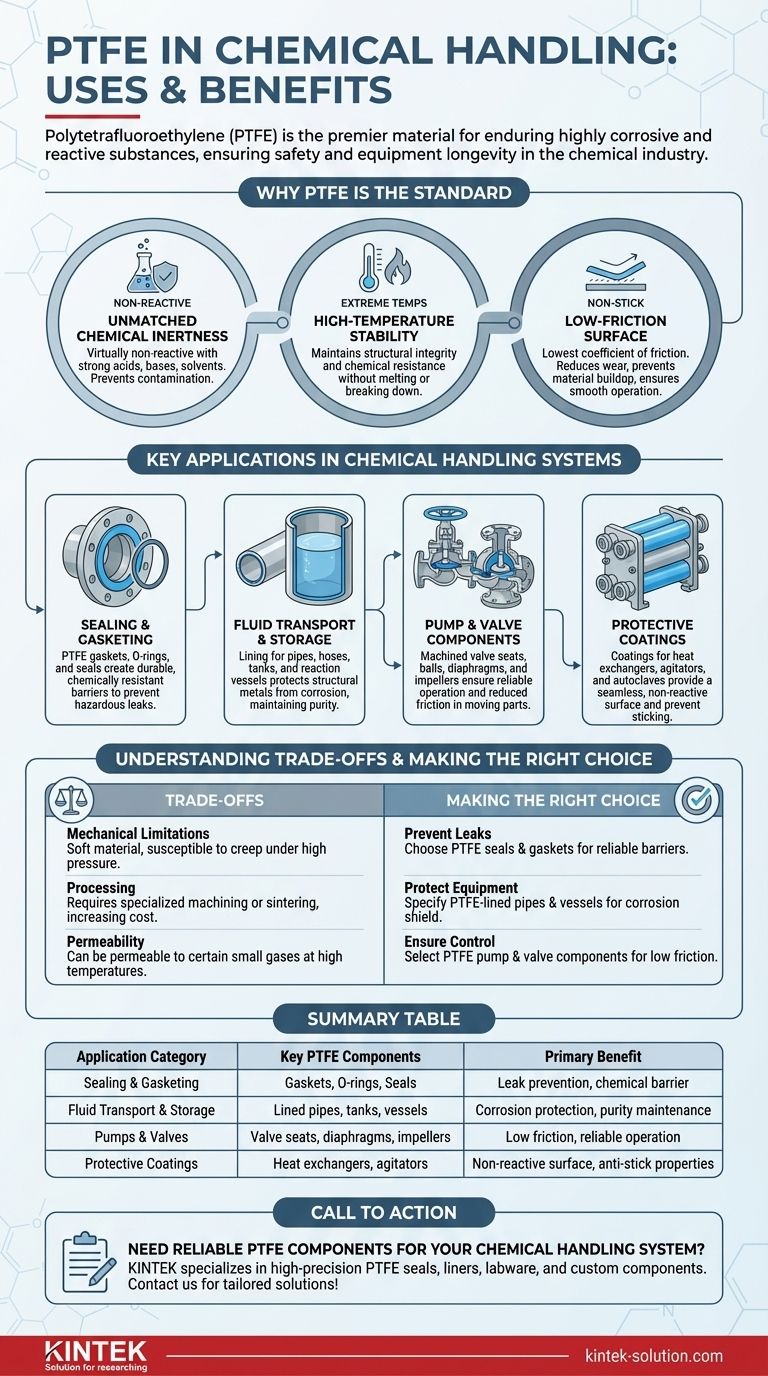
In the chemical handling industry, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the material of choice for components that must endure highly corrosive and reactive substances. Its primary uses are in creating durable seals, gaskets, valve seats, and pump internals, as well as lining pipes, tanks, and reaction vessels to prevent chemical attack and ensure operational safety.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread use is not just its versatility, but its fundamental chemical inertness. It provides a near-universal solution for containing and transporting aggressive chemicals that would degrade or destroy most other materials.

Why PTFE is the Standard for Chemical Containment
The selection of PTFE in demanding chemical environments is based on a unique combination of three critical properties. These characteristics work together to ensure safety, purity, and equipment longevity.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually non-reactive with almost all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizing agents. This inertness prevents the material itself from degrading and, just as importantly, prevents it from contaminating the chemical process.
High-Temperature Stability
Chemical processes often involve extreme temperatures. PTFE maintains its structural integrity and chemical resistance across a wide temperature range, withstanding harsh production conditions without melting or breaking down.
Low-Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, giving it a "non-stick" quality. In chemical handling, this is critical for components like valve seats and pump diaphragms, as it prevents material buildup, reduces wear, and ensures smooth, reliable operation.
Key Applications in Chemical Handling Systems
From large-scale storage to precision fluid control, PTFE is engineered into specific components where its properties are most needed.
Sealing and Gasketing
The most common application is preventing leaks of hazardous materials. PTFE gaskets, O-rings, and seals are used to create tight, durable connections between pipes, vessel flanges, and equipment housings, ensuring a chemically resistant barrier.
Fluid Transport and Storage
To protect structural materials like steel from corrosion, PTFE is used extensively as a lining for pipes, hoses, tanks, and reaction vessels. This creates an inert barrier that contains the chemical, extending the life of the infrastructure and maintaining product purity.
Internal Pump and Valve Components
Moving parts within a chemical stream are highly vulnerable. PTFE is machined into valve seats, balls, diaphragms, and pump impellers. Its combination of chemical resistance and low friction is essential for parts that must move, flex, and seal reliably without degrading.
Protective Coatings
For complex equipment like heat exchangers, agitators, and autoclaves, a PTFE coating can be applied. This provides a seamless, non-reactive surface that protects the underlying metal from corrosion and prevents product from sticking to the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptionally capable, PTFE is not a universal solution for every engineering problem. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under high mechanical loads or pressures, it can be susceptible to "creep" or cold flow, where the material slowly deforms over time. This must be considered in high-pressure sealing applications.
Processing and Fabrication
Unlike many common plastics, PTFE cannot be melt-processed using conventional injection molding. It is typically machined from stock shapes or formed through a sintering process, which can increase the cost and complexity of manufacturing components.
Permeability to Gases
While excellent for containing liquids, PTFE can be permeable to certain small-molecule gases, especially at higher temperatures. In high-purity or vacuum applications, this characteristic may need to be addressed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal within a chemical handling system will determine the ideal application of PTFE.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks: Utilize PTFE for seals, gaskets, and O-rings, where its chemical resistance and ability to conform under pressure create a reliable barrier.
- If your primary focus is protecting capital equipment: Specify PTFE-lined pipes, tanks, and vessels to shield structural metals from corrosion and extend their service life.
- If your primary focus is ensuring reliable fluid control: Choose PTFE for internal pump and valve components to reduce friction, prevent contamination, and guarantee consistent operation.
Ultimately, specifying PTFE is a strategic decision to enhance safety, reliability, and purity in demanding chemical environments.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key PTFE Components | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing and Gasketing | Gaskets, O-rings, Seals | Leak prevention, chemical barrier |
| Fluid Transport & Storage | Lined pipes, tanks, vessels | Corrosion protection, purity maintenance |
| Pumps & Valves | Valve seats, diaphragms, impellers | Low friction, reliable operation |
| Protective Coatings | Heat exchangers, agitators | Non-reactive surface, anti-stick properties |
Need reliable PTFE components for your chemical handling system?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment withstands corrosive chemicals, operates safely, and maintains purity—from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















