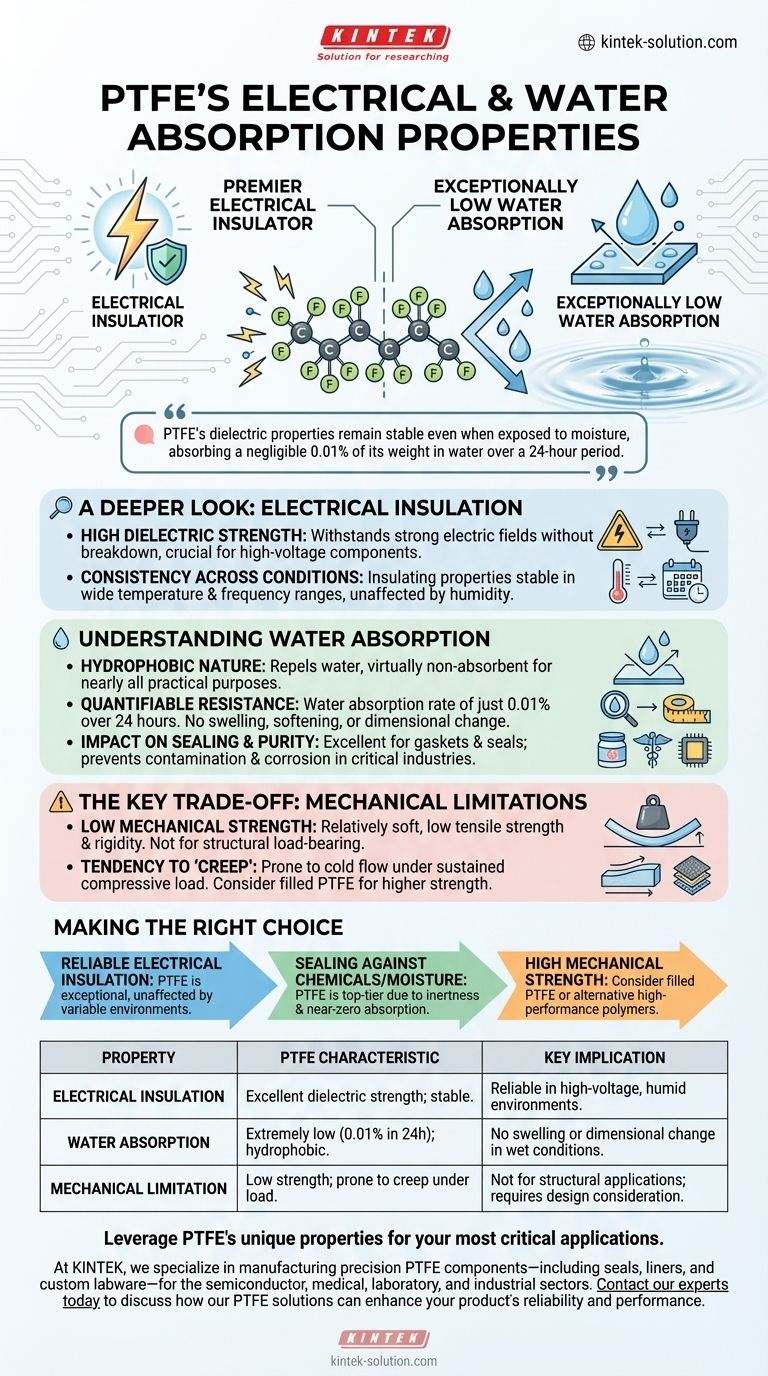
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a premier electrical insulator with exceptionally low water absorption. Its dielectric properties remain stable even when exposed to moisture, and it absorbs a negligible 0.01% of its weight in water over a 24-hour period. This unique combination makes it highly reliable for demanding electrical and sealing applications.
The true value of PTFE lies not just in its individual properties, but in their stability. Its excellent electrical insulation is not compromised by humidity, and its physical dimensions do not change in wet environments, ensuring predictable and consistent performance where other materials might fail.

A Deeper Look at PTFE's Electrical Insulation
PTFE's molecular structure, consisting of a carbon backbone shielded by fluorine atoms, is responsible for its exceptional performance as an electrical insulator. This structure prevents the easy flow of electrons through the material.
High Dielectric Strength
PTFE possesses a very high dielectric strength. This means it can withstand a strong electric field without experiencing electrical breakdown and becoming conductive.
This characteristic is critical for insulating high-voltage wiring and components, preventing short circuits and ensuring operational safety.
Consistency Across Conditions
Unlike many other polymers, PTFE's insulating properties are remarkably stable across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
Crucially, because it does not absorb water, its electrical resistance remains consistently high even in humid or submerged conditions. Moisture that would compromise the insulating capacity of other materials has virtually no effect on PTFE.
Understanding PTFE's Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE is fundamentally hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. This behavior is a direct result of its ultra-low surface energy and non-polar nature.
Quantifying Water Absorption
The material's resistance to water is quantifiable. With a water absorption rate of just 0.01% over 24 hours, PTFE is considered non-absorbent for nearly all practical purposes.
This means it will not swell, soften, or change its physical dimensions when exposed to moisture, a critical feature for creating stable, long-lasting seals and components.
The Impact on Sealing and Purity
This near-zero water absorption makes PTFE an excellent choice for gaskets and seals, especially in the food, medical, and semiconductor industries.
It does not harbor moisture that could lead to contamination or corrosion, ensuring the purity of the process it is part of.
The Key Trade-off: Mechanical Limitations
While PTFE's electrical and chemical properties are world-class, its mechanical performance presents a significant trade-off that must be understood for proper application.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and rigidity compared to engineering plastics like PEEK or nylon. It is not suitable for applications that require significant load-bearing or structural integrity.
Tendency to "Creep"
Under sustained compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE is prone to "creep" or cold flow. This means it can slowly deform over time.
This characteristic must be accounted for in seal and bearing design to prevent failure. In many cases, "filled" grades of PTFE (which include additives like glass or carbon) are used to improve creep resistance and mechanical strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is a decision based on leveraging its unique strengths while respecting its limitations. Its performance is nearly unrivaled in the right context.
- If your primary focus is reliable electrical insulation in variable environments: PTFE is an exceptional choice, as its dielectric properties will not degrade due to humidity or temperature fluctuations.
- If your primary focus is creating a seal against aggressive chemicals or moisture: PTFE's combination of chemical inertness and near-zero water absorption makes it a top-tier gasket material.
- If your application demands high mechanical strength or structural load-bearing: Standard PTFE is likely unsuitable, and you should consider filled PTFE grades or alternative high-performance polymers.
Ultimately, understanding this balance of properties empowers you to deploy PTFE precisely where its remarkable stability can be used to greatest effect.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Characteristic | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength; stable across temperatures & frequencies | Reliable performance in high-voltage, humid environments |
| Water Absorption | Extremely low (0.01% over 24 hours); hydrophobic | No swelling or dimensional change in wet conditions |
| Mechanical Limitation | Low strength; prone to creep under load | Not for structural applications; requires design consideration |
Leverage PTFE's unique properties for your most critical applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components deliver unmatched electrical stability and sealing performance, even in the most demanding conditions.
Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, we provide custom fabrication to meet your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance



















