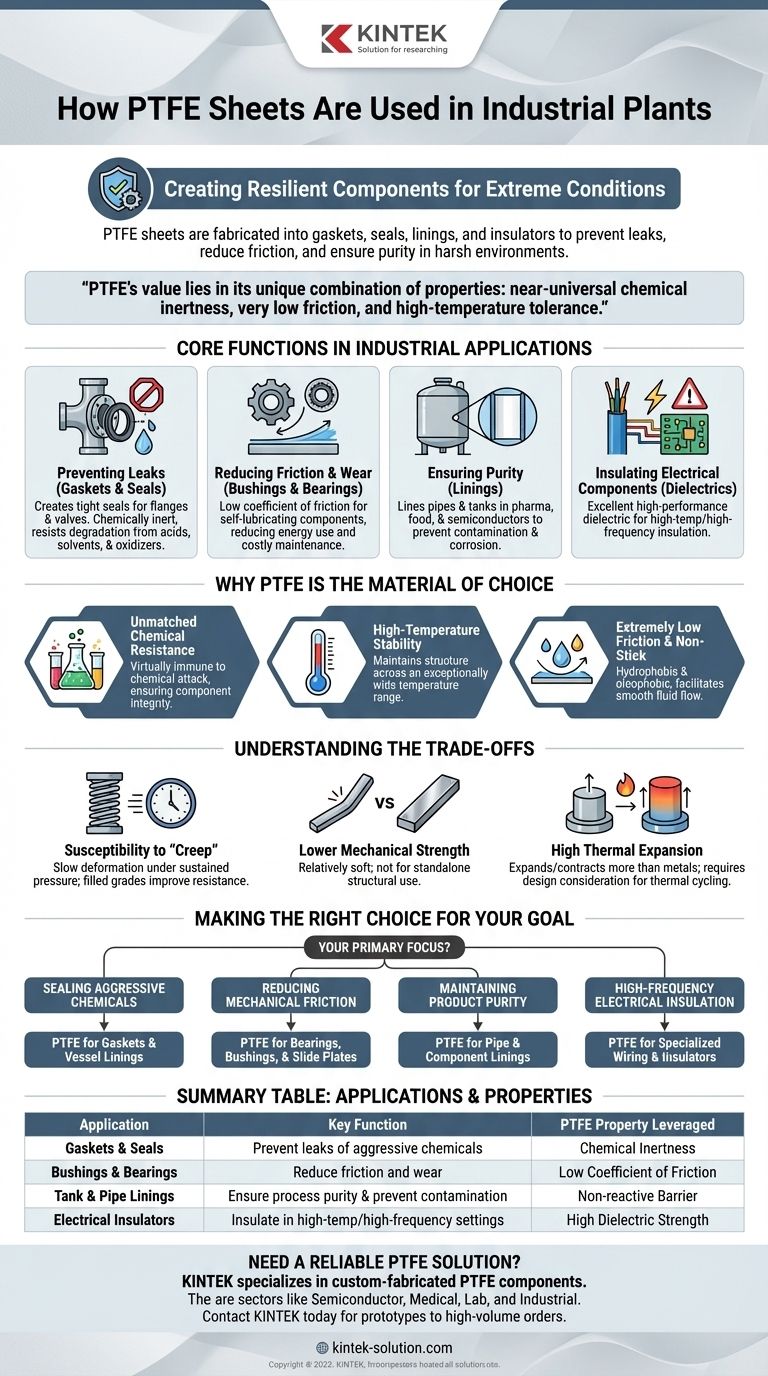
In industrial plants, PTFE sheets serve one primary purpose: to create highly resilient and reliable components that can withstand extreme operational conditions. They are fabricated into gaskets, seals, linings, and insulators to prevent leaks, reduce friction, and ensure process purity in environments where aggressive chemicals, high temperatures, and mechanical stress would cause other materials to fail.
The true value of PTFE in an industrial setting isn't just one feature, but its unique combination of properties. It offers near-universal chemical inertness, a very low coefficient of friction, and high-temperature tolerance, making it the default material for solving complex sealing and fluid handling challenges.

The Core Functions of PTFE in Industrial Applications
PTFE's versatility allows it to be used in several critical roles throughout a plant, each leveraging a different aspect of its unique molecular structure.
Preventing Leaks with Gaskets and Seals
The most common use for PTFE sheets is the fabrication of gaskets and packings. These components create a tight seal between pipe flanges, valve bodies, and vessel access points.
Because PTFE is chemically inert, these seals will not degrade when exposed to corrosive acids, solvents, or oxidizing agents, ensuring long-term containment of hazardous substances.
Reducing Friction and Wear
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, a property famously used in non-stick cookware.
In an industrial plant, this translates to creating self-lubricating bushings, bearings, and slide plates. These components reduce energy consumption in machinery and prevent the wear and tear that leads to costly maintenance and downtime.
Ensuring Purity with Linings
In industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and semiconductors, preventing contamination is paramount.
PTFE sheets are used to line pipes, tanks, and chemical reactors. This creates a non-reactive barrier that protects the product from the vessel's metal and, conversely, protects the vessel from corrosive process fluids.
Insulating Electrical Components
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a high melting point, known as a high-performance dielectric.
This makes it invaluable for insulating wiring and components in high-temperature or high-frequency applications where standard plastics like PVC would melt or fail.
Why PTFE Is the Material of Choice
Engineers specify PTFE when operational demands exceed the capabilities of conventional materials. Its selection is based on a powerful combination of characteristics.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually immune to chemical attack. It can handle everything from mineral oils and solvents to the most corrosive chemicals used in petrochemical and chemical processing plants.
This inertness ensures component integrity and prevents process contamination.
High-Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its structure and properties across an exceptionally wide temperature range. It remains functional in both high-heat processes and cryogenic applications where other polymers would become brittle or melt.
Extremely Low Friction
The material's surface is both hydrophobic (resists water) and oleophobic (resists oil). This non-stick quality facilitates the smooth flow of fluids in piping systems and prevents the buildup of viscous materials, improving process efficiency.
Durability and Safety
By resisting chemical degradation and thermal stress, PTFE components are highly durable. This reliability reduces the need for frequent replacement and minimizes the risk of catastrophic leaks or failures, directly enhancing industrial safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
Susceptibility to "Creep"
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, pure PTFE can slowly deform. This phenomenon, known as creep or cold flow, can cause seals to loosen over time.
To counteract this, filled grades of PTFE (mixed with materials like glass fiber or carbon) are often used to improve creep resistance and mechanical strength.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or many engineering plastics, PTFE is a relatively soft material with lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance. It is not typically used for standalone structural components.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes more than most metals. This must be accounted for in the design of components that will experience significant thermal cycling to avoid stress and potential failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about matching its specific strengths to a clear operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: PTFE's near-universal chemical inertness makes it the ideal choice for gaskets and vessel linings in chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is reducing mechanical friction: Its ultra-low coefficient of friction is perfect for creating self-lubricating bearings, bushings, and slide plates.
- If your primary focus is maintaining product purity: Use PTFE for lining pipes and components in the food, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor industries to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its excellent dielectric properties and high-temperature resistance make it a superior material for specialized wiring and insulators.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE effectively means understanding its unique combination of resistances to solve problems where lesser materials would quickly degrade and fail.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | PTFE Property Leveraged |
|---|---|---|
| Gaskets & Seals | Prevent leaks of aggressive chemicals | Chemical Inertness |
| Bushings & Bearings | Reduce friction and wear | Low Coefficient of Friction |
| Tank & Pipe Linings | Ensure process purity and prevent contamination | Non-reactive Barrier |
| Electrical Insulators | Insulate in high-temperature/high-frequency settings | High Dielectric Strength |
Need a reliable PTFE solution for your industrial challenge?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom-fabricated PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine precision production with expert material knowledge to deliver parts that withstand extreme conditions, reduce downtime, and enhance safety.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some examples of filled PTFE seals and their properties? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are some common components made from PTFE? Seals, Bearings & More for Demanding Applications
- How does the surface roughness of materials in contact with PTFE affect friction? Find the Critical 'Sweet Spot'
- How does PTFE contribute to the performance of metal expansion joints? Enhance Durability in Harsh Chemical Environments
- What are the key properties of PTFE? Unmatched Chemical, Thermal, and Friction Performance
- How is surface preparation performed for PTFE coating application? Achieve Unbreakable Adhesion for Your Components
- What are the main differences between PTFE and graphite packing? Choose the Right Seal for Your Application
- How does PTFE coating enhance corrosion resistance in fasteners? Achieve Unmatched Protection in Harsh Environments



















