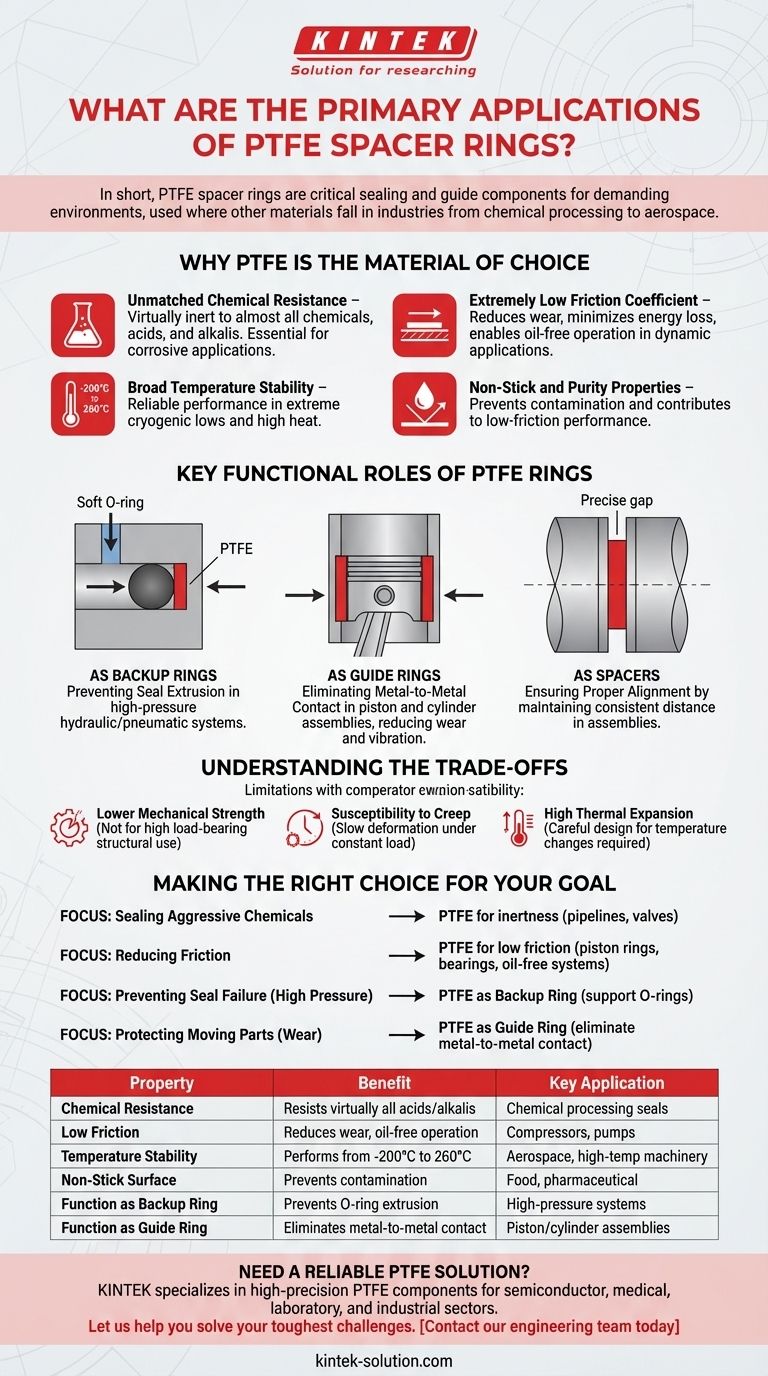
In short, PTFE spacer rings are primarily used as critical sealing and guide components in demanding industrial environments where other materials would quickly fail. Their applications span industries from chemical processing and aerospace to mechanical engineering, where they are found in equipment like reaction kettles, high-pressure pipelines, pumps, and compressors.
The core reason for using PTFE is not just its function as a spacer, but its unique combination of properties. Engineers select PTFE rings for their unparalleled chemical resistance, extremely low friction, and stability across a vast temperature range, allowing them to solve complex sealing, wear, and extrusion problems.

Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
The effectiveness of a PTFE ring comes from the fundamental properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene itself. These characteristics make it a superior choice for very specific, and often harsh, operational contexts.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert, meaning it resists degradation from almost all industrial chemicals, acids, and alkalis. This makes it essential for seals in chemical processing equipment, storage tanks, and transmission pipelines where corrosive substances are present.
Extremely Low Friction Coefficient
With one of the lowest friction coefficients of any solid material, PTFE is ideal for dynamic applications. In compressors, pumps, and piston assemblies, PTFE rings reduce wear, minimize energy loss, and enable oil-free operation, which is critical in food, pharmaceutical, and dental industries.
Broad Temperature Stability
PTFE performs reliably across an exceptionally wide temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to high-heat environments of 260°C (500°F). This stability is crucial for components in aerospace technology and specialized industrial machinery that experience extreme temperature fluctuations.
Non-Stick and Purity Properties
Almost nothing adheres to a PTFE surface. This non-stick characteristic is vital for preventing contamination in applications like oil-free air compressors for food processing. It also contributes to its low-friction performance in seals.
Key Functional Roles of PTFE Rings
While often generally called "spacer rings," these components perform distinct technical functions depending on the system's design and operational stresses.
As Backup Rings: Preventing Seal Extrusion
In high-pressure hydraulic or pneumatic systems, a softer elastomer seal (like a rubber O-ring) can be forced into the small clearance gap between moving parts, causing it to shred and fail. A PTFE ring is installed alongside the O-ring as a backup ring to close this gap, providing rigid support and preventing this extrusion failure.
As Guide Rings: Eliminating Metal-to-Metal Contact
In piston and cylinder applications, lateral forces can cause the piston to scrape against the cylinder wall, leading to catastrophic damage. A PTFE guide ring (or wear ring) is fitted to the piston to absorb these side loads, ensuring smooth movement and preventing direct metal-to-metal contact. It also helps dampen mechanical vibrations.
As Spacers: Ensuring Proper Alignment
In its most basic function, a PTFE ring acts as a simple spacer, maintaining a precise distance between two other components in an assembly. Its chemical and thermal stability ensure this spacing remains consistent even in challenging conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations.
Lower Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to metals. It is not suitable for high load-bearing structural applications on its own and can be susceptible to damage from sharp edges or abrasive contaminants.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a constant, sustained load (especially at elevated temperatures), PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as "creep," must be accounted for in the design of long-term, high-pressure sealing systems.
High Thermal Expansion
Compared to metals, PTFE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion. Engineers must carefully design clearances and tolerances to accommodate the material's expansion and contraction with temperature changes to prevent parts from binding or seals from leaking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a PTFE ring is about matching its unique strengths to a specific engineering problem.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: PTFE's inertness makes it the definitive choice for pipelines, valves, and reaction vessels.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in dynamic systems: Its low friction coefficient is ideal for piston rings, bearings, and compressor components, especially where lubrication is undesirable.
- If your primary focus is preventing seal failure under high pressure: Use PTFE as a backup ring to support softer O-rings and stop extrusion.
- If your primary focus is protecting moving parts from wear: Implement PTFE as a guide ring to eliminate metal-to-metal contact in piston and rod applications.
By understanding these core properties and functions, you can leverage PTFE rings to ensure reliability in applications where other materials would certainly fail.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resists virtually all acids and alkalis | Chemical processing seals, pipelines |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear, enables oil-free operation | Compressors, pumps, piston rings |
| Temperature Stability | Performs from -200°C to 260°C | Aerospace, high-temperature machinery |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents contamination | Food, pharmaceutical compressors |
| Function as Backup Ring | Prevents O-ring extrusion in high pressure | Hydraulic/pneumatic systems |
| Function as Guide Ring | Eliminates metal-to-metal contact | Piston/cylinder assemblies |
Need a reliable PTFE solution for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including custom spacer rings, seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a prototype or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards for chemical resistance, temperature stability, and performance.
Let us help you solve your toughest sealing and wear challenges. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















