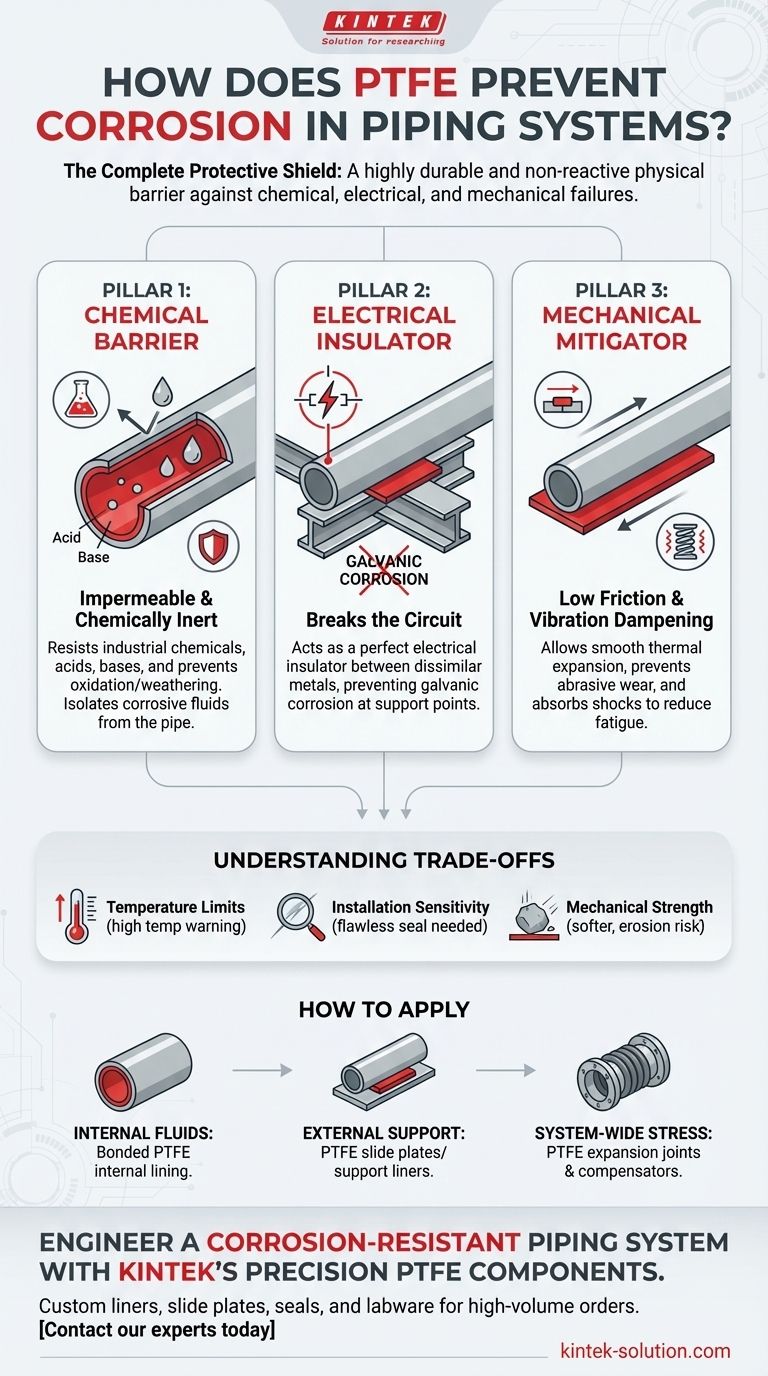
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) prevents corrosion by creating a highly durable and non-reactive physical barrier. This barrier isolates the pipe material from corrosive fluids, atmospheric conditions, and even the electrical currents that cause galvanic corrosion at support points. Its unique combination of chemical inertness, low friction, and electrical insulation makes it a uniquely effective solution.
Corrosion in piping is not a single problem but a combination of chemical, electrical, and mechanical failures. PTFE's effectiveness comes from its ability to simultaneously address all three of these failure modes, acting as a complete protective shield.

The Three Pillars of PTFE Corrosion Protection
PTFE's protective capabilities are not based on a single property but on a trio of powerful characteristics that work in concert to preserve the integrity of a piping system.
Pillar 1: The Chemically Inert Barrier
The most fundamental role of PTFE is to serve as an impermeable and non-reactive lining or coating.
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert substances known. This means it does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and bases. When used as an internal liner, it prevents corrosive fluids from ever touching the pipe wall.
It is also highly resistant to oxidation and weathering. Unlike many plastics or coatings, PTFE does not degrade when exposed to moisture, UV light, or other atmospheric elements, making it ideal for outdoor applications.
Pillar 2: The Electrical Insulator
A common and often overlooked form of corrosion occurs when two different metals are in contact, creating a galvanic cell.
Galvanic corrosion occurs when a pipe and its metal support interact. This electrochemical reaction can rapidly degrade the pipe material at the point of contact.
PTFE acts as a perfect electrical insulator. By placing a PTFE liner or slide plate between the pipe and its support, you break the electrical circuit. This physically separates the dissimilar metals, completely preventing galvanic corrosion from occurring.
Pillar 3: The Mechanical Damage Mitigator
Physical wear and tear can strip away protective coatings or create stress points that become origins for corrosion. PTFE mitigates this mechanical damage.
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction. When used in pipe supports, it allows pipes to glide smoothly during thermal expansion and contraction. This prevents the abrasive wear and surface erosion that would otherwise compromise the pipe's integrity.
It also provides excellent vibration dampening. PTFE pads and liners absorb shocks and vibrations from equipment, cushioning the impact between pipes and their supports. This reduces fatigue and preserves the structural integrity of the system.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While remarkably effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its operational limits is critical for successful implementation.
Temperature Limitations
PTFE has a distinct operational temperature range. While suitable for many applications, it can lose its structural integrity and protective properties in extremely high-temperature environments.
Installation Sensitivity
The performance of a PTFE liner is highly dependent on a flawless installation. Any pinholes, scratches, or improper seals in the liner can create a localized point for aggressive corrosion to attack the underlying pipe.
Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals, PTFE is a softer material. In applications with high-velocity fluids containing abrasive particles, the liner itself can be subject to erosion over time, which must be accounted for in the system design.
How to Apply This to Your System
Your specific goal will determine the most effective way to leverage PTFE's protective properties.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive internal fluids: Use pipes with a bonded PTFE internal lining to ensure total chemical inertness and prevent internal corrosion.
- If your primary focus is preventing external corrosion at support points: Implement PTFE slide plates or support liners to insulate the pipe from its metal supports, eliminating galvanic corrosion and friction damage.
- If your primary focus is managing system-wide mechanical stress: Incorporate PTFE components like expansion joints and compensators to safely absorb thermal movement and vibration, preventing joint failure.
By strategically applying PTFE, you move beyond merely resisting corrosion to engineering a truly resilient and long-lasting piping system.
Summary Table:
| Protection Pillar | How PTFE Works | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Barrier | Acts as a non-reactive liner, isolating pipe walls from corrosive fluids. | Resists acids, bases, and solvents. |
| Electrical Insulator | Breaks the circuit between dissimilar metals at support points. | Prevents galvanic corrosion. |
| Mechanical Mitigator | Low friction allows pipes to glide; dampens vibrations. | Reduces wear and fatigue from movement. |
Engineer a corrosion-resistant piping system with KINTEK's precision PTFE components.
Whether you need custom PTFE liners for aggressive chemicals, slide plates to prevent galvanic corrosion at supports, or specialized labware, KINTEK delivers. We manufacture high-quality PTFE seals, liners, and components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and receive a custom solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE's ease of sterilization important for medical devices? Ensuring Patient Safety and Device Integrity
- What is the production process for PTFE seals? From Raw PTFE to Precision Sealing Components
- What are the advantages of mechanical seals with PTFE rings? Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are common mistakes to avoid when using PTFE gaskets? Prevent Costly Leaks and Downtime
- How do Teflon bearings perform in demanding applications? Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What are the standard sheet sizes for PTFE? Optimize Your Material Selection
- What non-standard options are available for PTFE slide bearings? Customize for Temperature, Load, and Movement
- How does the large expansion coefficient of PTFE material affect processing? Master Dimensional Stability



















