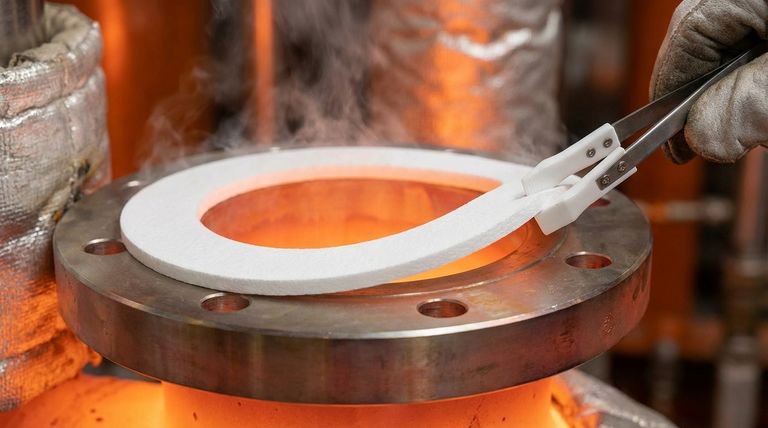
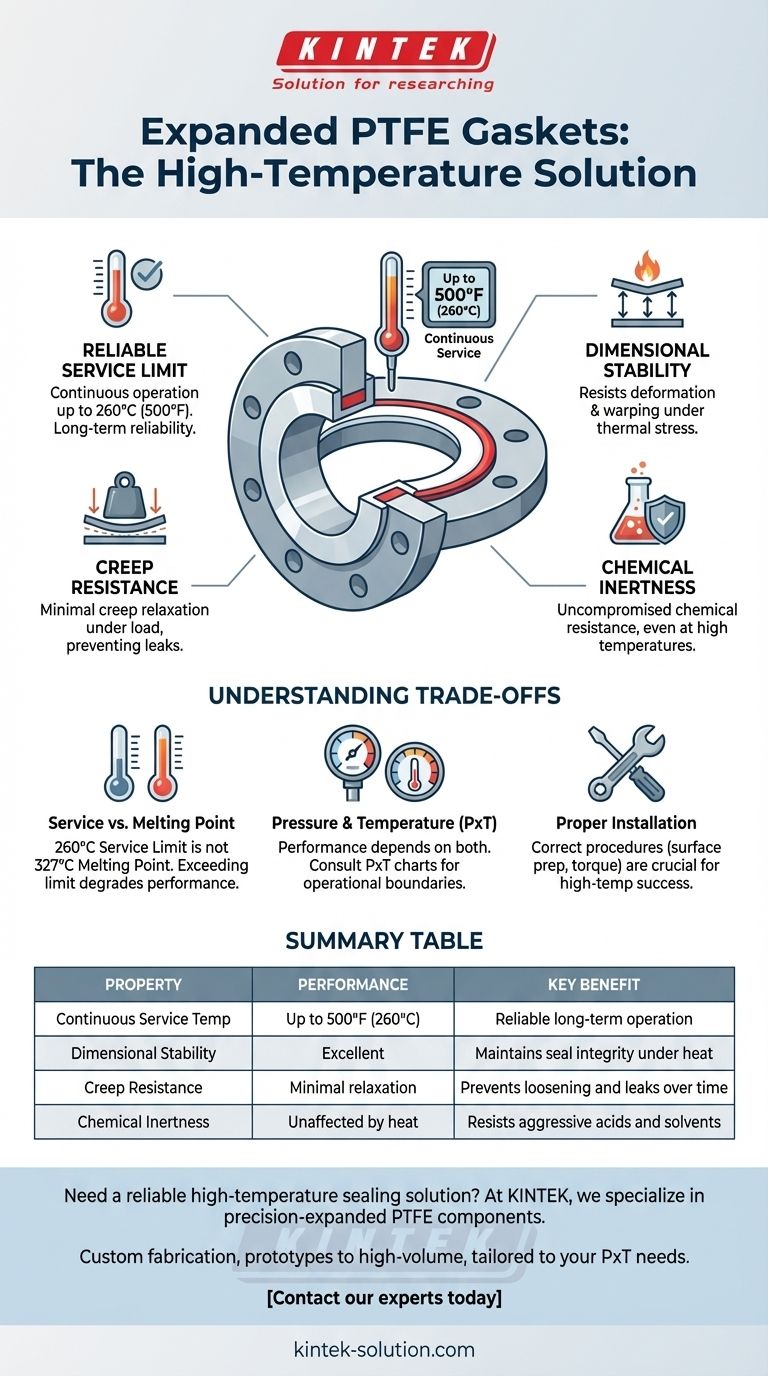
Yes, expanded PTFE gaskets are exceptionally well-suited for high-temperature applications. They reliably maintain their sealing integrity in continuous service up to 500°F (260°C). This thermal stability, combined with their chemical inertness and resistance to deformation, makes them a premier choice for demanding industrial environments.
While many materials can resist heat, expanded PTFE excels by maintaining its critical mechanical properties and dimensional stability under high temperatures, ensuring a reliable, long-term seal where other materials might fail.

What Defines PTFE's High-Temperature Performance?
Simply stating a temperature limit doesn't capture why expanded PTFE is so effective. Its performance is a combination of several key properties that work together under thermal stress.
The Reliable Service Limit
The widely accepted continuous service temperature for expanded PTFE is 260°C (500°F). While some specialized grades may tolerate brief excursions to higher temperatures (up to 315°C), using 260°C as the operational ceiling is the standard for ensuring long-term reliability and safety.
Maintaining Dimensional Stability
A key advantage of PTFE is its ability to withstand high temperatures without significant deformation. Unlike some metal or elastomeric components that can warp or lose their shape due to thermal expansion, PTFE maintains its structural integrity, which is critical for a consistent seal.
Resisting Creep and Cold Flow
Gaskets are under constant compressive load. At high temperatures, many materials will "creep" or "flow" away from this pressure, causing the connection to loosen and leak. Expanded PTFE is specifically engineered to have minimal creep relaxation, ensuring it maintains a tight seal over time, even under heat and pressure.
Uncompromised Chemical Inertness
PTFE's renowned chemical resistance is not diminished by heat. It remains inert to the most aggressive acids, solvents, and chemicals even when operating at its maximum temperature limit. This makes it invaluable in chemical processing and other corrosive environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To use expanded PTFE gaskets effectively, it's crucial to understand their operational boundaries and the factors that influence their performance.
Service Temperature vs. Melting Point
The service limit of 260°C is not PTFE's melting point, which is significantly higher at around 327°C. The service limit is the temperature at which the material's mechanical properties begin to degrade, impacting its ability to function as a reliable seal. Operating above this limit risks compromising the gasket's integrity long before it melts.
The Pressure and Temperature Link (PxT)
A gasket's performance is not defined by temperature alone. It is determined by a combination of Pressure (P) and Temperature (T). A gasket's ability to handle high temperatures is reduced as the system pressure increases. Always consult the manufacturer's PxT chart to ensure the gasket is suitable for your specific operating conditions.
The Importance of Proper Installation
High-temperature applications magnify the importance of correct installation procedures. Proper flange surface preparation, clean and lubricated bolts, and achieving the correct bolt torque are essential. An improperly installed gasket is far more likely to fail under the added stress of high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Based on this understanding, here is how to apply this knowledge to your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is continuous operation at high temperatures: Select a gasket with a manufacturer-rated continuous service temperature of at least 260°C (500°F) and verify its PxT value against your system's pressure.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals at elevated temperatures: Expanded PTFE is an ideal choice, as its chemical inertness and thermal stability provide a uniquely robust sealing solution.
- If your primary focus is thermal cycling from cryogenic to hot: PTFE’s exceptionally wide operating range (from -200°C to +260°C) makes it one of the few materials that can handle such extreme temperature swings without failing.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently specify expanded PTFE for applications where thermal resilience and unwavering reliability are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service Temp | Up to 500°F (260°C) | Reliable long-term operation |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent | Maintains seal integrity under heat |
| Creep Resistance | Minimal relaxation | Prevents loosening and leaks over time |
| Chemical Inertness | Unaffected by heat | Resists aggressive acids and solvents |
Need a high-temperature sealing solution that won't fail?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision-expanded PTFE components, including gaskets, seals, and liners, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our gaskets are engineered to deliver unmatched thermal stability and chemical resistance, ensuring your critical processes remain secure.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specific pressure and temperature requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a reliable PTFE sealing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does the fiber structure of ePTFE gaskets provide mechanical compensation? Sealing Imperfect Flanges
- How can PTFE lip seals be enhanced for extreme temperature performance? Optimize with Fillers & Design
- How is the bolt length determined for PTFE lined butterfly valves? Ensure a Safe, Leak-Proof Seal
- What are the key reasons to choose PTFE washers? Unmatched Performance in Demanding Environments
- What are the two common application methods for PTFE in slide bearings? A Guide to Linear and Rotational Movement
- How do PTFE O-Rings perform under high heat conditions? Achieve Extreme Temperature Sealing
- What factors should be considered when choosing a PTFE expansion joint? Ensure System Safety and Longevity
- Can a towel be used instead of a Teflon sheet for heat press? A High-Risk Shortcut Explained



















