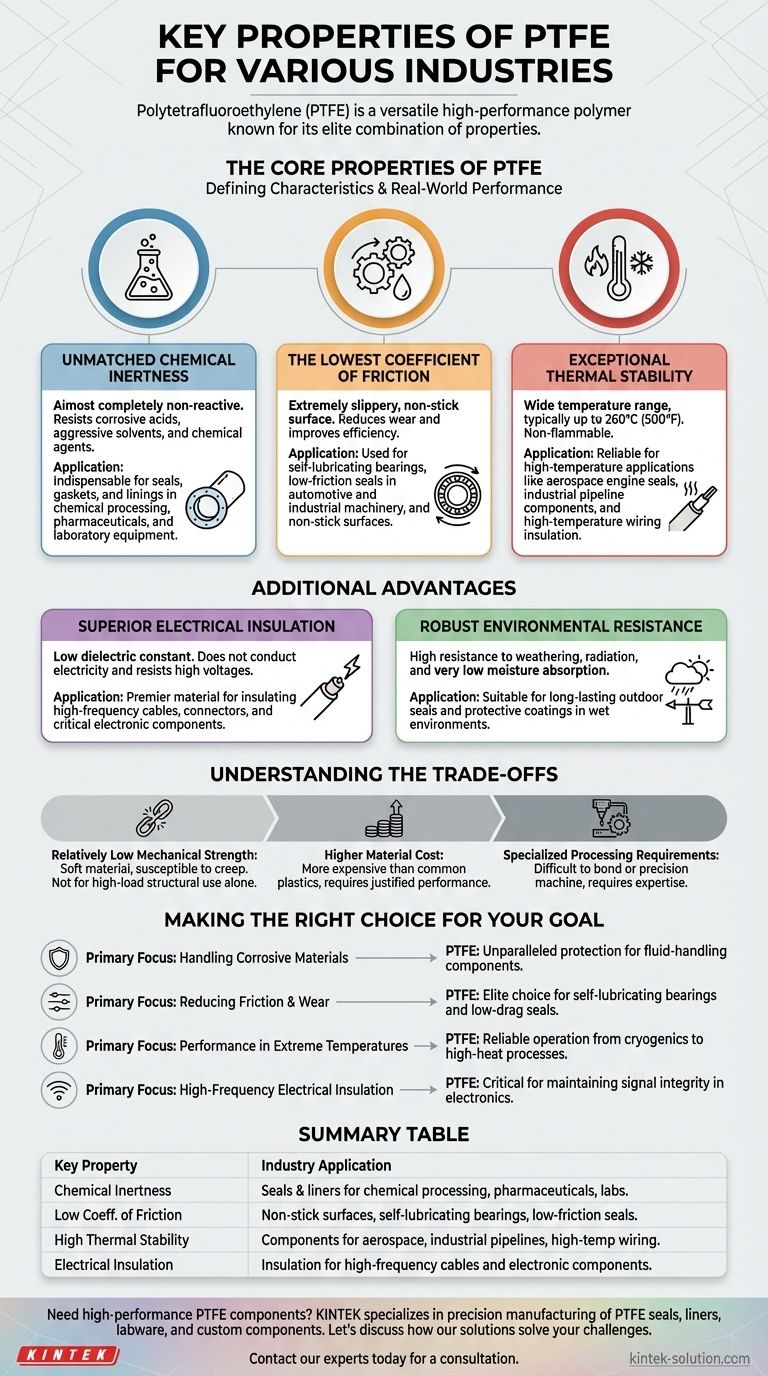
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most versatile high-performance polymers because of three defining characteristics. Its suitability across demanding industries stems from its extreme chemical inertness, an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, and its ability to remain stable across a wide range of temperatures.
While many materials excel in one area, PTFE's value comes from its unique combination of elite properties. It simultaneously resists harsh chemicals, provides a nearly frictionless surface, and withstands extreme temperatures where most other polymers would fail.

The Core Properties of PTFE Explained
To understand if PTFE is the right choice for your application, it's essential to look beyond the surface and see how each property translates into real-world performance.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is almost completely non-reactive. It does not react with the vast majority of corrosive acids, aggressive solvents, or other chemical agents.
This inertness makes it an indispensable material for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and laboratory equipment where material degradation is not an option.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This gives it an extremely slippery, non-stick surface.
This property is the reason it's used for everything from non-stick cookware to self-lubricating bearings and low-friction seals in automotive and industrial machinery, reducing wear and improving efficiency.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
This material maintains its integrity over an incredibly wide temperature range, typically up to 260°C (500°F). It is also non-flammable.
This makes it a reliable choice for high-temperature applications, such as seals in aerospace engines, insulation for high-temperature wiring, and components in industrial pipelines that experience significant thermal cycling.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE possesses excellent electrical properties, most notably a low dielectric constant. It does not conduct electricity and resists high voltages effectively.
This characteristic makes it a premier material for insulating high-frequency cables, connectors, and other critical electronic components where signal integrity and safety are paramount.
Robust Environmental Resistance
Beyond its core properties, PTFE exhibits high resistance to weathering and radiation, and has a very low moisture absorption rate.
This durability ensures it performs reliably in outdoor or wet environments without degrading, making it suitable for long-lasting seals and protective coatings.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. While PTFE's properties are exceptional, its limitations are a critical factor in the selection process.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. While it has high impact strength, it can be susceptible to creep (deformation under sustained load) and is not suitable for high-load structural applications on its own. Its moderate hardness, however, allows it to conform well to metal parts in sealing applications.
Higher Material Cost
As a high-performance fluoropolymer, PTFE is significantly more expensive than common plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its cost must be justified by the performance requirements of the application.
Specialized Processing Requirements
PTFE can be more difficult to process than other thermoplastics. Techniques like bonding it to other surfaces or precision machining require specialized knowledge and equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine if PTFE's unique profile is the correct fit.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive materials: PTFE's chemical inertness provides unparalleled protection for seals, linings, and fluid-handling components.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: PTFE is an elite choice for creating self-lubricating bearings, non-stick surfaces, and low-drag seals.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: PTFE's thermal stability ensures reliable operation in applications ranging from cryogenics to high-heat industrial processes.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: The low dielectric constant of PTFE is critical for maintaining signal integrity in advanced electronics and communications hardware.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a decision to prioritize extreme reliability and performance in environments where other materials would quickly degrade.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Industry Application |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Seals & liners for chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and labs. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Non-stick surfaces, self-lubricating bearings, and low-friction seals. |
| High Thermal Stability | Components for aerospace, industrial pipelines, and high-temperature wiring. |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Insulation for high-frequency cables and critical electronic components. |
Need high-performance PTFE components?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Our expertise ensures your products deliver maximum reliability in the most demanding environments—from semiconductor and medical equipment to industrial machinery.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your exact specifications. Let's discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your unique challenges.
Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















