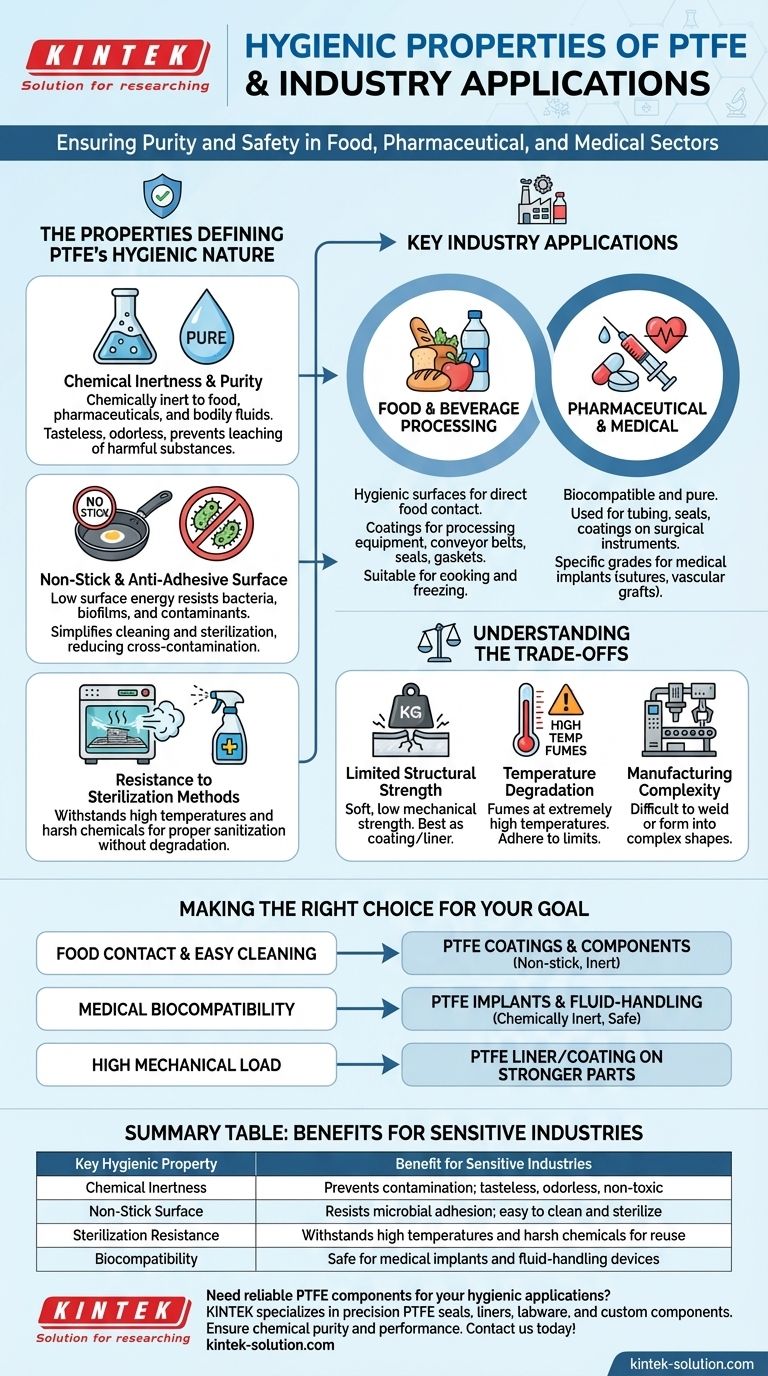
Due to its unique hygienic properties, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of choice in industries where purity and safety are non-negotiable. Its primary applications are found in the food processing, pharmaceutical, and medical sectors, largely because it is chemically inert, tasteless, odourless, and features a non-stick surface that resists contamination.
The decision to use PTFE in sensitive applications is not based on a single feature, but on the powerful combination of its chemical purity and its inherently non-stick surface. This dual advantage prevents the leaching of chemicals and discourages microbial adhesion, making it exceptionally safe and easy to clean.
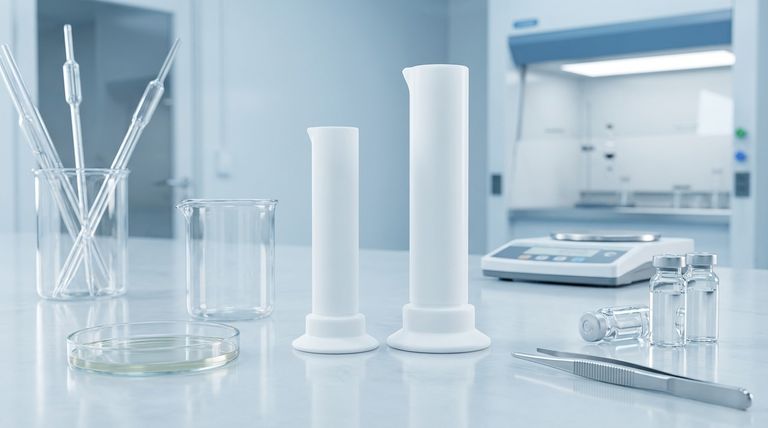

The Properties Defining PTFE's Hygienic Nature
To understand where PTFE is used, it is essential to understand why it is considered a hygienic material. Its suitability comes down to a few fundamental characteristics.
Chemical Inertness and Purity
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert polymers known. This means it does not react with food products, pharmaceuticals, or bodily fluids.
This inertness is the source of its tasteless and odourless properties, ensuring that it does not alter the product it contacts. It also guarantees that no harmful substances will leach from the material.
Non-Stick and Anti-Adhesive Surface
The famous non-stick quality of PTFE is critical for hygiene. This property, known as low surface energy, makes it extremely difficult for bacteria, biofilms, and other contaminants to attach to the surface.
This significantly simplifies cleaning and sterilization protocols, reducing the risk of cross-contamination in food and medical environments.
Resistance to Sterilization Methods
PTFE components can withstand the aggressive conditions required for sterilization. This includes high temperatures and exposure to harsh cleaning chemicals.
This durability ensures that equipment can be properly sanitized for reuse without degrading the material, a crucial requirement in both medical and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Key Industry Applications
These properties translate directly into critical applications across several highly regulated industries.
Food and Beverage Processing
In this industry, PTFE is used for hygienic, non-stick surfaces that come into direct contact with food. Common examples include coatings for processing equipment, conveyor belt components, seals, and gaskets.
Its ability to function in a wide temperature range makes it suitable for both cooking and freezing processes.
Pharmaceutical and Medical
PTFE's biocompatibility and purity make it indispensable in medicine. It is used for tubing, seals on processing equipment, and coatings on surgical instruments.
Because it is non-toxic and well-tolerated by the human body, specific grades of PTFE are even used for medical implants, such as surgical sutures and vascular grafts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its significant advantages, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations.
Limited Structural Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low mechanical strength. It is not suitable for high-load or structural applications on its own.
For this reason, it is most often used as a coating, a liner for pipes, or in components like seals and gaskets where its surface properties are the primary concern.
Temperature Degradation
While PTFE has an excellent service temperature range, it can begin to degrade and release fumes at extremely high temperatures (well above those used for cooking or typical industrial processing).
Proper engineering and adherence to specified temperature limits are essential to ensure safe operation.
Manufacturing Complexity
The same chemical resistance that makes PTFE so valuable also makes it more difficult to process than common plastics. Techniques like welding are not feasible, and forming it into complex shapes can be more challenging and costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is food contact and easy cleaning: PTFE's non-stick and inert properties make it an exceptional choice for coatings and components that require frequent sanitization.
- If your primary focus is medical biocompatibility: PTFE is a proven material for implants and fluid-handling devices where chemical inertness is paramount to patient safety.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load: Consider using PTFE as a liner or coating on a stronger metal or composite part, rather than as a standalone structural component.
By understanding its core hygienic properties alongside its physical limitations, you can confidently leverage PTFE in applications where purity and safety are critical.
Summary Table:
| Key Hygienic Property | Benefit for Sensitive Industries |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination; tasteless, odorless, and non-toxic |
| Non-Stick Surface | Resists microbial adhesion; easy to clean and sterilize |
| Sterilization Resistance | Withstands high temperatures and harsh chemicals for reuse |
| Biocompatibility | Safe for medical implants and fluid-handling devices |
Need reliable PTFE components for your hygienic applications? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we ensure chemical purity and performance for your critical needs. Contact us today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the main drawbacks of PEEK? Key Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What does PTFE stand for and what is its composition? Unlocking the Power of a Two-Element Polymer
- What makes PTFE ideal for electrical insulation? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE and how does its chemical structure compare to polyethylene? Unlocking Superior Material Performance
- What are the chemical properties of Teflon? The Science Behind Its Extreme Inertness
- How does PTFE compare to Polyethylene (PE) in terms of chemical and temperature resistance? Choose the Right Polymer for Extreme Conditions
- What is the chemical composition of Teflon? The Science Behind Its Non-Stick Properties
- Are there any significant differences between PTFE and Teflon? The Truth About Brand vs. Material



















