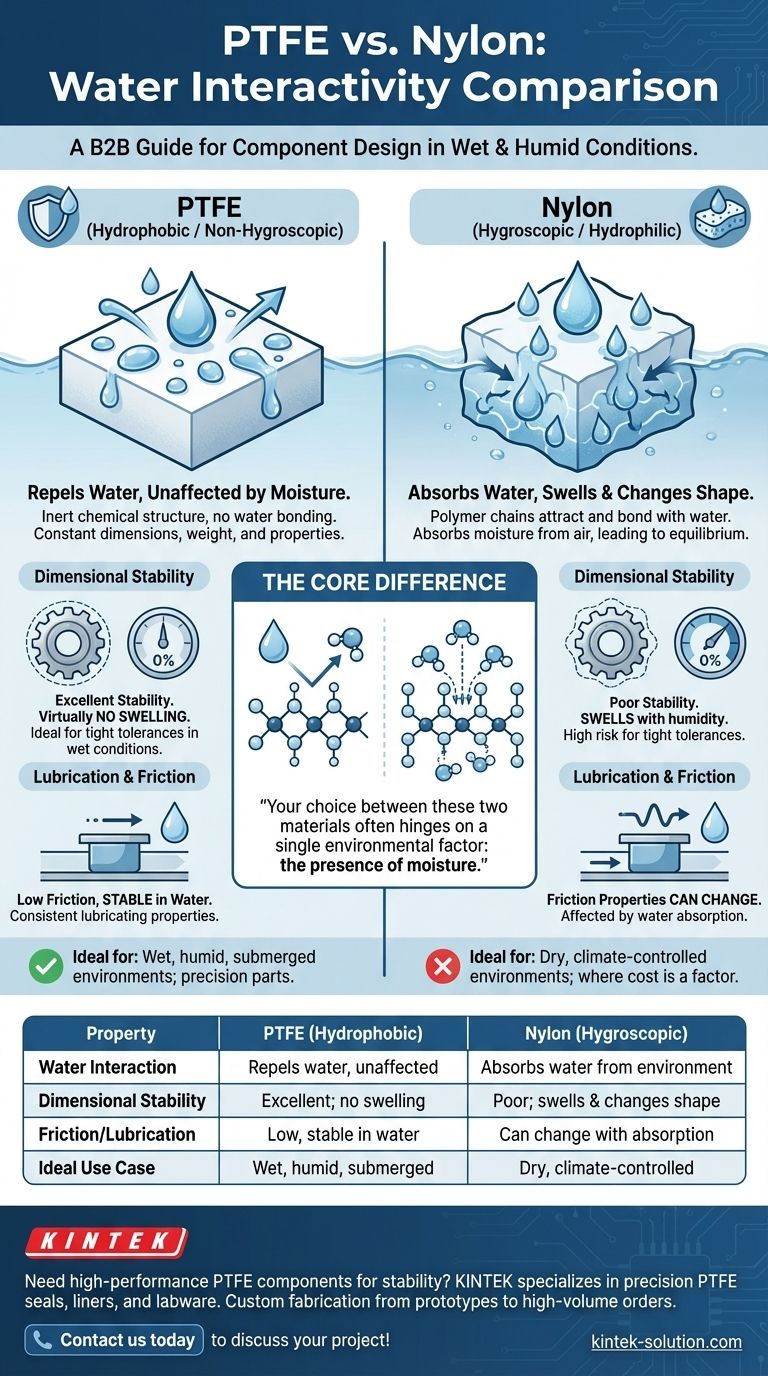
The fundamental difference is that PTFE repels water while nylon absorbs it. PTFE is a hydrophobic (or non-hygroscopic) material, meaning it is entirely unaffected by the presence of moisture. In direct contrast, nylon is hygroscopic (or hydrophilic), causing it to actively draw in and retain water from its surroundings, which significantly alters its physical properties.
Your choice between these two materials often hinges on a single environmental factor: the presence of moisture. Nylon's tendency to absorb water causes it to swell and change shape, making PTFE the definitive choice for any application requiring stability in wet or humid conditions.

The Core Difference: Water Interaction
The terms hydrophobic and hygroscopic describe the core chemical behavior of these materials when exposed to water. Understanding this distinction is critical for predicting a component's real-world performance.
What "Hydrophobic" Means for PTFE
PTFE is fundamentally inert to water. Its chemical structure creates a surface that water molecules cannot bond with, effectively repelling them.
This non-hygroscopic nature means PTFE does not absorb moisture from the air or when submerged. Its physical dimensions, weight, and material properties remain constant regardless of humidity.
What "Hygroscopic" Means for Nylon
Nylon, by contrast, acts like a sponge at a molecular level. Its polymer chains contain sites that attract and bond with water molecules.
This hydrophilic behavior means nylon will absorb moisture directly from the atmosphere. The amount of water it absorbs is proportional to the ambient humidity, a process that continues until it reaches equilibrium.
Practical Implications of Water Absorption
This single difference in water interaction has profound consequences for component design, especially where precision and reliability are required.
Dimensional Stability
The most critical consequence of nylon's water absorption is swelling. As nylon parts absorb moisture, their physical dimensions increase.
This dimensional instability can be catastrophic for components with tight tolerances, such as gears, bushings, or precision fittings. A part that fits perfectly in a dry environment may seize or fail when humidity rises.
PTFE, being hydrophobic, exhibits virtually no swelling or dimensional change, ensuring consistent performance in any moisture condition.
Lubrication and Friction
PTFE is renowned for its extremely low coefficient of friction. This property is inherent to the material and is not affected by water.
This makes PTFE an ideal choice for bearings or sliding components in high-moisture applications, as its lubricating characteristics remain stable and predictable. While nylon also has good friction properties, they can be altered as it absorbs water.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is always about balancing properties. The clear advantage of PTFE in wet environments is just one part of the equation.
When Nylon's Hygroscopicity is a Liability
If your component must maintain precise dimensions, operate in a humid or wet environment, or be submerged, nylon is a high-risk choice. The potential for swelling and dimensional variation makes it unsuitable for such applications.
When PTFE is the Default Choice
For any application involving direct water contact, high humidity, or outdoor exposure where dimensional stability is paramount, PTFE is the superior material. Its immunity to moisture ensures predictable and reliable performance over the component's lifetime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires you to prioritize your application's most critical needs.
- If your primary focus is performance in high-moisture or submerged conditions: Choose PTFE for its unmatched dimensional stability and consistent properties.
- If your primary focus is a component for a dry, climate-controlled environment: Nylon may be a suitable option where its other properties, like toughness or cost, are advantageous.
- If your primary focus is consistent lubrication regardless of environmental humidity: PTFE is the more reliable choice to guarantee stable, low-friction performance.
Understanding how a material interacts with its operating environment is the foundation of robust engineering design.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE (Hydrophobic) | Nylon (Hygroscopic) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Interaction | Repels water, unaffected by moisture | Absorbs water from the air/environment |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent; no swelling or change in wet/humid conditions | Poor; swells and changes shape with humidity |
| Friction/Lubrication | Low coefficient of friction, stable in water | Friction properties can change with water absorption |
| Ideal Use Case | Wet, humid, or submerged environments; precision parts | Dry, climate-controlled environments where cost is a factor |
Need high-performance PTFE components that guarantee stability in wet or humid conditions? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure your components perform reliably, no matter the environment. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and benefit from our expertise in material solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments



















