At its core, PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene. It is a high-performance synthetic polymer, a type of fluorocarbon, composed of only two elements: carbon and fluorine. Its unique molecular structure is the source of its well-known properties, such as being chemically inert and having an extremely low-friction (non-stick) surface.
The essential thing to understand is that PTFE's remarkable characteristics are not due to a complex mixture of ingredients, but rather the simple, powerful, and unique bond between carbon and fluorine atoms arranged in a highly stable structure.
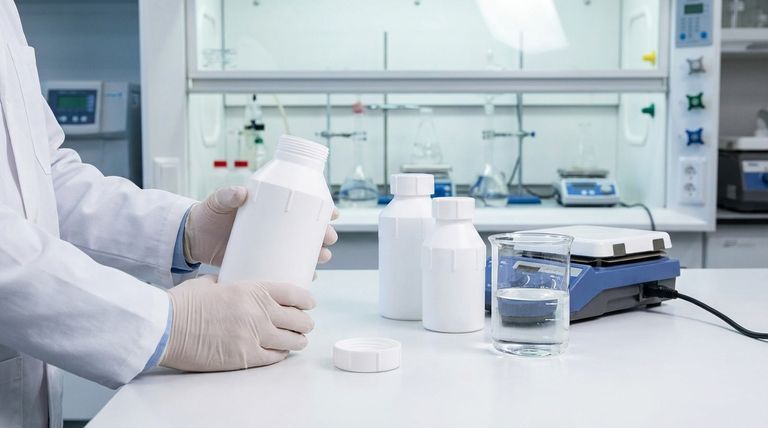

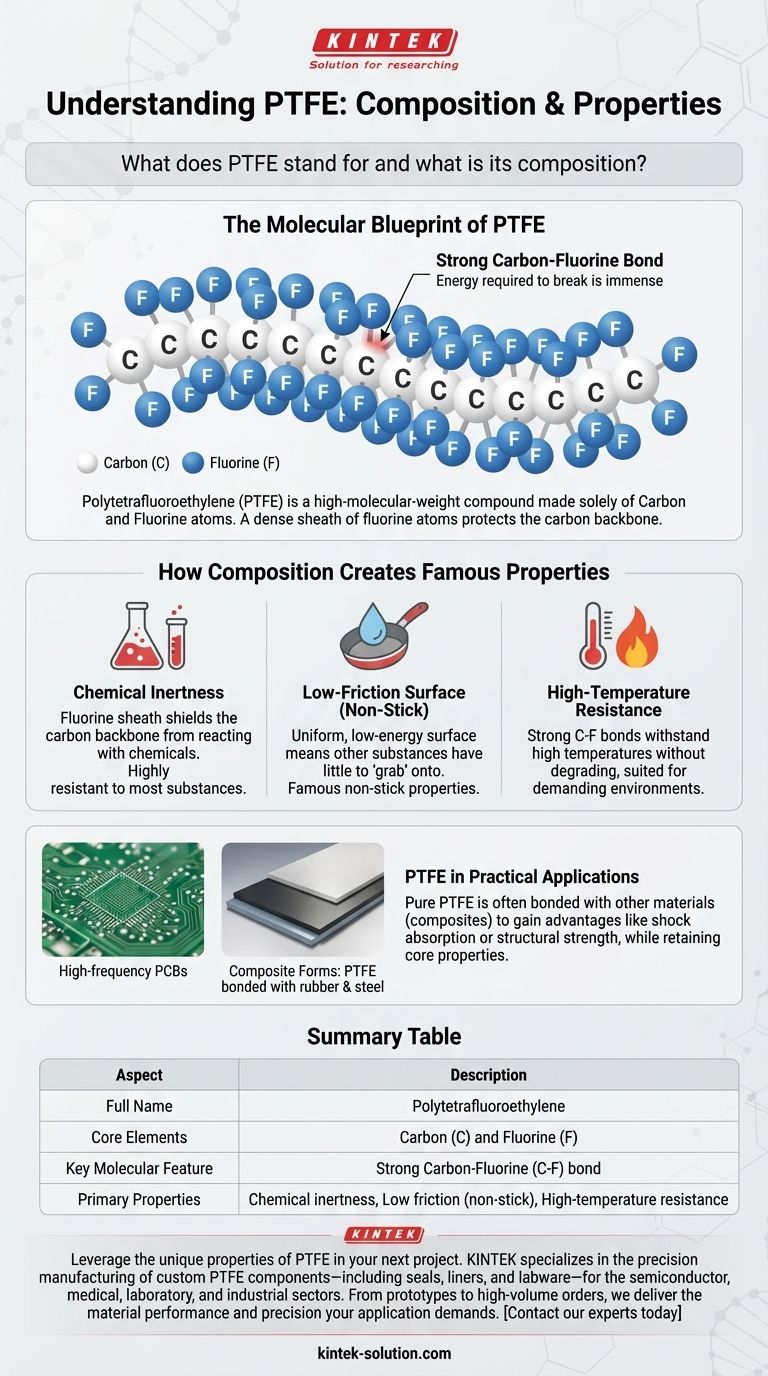
The Molecular Blueprint of PTFE
To truly understand PTFE, we must look at its atomic composition. Its simplicity is the key to its strength.
The Core Elements: Carbon and Fluorine
Polytetrafluoroethylene is a high-molecular-weight compound made up solely of carbon and fluorine atoms. As a synthetic fluoropolymer, it contains no other elements in its pure form.
The Atomic Structure
At a molecular level, PTFE consists of a long, repeating chain of carbon atoms that form a stable backbone. Each carbon atom in this chain is bonded to two fluorine atoms.
These fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms and effectively form a dense, protective sheath around the entire carbon chain.
The Exceptionally Strong Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between the carbon and fluorine atoms is extremely strong and stable. This powerful bond is one of the primary reasons for PTFE's signature properties, as it requires a great deal of energy to break.
How Composition Creates Its Famous Properties
The simple two-element structure directly translates into the material's valuable real-world performance characteristics.
Chemical Inertness
The dense sheath of fluorine atoms shields the vulnerable carbon backbone from reacting with outside chemicals. This structure makes PTFE one of the most chemically resistant materials known.
Low-Friction Surface (Non-Stick)
The fluorine atoms create a very uniform, low-energy surface. This means other substances have very little to "grab" onto, resulting in its famous non-stick and low-friction properties, best known by the brand name Teflon.
High-Temperature Resistance
Because the carbon-fluorine bonds are so strong, PTFE can withstand high temperatures without degrading, contributing to its use in demanding industrial and electronic applications.
PTFE in Practical Applications
While pure PTFE is a distinct material, it is often combined with other elements in real-world products to enhance specific capabilities. This is not a change in its core composition but rather the creation of a composite material.
Pure vs. Composite Forms
You will often find PTFE bonded to other materials to gain new advantages. For example, a PTFE sliding pad might bond the PTFE to a rubber pad for shock absorption and a stainless steel plate for structural strength.
A Material for Demanding Environments
In these composite forms, the core PTFE layer still provides the essential benefits of low friction and chemical resistance. This versatility makes it a material of choice for everything from high-frequency PCBs to industrial support discs.
Key Takeaways on PTFE's Composition
Understanding the link between PTFE's simple makeup and its powerful properties is essential for applying it correctly.
- If your primary focus is material science: The key insight is that the strength of the carbon-fluorine bond and the protective fluorine sheath are the direct source of PTFE's thermal stability and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is practical application: The key insight is that the molecular composition creates an intrinsically low-energy surface, which is why it excels as a non-stick coating and low-friction bearing material.
Ultimately, the extraordinary performance of Polytetrafluoroethylene is a direct result of its remarkably simple and stable two-element composition.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| Core Elements | Carbon (C) and Fluorine (F) |
| Key Molecular Feature | Strong Carbon-Fluorine (C-F) bond |
| Primary Properties | Chemical inertness, Low friction (non-stick), High-temperature resistance |
Leverage the unique properties of PTFE in your next project. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver the material performance and precision your application demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- How does the PTFE bottle perform in terms of chemical resistance? Unmatched Protection for Harsh Chemicals
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of PTFE as a material for laboratory bottles? Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the temperature limits for the PTFE bottle? Ensure Safety from -200°C to 260°C
- Is the PTFE bottle suitable for ultra-pure applications? Ensure Absolute Sample Integrity



















