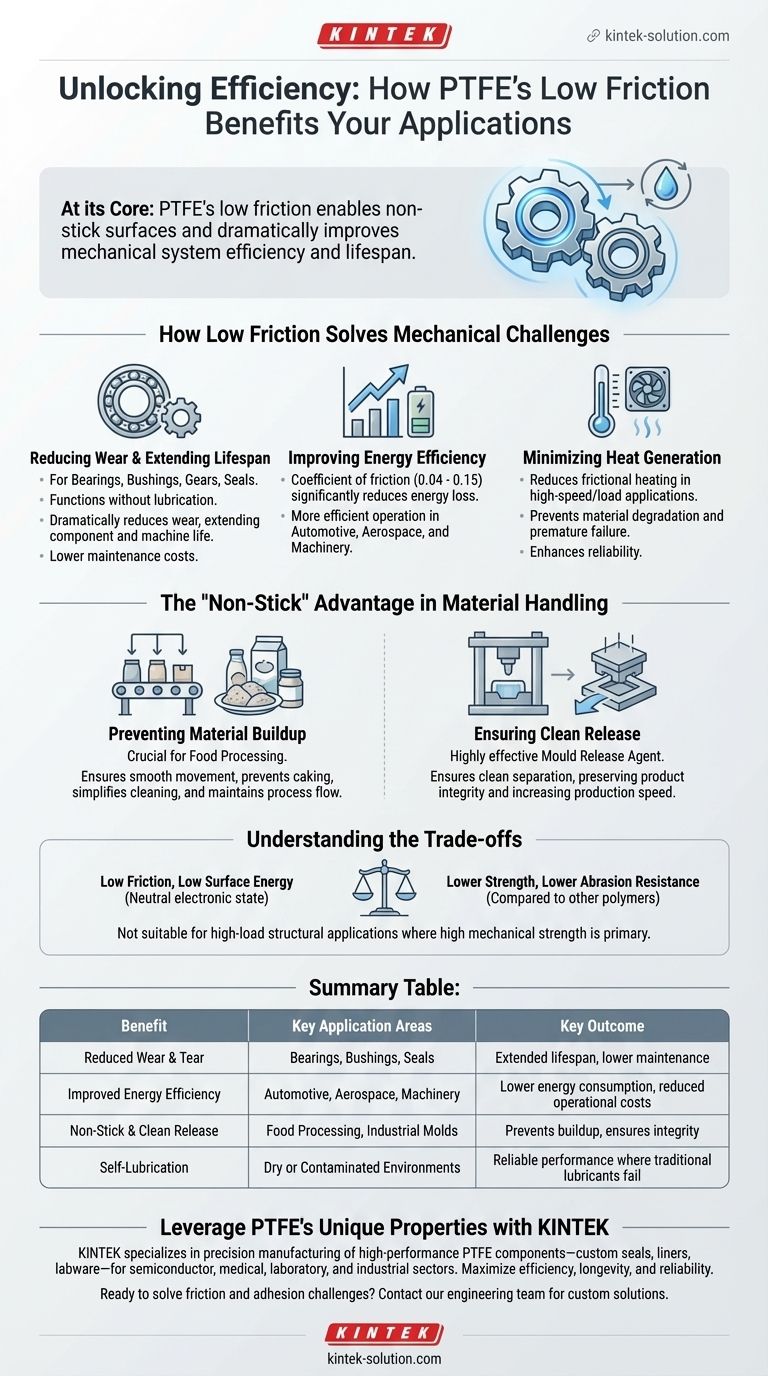
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene's (PTFE) low friction coefficient delivers two primary benefits: enabling non-stick surfaces and dramatically improving the efficiency and lifespan of mechanical systems. This unique property allows materials to slide against PTFE with minimal resistance, solving critical engineering challenges related to wear, energy loss, and material buildup.
The true value of PTFE's low friction is not just its "slipperiness." It is a fundamental engineering property that reduces energy consumption, minimizes wear and tear on moving parts, and prevents unwanted adhesion in a wide range of industrial and consumer applications.
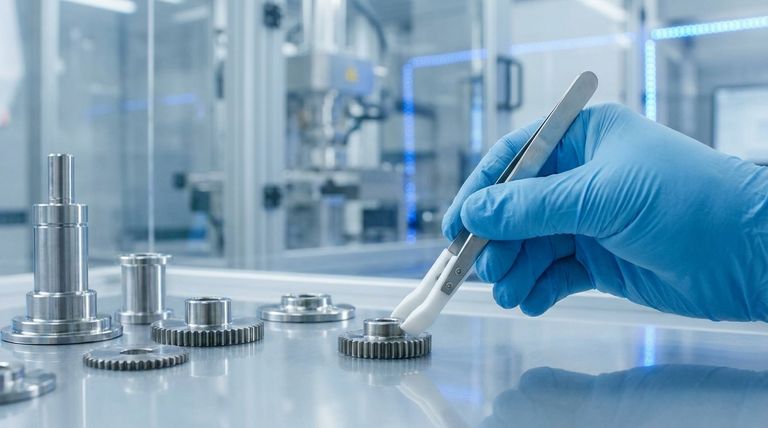

How Low Friction Solves Mechanical Challenges
One of the most significant applications of PTFE is in dynamic systems where components move against each other. The low friction coefficient directly translates into superior performance and longevity.
Reducing Wear and Extending Component Lifespan
PTFE is an exceptional material for components like bearings, bushings, gears, and seals. Its ability to function even in non-lubricated conditions is a key advantage.
By minimizing the frictional forces between moving parts, PTFE dramatically reduces wear and tear. This extends the operational life of the components and, by extension, the entire machine, leading to lower maintenance costs.
Improving Energy Efficiency
Friction is a primary source of energy loss in any mechanical system. Work must be done to overcome this resistance, and that energy is typically wasted as heat.
Because PTFE has a coefficient of friction between 0.04 and 0.15, it requires significantly less energy to move components. This improves the overall efficiency of machinery in industries from automotive to aerospace.
Minimizing Heat Generation
In high-speed or high-load applications, friction can generate a significant amount of heat. This thermal buildup can degrade materials, compromise seals, and lead to premature failure.
PTFE's low friction coefficient reduces this potential for frictional heating, which enhances its performance and reliability, especially as a sealing material in dynamic applications.
The "Non-Stick" Advantage in Material Handling
The same property that benefits mechanical gears also makes PTFE famous for its non-stick qualities, which are critical in applications where preventing material adhesion is the primary goal.
Preventing Material Buildup
In industrial settings like food processing equipment, preventing materials from sticking to surfaces is crucial for hygiene and operational efficiency.
PTFE coatings ensure that products move smoothly through the system without caking or building up, simplifying cleaning and maintaining process flow.
Ensuring Clean Release
For applications like industrial molds, the ability to release the finished product easily and without damage is paramount.
PTFE's non-stick surface acts as a highly effective mould release agent. This ensures a clean separation, preserving the integrity of the molded part and increasing production speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PTFE's exceptional properties do not come without compromises. The molecular structure that provides its famous low friction also results in other material characteristics that must be considered.
The Link Between Friction and Strength
The unique symmetrical structure of PTFE creates a neutral electronic state. This molecular arrangement is responsible for its low friction and low surface energy.
However, this same structure also leads to relatively low strength and low abrasion resistance compared to other engineering polymers. This means PTFE is not suitable for high-load structural applications where mechanical strength and hardness are the primary requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique low-friction benefits to a specific engineering problem.
- If your primary focus is mechanical efficiency and lifespan: Use PTFE for bearings, seals, or sliding components to reduce energy loss and extend the life of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is preventing adhesion: Apply PTFE coatings to cookware, food processing machinery, or industrial molds to ensure a clean release and prevent material buildup.
- If your primary focus is self-lubrication: Choose PTFE for dynamic components in environments where traditional lubricants cannot be used or may fail.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE's low coefficient of friction allows you to design systems that are more efficient, reliable, and durable.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Application Areas | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Wear & Tear | Bearings, Bushings, Seals | Extended component lifespan, lower maintenance costs |
| Improved Energy Efficiency | Automotive, Aerospace, Machinery | Lower energy consumption, reduced operational costs |
| Non-Stick & Clean Release | Food Processing, Industrial Molds | Prevents material buildup, ensures product integrity |
| Self-Lubrication | Dry or Contaminated Environments | Reliable performance where traditional lubricants fail |
Leverage PTFE's unique properties for your application.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your systems achieve maximum efficiency, longevity, and reliability.
Ready to solve your friction and adhesion challenges? Contact our engineering team today to discuss your custom PTFE solution from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Is PTFE the same as Teflon? Understanding the Brand vs. Material Distinction
- What are the electrical and water absorption properties of PTFE? Unmatched Stability for Demanding Applications
- What happens when PTFE is incinerated? The Hidden PFAS Pollution Risk
- How is PTFE laminated fabric used in shoe materials? Creating Waterproof & Breathable Footwear
- Are there any chemicals that PTFE is not compatible with? Key Exceptions for Safe Use
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? A Guide to High-Performance CNC Machining
- How does Nylon perform in chemical-heavy environments? A Guide to Its Strengths and Critical Weaknesses
- What are some specific applications of PTFE in industrial manufacturing? Unlock Chemical, Friction, and Electrical Solutions



















