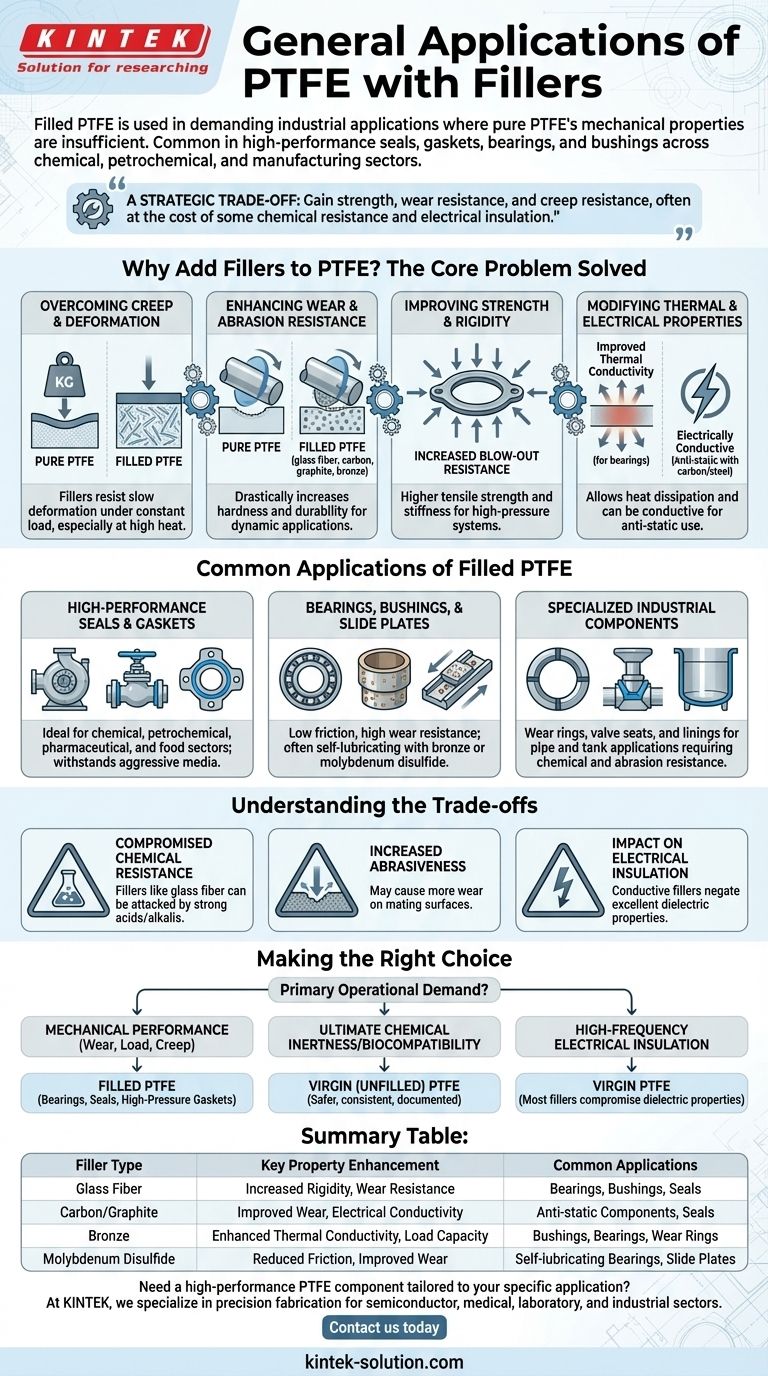
In short, filled PTFE is used in demanding industrial applications where pure PTFE's mechanical properties are insufficient. It is commonly found in high-performance seals, gaskets, bearings, and bushings across the chemical, petrochemical, and manufacturing sectors. The fillers are added to improve strength, reduce deformation under load, and increase wear resistance.
The decision to use filled PTFE is a strategic trade-off. You gain significant improvements in mechanical strength, wear resistance, and resistance to creep, but often at the cost of some of the material's inherent chemical resistance and electrical insulating properties.
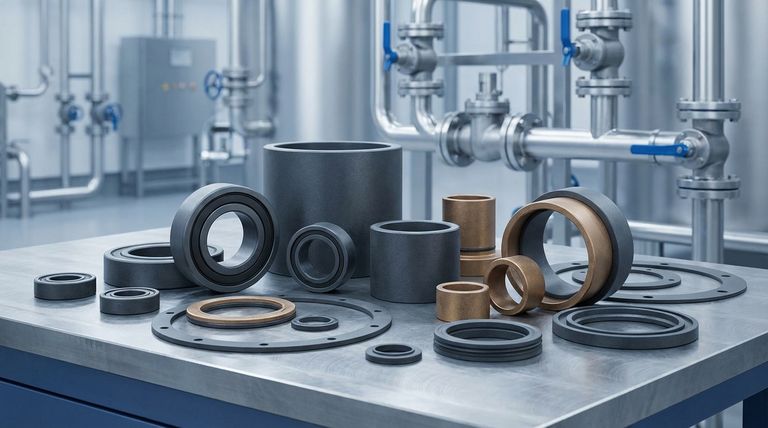

Why Add Fillers to PTFE? The Core Problem Solved
Virgin, or unfilled, PTFE is renowned for its extreme chemical inertness and exceptionally low coefficient of friction. However, it is a relatively soft material with several mechanical limitations that make it unsuitable for certain demanding roles.
Overcoming Creep and Deformation
Pure PTFE has a tendency to "creep," or slowly deform, when subjected to a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures.
Fillers act as a reinforcing matrix within the PTFE, significantly improving its structural integrity and its ability to resist deformation under heavy compressive loads.
Enhancing Wear and Abrasion Resistance
While PTFE is famously "slippery," it has poor abrasion resistance on its own. In dynamic applications like rotating seals or sliding bearings, it can wear away quickly.
Common fillers like glass fiber, carbon, graphite, or bronze drastically increase the material's hardness and durability, making it suitable for high-wear environments.
Improving Strength and Rigidity
Fillers increase the overall tensile strength and stiffness of PTFE. This is critical for applications like gaskets in high-pressure systems.
This added rigidity provides increased blow-out resistance for gaskets used on flanges for pipelines, pumps, and valves, ensuring a more reliable seal.
Modifying Thermal and Electrical Properties
Fillers can also improve PTFE's thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate more effectively in applications like bearings.
Furthermore, while virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator, fillers like carbon or stainless steel can be added to make the material electrically conductive for anti-static applications.
Common Applications of Filled PTFE
By addressing the mechanical weaknesses of virgin PTFE, fillers open up a wide range of demanding industrial applications.
High-Performance Seals and Gaskets
Filled PTFE is a go-to material for non-metallic gaskets and seals in the chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and food sectors.
Its ability to withstand aggressive media while resisting creep under the clamping force of flanges makes it ideal for sealing pumps, valves, and pipelines.
Bearings, Bushings, and Slide Plates
In machinery, filled PTFE is used for components that require low friction but high wear resistance.
Bronze or molybdenum disulfide-filled PTFE, for example, is often used for bearings and bushings that operate without external lubrication.
Specialized Industrial Components
The enhanced properties of filled PTFE make it suitable for a variety of other custom parts. This includes wear rings, valve seats, and linings for pipes and tanks where both chemical and abrasion resistance are needed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is not a universal improvement. It involves a careful balancing of properties, and understanding the downsides is critical for proper material selection.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
The single most important trade-off is a potential reduction in chemical resistance.
Fillers like glass fiber can be attacked by strong acids or alkalis that virgin PTFE would easily resist. The chemical compatibility of the specific filler must always be verified for the intended service.
Increased Abrasiveness to Mating Surfaces
While the filler improves the PTFE's own wear resistance, it can also make the material more abrasive to the surfaces it slides against.
A glass-filled PTFE bearing, for instance, may cause more wear on a soft steel shaft than an unfilled or graphite-filled version would.
Impact on Electrical Insulation
The outstanding dielectric properties of virgin PTFE are negated when conductive fillers like carbon, graphite, or steel are introduced. This is a benefit when static dissipation is required, but a critical failure point if electrical insulation is the goal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between virgin and filled PTFE requires a clear understanding of your primary operational demand.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance (wear, load, or creep resistance): A filled PTFE is almost always the correct choice for applications like bearings, dynamic seals, or high-pressure gaskets.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical inertness or biocompatibility: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the safer and more reliable option, as its properties are consistent and well-documented.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: You must use virgin PTFE, as most common fillers will compromise its excellent dielectric properties.
Ultimately, selecting the correct material is about matching the enhanced properties of a specific filled PTFE compound to the precise demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Property Enhancement | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | Increased Rigidity, Wear Resistance | Bearings, Bushings, Seals |
| Carbon/Graphite | Improved Wear, Electrical Conductivity | Anti-static Components, Seals |
| Bronze | Enhanced Thermal Conductivity, Load Capacity | Bushings, Bearings, Wear Rings |
| Molybdenum Disulfide | Reduced Friction, Improved Wear | Self-lubricating Bearings, Slide Plates |
Need a high-performance PTFE component tailored to your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require custom prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise in filled PTFE formulations ensures optimal performance for your most demanding environments.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK’s precision fabrication can solve your unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE spacer rings? Solve Critical Sealing & Wear Problems
- Why is understanding material limits important when choosing PTFE seals? Avoid Premature Failure
- What future advancements are expected for PTFE oil seals? From Smart Seals to 3D Printing
- Why is Teflon often used in products requiring reduced friction? Leverage its Extreme Slipperiness
- What are the key features and benefits of PTFE lip seals? Superior Performance for Extreme Conditions
- How can users obtain customized PTFE gaskets and sheets? Get Precision Parts for Your Industry
- What are PTFE bellows and diaphragms, and why are they important in critical systems?
- How can the mechanical properties of PTFE be improved? Enhance Strength & Durability with Fillers



















