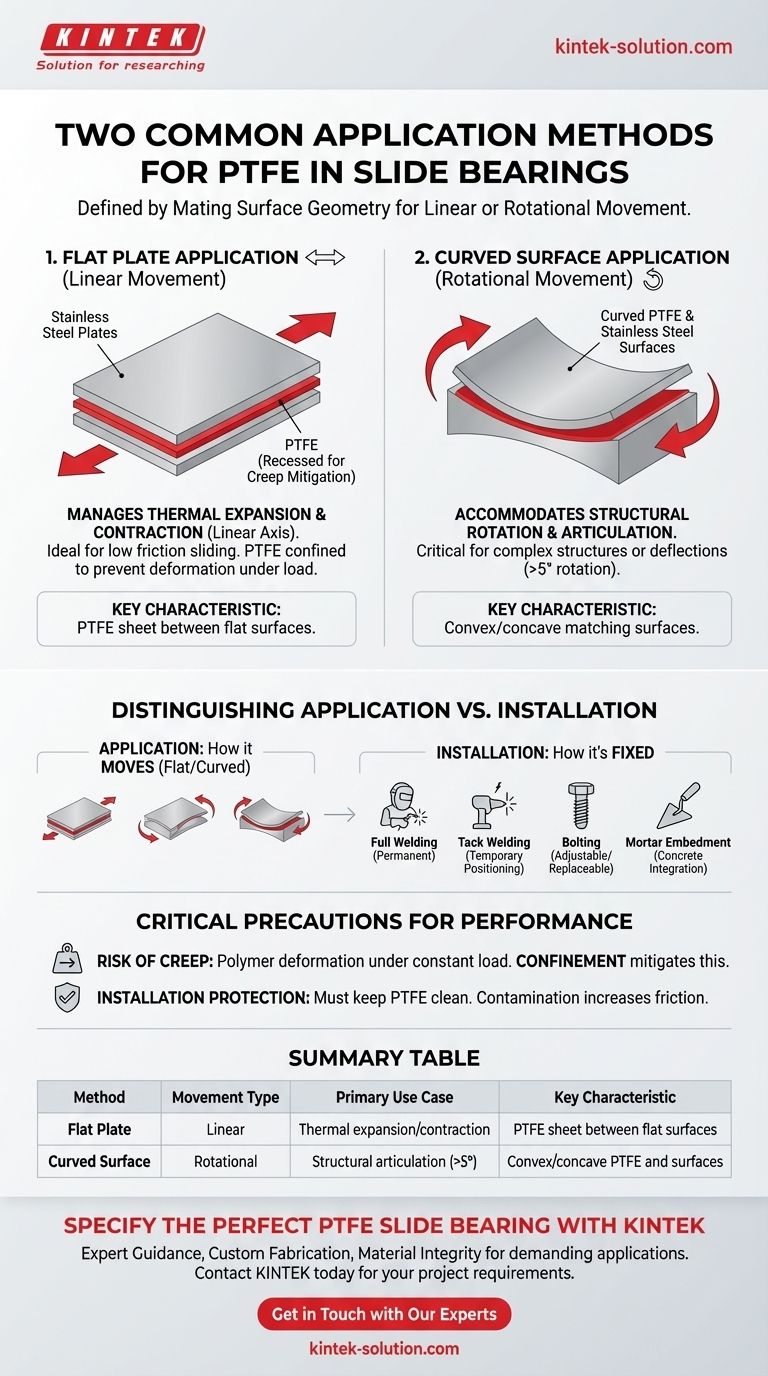
The two common application methods for PTFE in slide bearings are defined by the geometry of the mating surfaces. The first method uses PTFE between two flat stainless steel plates to allow for linear movement, while the second uses PTFE on curved stainless steel surfaces to accommodate structural rotation.
The fundamental choice between flat and curved PTFE applications is determined by the specific type of movement a structure must accommodate. Flat bearings manage linear expansion and contraction, while curved bearings are engineered to allow for rotational articulation.

The Two Core Application Methods Explained
The design of a PTFE slide bearing is dictated by the forces it must manage. The configuration of the PTFE itself is the primary factor in how the bearing will function under load.
Flat Plate Application (For Linear Movement)
This is the most common configuration for slide bearings. PTFE, often in a recessed or dimpled sheet, is placed between two flat steel plates, typically stainless steel.
This design is ideal for managing thermal expansion and contraction along a single axis. The flat surfaces slide past one another with minimal friction. To prevent the PTFE from deforming under sustained load—a phenomenon known as creep—it is often confined within a smaller surface area on the steel plate.
Curved Surface Application (For Rotational Movement)
When a structure needs to rotate or articulate in addition to sliding, a curved bearing is required. In this design, the PTFE and mating stainless steel plate have a matching convex and concave radius.
This geometry allows the bearing to accommodate rotations, which is critical in complex bridges or structures that may settle or deflect. This method is typically specified when rotational requirements are expected to exceed five degrees.
Distinguishing Application from Installation
It is crucial to differentiate between the PTFE application method (flat vs. curved) and the bearing installation method. The application defines how the bearing accommodates movement, while the installation defines how the entire bearing assembly is fixed to the structure.
Full Welding
This method creates a permanent, high-strength bond between the bearing's steel backing plates and the structure. It is used when no future adjustment is needed.
Tack Welding
Tack welding involves using smaller, intermittent welds. It can be used for positioning before full welding or in applications where a continuous weld is not required.
Bolting
Bolted connections allow for precise adjustment during installation and make future replacement of the bearing possible. This method is often chosen for its adjustability and serviceability.
Mortar Embedment
This technique is used to integrate the bearing directly into concrete structures. The backing plate is designed to be cast into the wet concrete or grouted into a prepared recess.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Precautions
While highly effective, PTFE bearings require careful consideration during design and installation to ensure their long-term performance and the integrity of the structure.
The Risk of Creep
PTFE is an incredibly low-friction material but is also a polymer that can slowly deform under a constant, heavy load. Confining the PTFE within a recessed area of the steel plate provides lateral support and significantly mitigates this risk.
Protection During Installation
The performance of a PTFE bearing depends entirely on its clean, low-friction surface. During installation, the PTFE surface must be protected from weld spatter, paint spray, construction debris, and metal swarf. Contamination can score the surface and dramatically increase the coefficient of friction.
Matching the Bearing to the Installation
The design of the bearing assembly must be compatible with the chosen installation method. A bearing designed for mortar embedment will have a different backing plate configuration than one designed to be bolted into place.
Making the Right Choice for Your Structure
Selecting the correct PTFE bearing configuration and installation method is essential for ensuring structural longevity and performance.
- If your primary focus is managing linear thermal expansion: A flat plate PTFE slide bearing is the standard and most effective choice.
- If your structure must accommodate both sliding and rotation: You must specify a curved surface PTFE bearing designed for the required degree of articulation.
- If you require a permanent bond with maximum structural integrity: Choose a bearing assembly designed for full welding.
- If your design prioritizes future serviceability or adjustment: A bolted bearing configuration provides the necessary flexibility.
Understanding these fundamental choices empowers you to specify a solution that precisely matches the intended structural behavior.
Summary Table:
| Application Method | Movement Type | Primary Use Case | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Plate | Linear | Thermal expansion/contraction | PTFE sheet between flat stainless steel plates |
| Curved Surface | Rotational | Structural articulation (>5°) | Convex/concave PTFE and stainless steel surfaces |
Specify the Perfect PTFE Slide Bearing for Your Project
Choosing the correct application and installation method is critical for the longevity and safety of your structure. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including slide bearings for demanding applications in bridge construction, heavy machinery, and industrial plants.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our engineers will help you select the ideal flat or curved bearing configuration.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we tailor PTFE seals, liners, and bearings to your exact specifications.
- Material Integrity: We ensure your PTFE surfaces are protected from contamination, guaranteeing low friction and long-term performance.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss your project requirements and receive a quote. Let our expertise in PTFE solutions ensure your structure moves as intended.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















