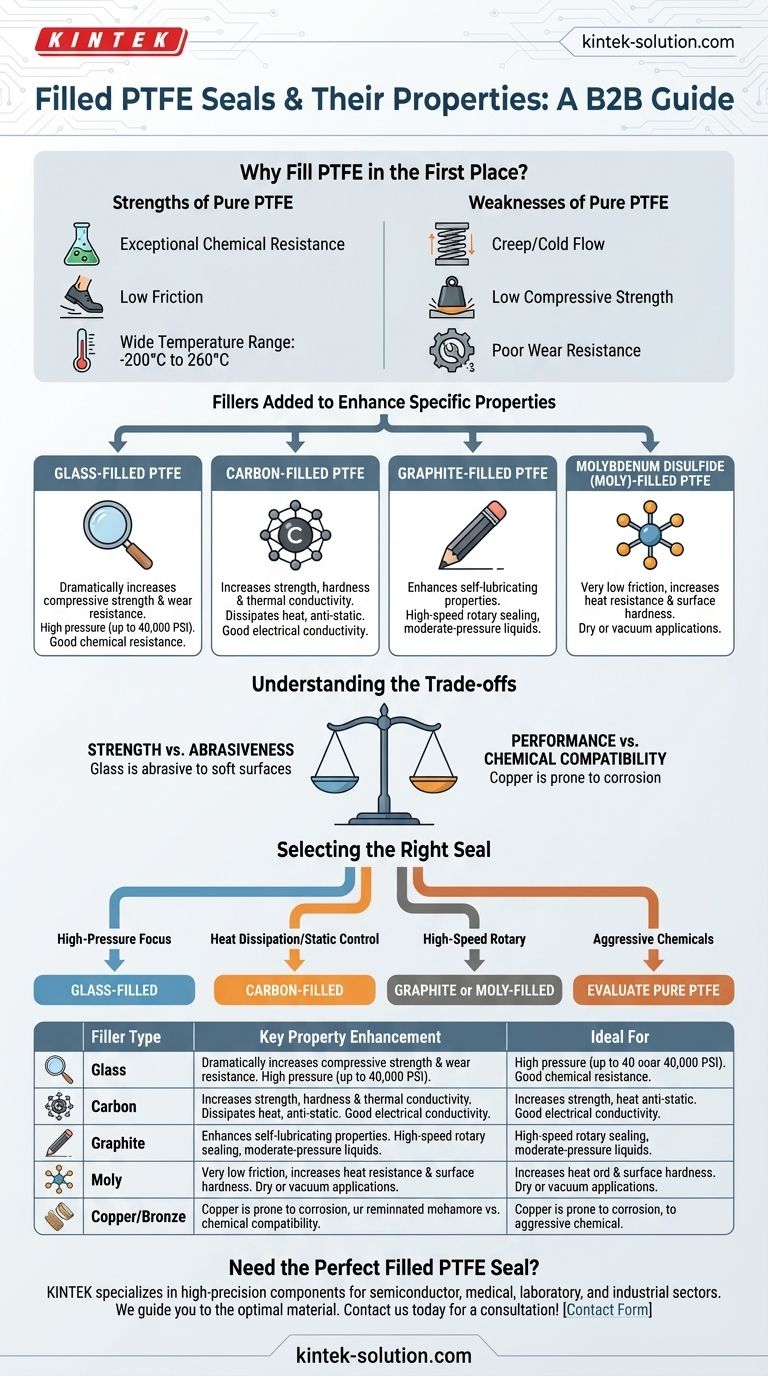
The most common filled PTFE seals include glass-filled, carbon-filled, graphite-filled, and molybdenum disulfide (moly)-filled variants. Each filler is added to enhance specific properties of the base PTFE, such as compressive strength, thermal conductivity, or wear resistance, making the seal suitable for demanding applications where pure PTFE would fail.
While pure PTFE offers exceptional chemical resistance and a low coefficient of friction, its primary weaknesses are low mechanical strength and a tendency to deform under load. Adding fillers is the essential engineering solution to overcome these limitations, but it always introduces a series of performance trade-offs.
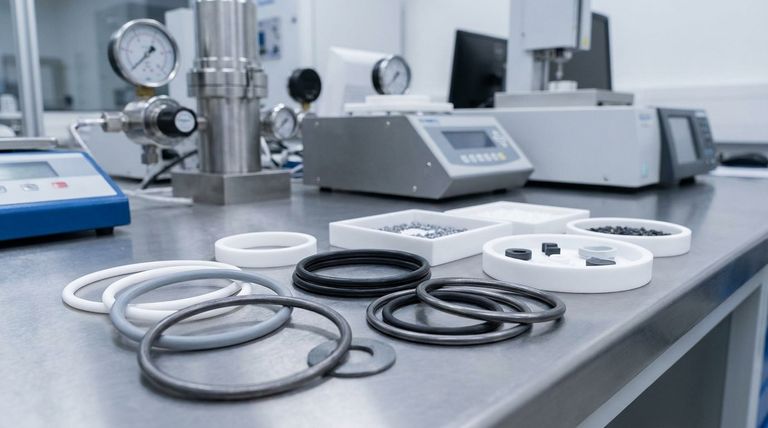

Why Fill PTFE in the First Place?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a remarkable polymer on its own. It is prized for a unique combination of characteristics that make it a go-to material for sealing applications.
The Strengths of Pure PTFE
Pure, or "virgin," PTFE provides exceptional chemical resistance, making it nearly inert to most acids, solvents, and aggressive fluids. It also has an extremely low coefficient of friction, giving it a non-stick, self-lubricating quality that reduces wear and energy loss in dynamic systems.
Finally, it operates effectively across a vast temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
The Weaknesses of Pure PTFE
Despite these strengths, pure PTFE suffers from poor mechanical properties. It exhibits creep, or cold flow, meaning it will slowly deform when subjected to a persistent load. It also has relatively low compressive strength and poor wear resistance, especially in high-pressure or abrasive conditions.
Fillers are added directly into the PTFE matrix to specifically target and improve these mechanical weaknesses.
A Guide to Common PTFE Fillers and Their Properties
Choosing the right filler is critical, as each one imparts a distinct set of characteristics to the final seal. The percentage of filler used also significantly impacts the final properties.
Glass-Filled PTFE
Glass is one of the most common fillers. It dramatically increases the compressive strength and wear resistance of PTFE.
Glass-filled seals are excellent for high-pressure applications and can withstand pressures up to 40,000 PSI. They maintain good chemical resistance, though not quite as universal as pure PTFE.
Carbon-Filled PTFE
Adding carbon to PTFE increases its compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
A key benefit of carbon is that it also enhances thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat from the sealing surface. It also provides good electrical conductivity, making it suitable for anti-static applications.
Graphite-Filled PTFE
Graphite is often used in combination with other fillers, like carbon. Its primary contribution is enhancing the material's self-lubricating properties.
This makes graphite-filled seals ideal for high-speed dynamic applications, particularly in moderate-pressure liquids and steam, where minimizing friction is paramount.
Molybdenum Disulfide (Moly)-Filled PTFE
Molybdenum disulfide, or "moly," is another lubricant filler that provides a very low coefficient of friction, often even lower than graphite.
It is particularly valued for increasing heat resistance and surface hardness. Moly-filled seals perform exceptionally well in dry or vacuum applications where external lubrication is not possible.
Copper-Filled PTFE
For applications requiring the highest levels of thermal and electrical conductivity, copper (or bronze) is the filler of choice.
These seals are excellent at dissipating heat quickly. However, this performance comes at the cost of chemical resistance, as copper is much more reactive than other fillers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no "perfect" filler. Enhancing one property almost always means compromising on another. Understanding these trade-offs is the key to proper material selection.
Strength vs. Abrasiveness
While glass-filled PTFE is incredibly strong and durable, it is also highly abrasive. Using a glass-filled seal against a soft mating surface, like an aluminum or brass shaft, can cause rapid wear of the shaft itself.
Performance vs. Chemical Compatibility
Copper-filled PTFE offers unmatched thermal conductivity, but it is prone to corrosion and cannot be used with many aggressive chemicals that pure PTFE would easily handle. Its use is limited to non-corrosive media.
Sealing Ability vs. Hardness
Adding hard fillers like glass or carbon increases the material's modulus, making it less flexible. A harder seal may not conform as easily to surface irregularities, potentially compromising its sealing ability in applications with rougher finishes.
Selecting the Right Filled PTFE for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the specific demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing: Choose glass-filled PTFE for its exceptional compressive strength and durability, but ensure your mating surface is hardened.
- If your primary focus is heat dissipation or static control: Carbon-filled PTFE is a balanced choice, while copper-filled PTFE offers the best performance if chemical compatibility is not a concern.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotary sealing: Graphite-filled or moly-filled PTFE provides the best self-lubricating properties to minimize friction and wear.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: You must carefully evaluate if a filled PTFE is appropriate, as pure (virgin) PTFE offers the most reliable chemical resistance.
Ultimately, understanding how each filler modifies the base properties of PTFE empowers you to select the optimal material for maximum performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Property Enhancement | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | High Compressive Strength & Wear Resistance | High-pressure applications (up to 40,000 PSI) |
| Carbon | Increased Strength & Thermal Conductivity | Heat dissipation, anti-static applications |
| Graphite | Superior Self-Lubrication | High-speed rotary sealing, moderate-pressure liquids |
| Molybdenum Disulfide (Moly) | Extremely Low Friction & Heat Resistance | Dry or vacuum applications, high temperatures |
| Copper/Bronze | Maximum Thermal & Electrical Conductivity | Non-corrosive environments requiring rapid heat dissipation |
Need the Perfect Filled PTFE Seal for Your Application?
Selecting the right filled PTFE seal is critical for performance and longevity. The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand the trade-offs and can guide you to the optimal material choice, balancing strength, chemical resistance, and wear for your unique operating environment. From prototyping to high-volume production, we prioritize precision and reliability.
Let's solve your sealing challenge together. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications



















