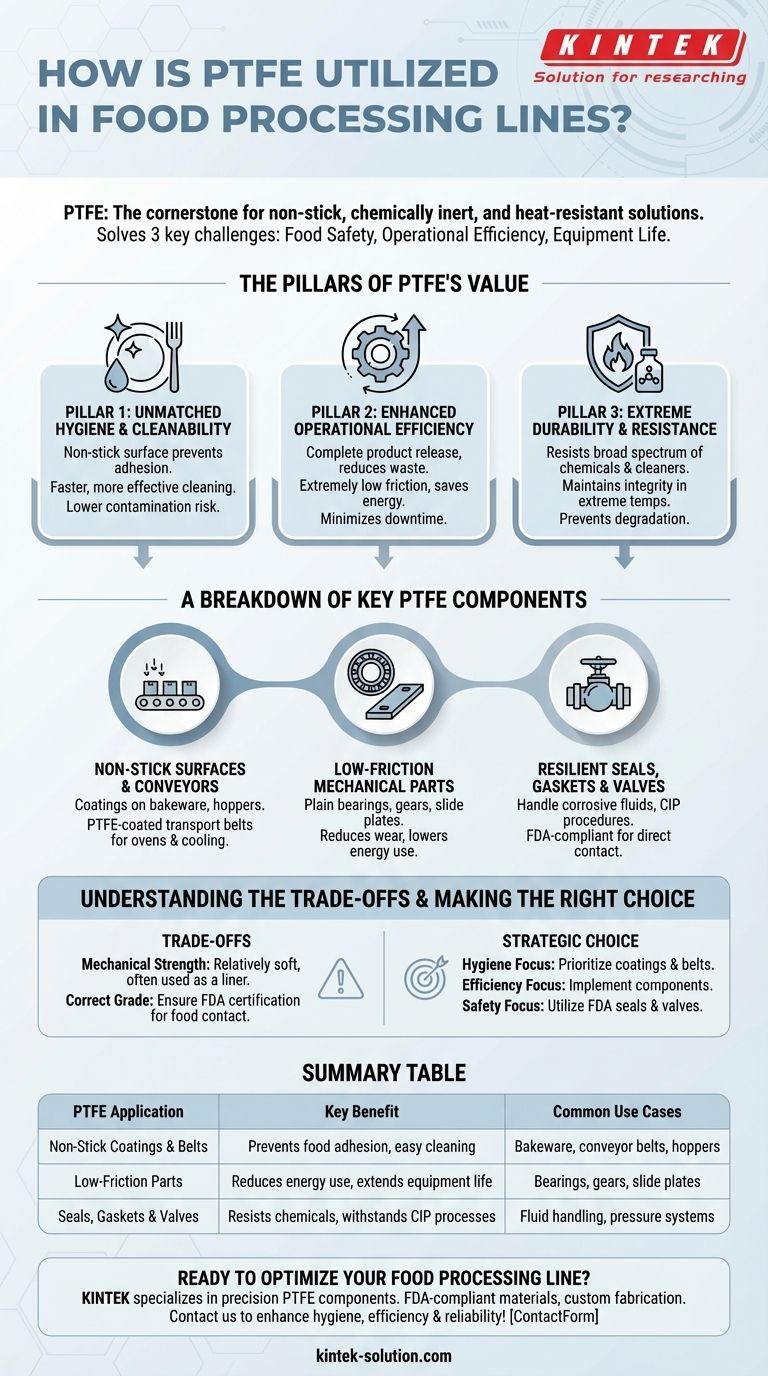
In the food processing industry, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a cornerstone material used for its unique combination of non-stick surfaces, chemical inertness, and heat resistance. It is most commonly found as coatings on bakeware and machinery, as conveyor belts for high-temperature applications, and as critical components like seals, gaskets, and valves for handling a wide range of food products.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread adoption is not just one property, but its unique ability to solve three of the industry's biggest challenges simultaneously: ensuring food safety and hygiene, improving operational efficiency, and extending the life of processing equipment.
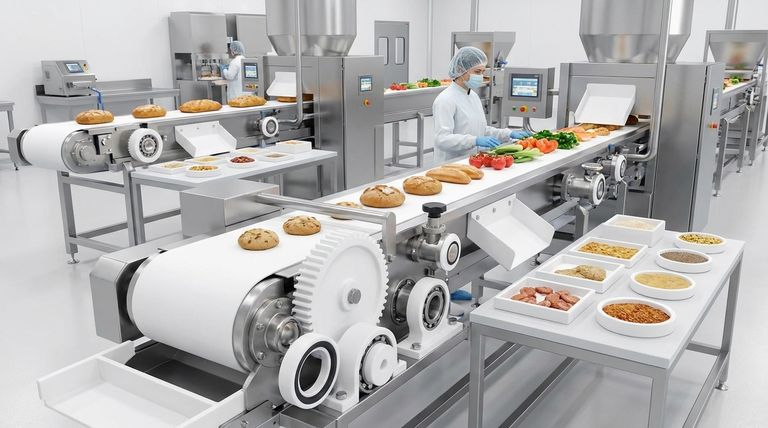

The Pillars of PTFE's Value in Food Processing
To understand why PTFE is so prevalent, it's essential to look beyond its specific applications and focus on the fundamental problems it solves. Its value rests on three key characteristics that directly address the demanding environment of food production.
Pillar 1: Unmatched Hygiene and Cleanability
The most recognized property of PTFE is its non-stick surface. This low-adhesion characteristic is critical in a food-grade environment.
Food residue, contaminants, and cleaning agents do not easily adhere to PTFE surfaces. This directly translates to faster, more effective cleaning cycles and a lower risk of microbial contamination between batches.
Pillar 2: Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Efficiency in food processing is a measure of speed, waste reduction, and energy consumption. PTFE contributes positively to all three.
Its non-stick nature ensures the complete and easy release of products—from baked goods on a conveyor to confectionery in a mold—which significantly reduces product waste.
Furthermore, its extremely low coefficient of friction makes it ideal for mechanical parts. This reduces the energy needed to operate machinery and minimizes downtime associated with part failure.
Pillar 3: Extreme Durability and Resistance
Food processing lines are harsh environments, involving extreme temperatures and a wide range of product chemistries.
PTFE is highly resistant to a broad spectrum of chemicals, including the acidic and alkaline substances found in many foods and aggressive cleaning solutions. This prevents the material from degrading and contaminating the product.
It also maintains its integrity across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for both cooking and freezing applications without becoming brittle or losing its properties.
A Breakdown of Key PTFE Components
These core properties translate into several key applications throughout a processing facility, each chosen to solve a specific operational challenge.
Non-Stick Surfaces and Conveyors
PTFE is frequently applied as a coating on equipment surfaces. This includes bakeware, hoppers, and chutes where sticky materials would otherwise cause blockages and increase cleaning time.
PTFE-coated transport belts are used extensively in ovens and cooling tunnels. They combine high heat resistance with a non-stick surface, ensuring products are cooked evenly and released cleanly.
Low-Friction Mechanical Parts
For sliding-action components, PTFE is often a superior choice to materials like nylon or acetal.
It is fabricated into plain bearings, gears, and slide plates where its low friction reduces wear and tear, lowers energy consumption, and extends the lifetime of the machinery.
Resilient Seals, Gaskets, and Valves
Handling fluids and maintaining pressure are critical functions. PTFE's chemical inertness makes it an ideal material for sealing applications.
Gaskets, seals, and valve components made from PTFE can handle highly corrosive fluids and withstand rigorous clean-in-place (CIP) procedures without degrading.
Critically, specific grades of PTFE are compliant with FDA regulations, ensuring they are safe for direct contact with food products.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE's benefits are significant, it is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations to ensure proper application.
Consider Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. In applications requiring high structural rigidity or resistance to high pressure and load, it may not be suitable on its own. It is often used as a liner or coating on a stronger metal substrate to gain the benefits of both materials.
Ensure Correct Grade and Certification
Not all PTFE is created equal. It is absolutely critical to verify that the specific PTFE material or component being used is certified for food contact by regulatory bodies like the FDA. Using an industrial grade in a food line can lead to contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material is about matching its properties to your most pressing operational need.
- If your primary focus is improving hygiene and reducing cleaning time: Prioritize PTFE coatings on product contact surfaces and the use of PTFE conveyor belts.
- If your primary focus is boosting mechanical efficiency and longevity: Implement PTFE components like bearings, gears, and slide plates to reduce friction and wear.
- If your primary focus is safely handling diverse or aggressive products: Utilize FDA-compliant PTFE seals, gaskets, and valves for their unparalleled chemical and thermal resilience.
By understanding the distinct advantages of PTFE in different contexts, you can strategically improve the safety, efficiency, and reliability of your food processing operations.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Application | Key Benefit | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Stick Coatings & Belts | Prevents food adhesion, easy cleaning | Bakeware, conveyor belts, hoppers |
| Low-Friction Parts | Reduces energy use, extends equipment life | Bearings, gears, slide plates |
| Seals, Gaskets & Valves | Resists chemicals, withstands CIP processes | Fluid handling, pressure systems |
Ready to optimize your food processing line with high-performance PTFE components? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the food processing, semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our FDA-compliant materials ensure safety and durability, while our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—deliver solutions tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operation's hygiene, efficiency, and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key chemical properties of PTFE balls? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What is the purpose of PTFE piston guide rings? Prevent Costly Wear in Your Equipment
- What are static applications and how are PTFE O-Rings used in them? Ensure Leak-Proof Seals in Demanding Environments
- What types of resistance do PTFE lined pipes provide? Unlock Superior Chemical and Thermal Performance
- How do PTFE gaskets stabilize pump and gear housing? Prevent Degradation for Long-Term Stability
- What are the advantages of solid Teflon O-rings? Achieve Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How is PTFE used in structural sliding bearings? Enable Smooth Movement Under Immense Loads
- What are the standard sizes available for PTFE wear strips and bands? Custom Sizes for Optimal Performance



















