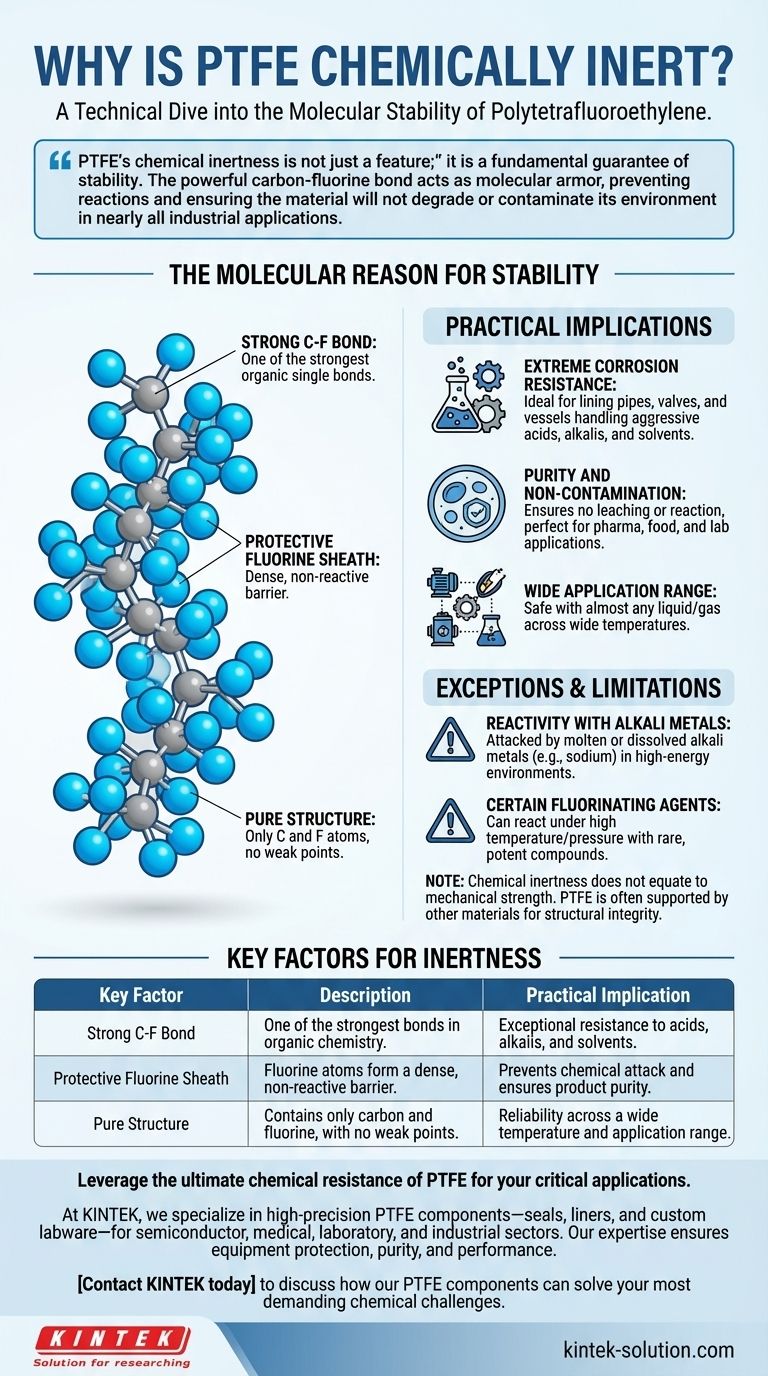
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is considered chemically inert because of the immense strength and stability of its molecular structure. The bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms are exceptionally powerful, creating a dense, non-reactive protective sheath around the molecule's carbon backbone. This molecular armor effectively prevents other chemicals from initiating a reaction.
PTFE's chemical inertness is not just a feature; it is a fundamental guarantee of stability. The powerful carbon-fluorine bond acts as molecular armor, preventing reactions and ensuring the material will not degrade or contaminate its environment in nearly all industrial applications.
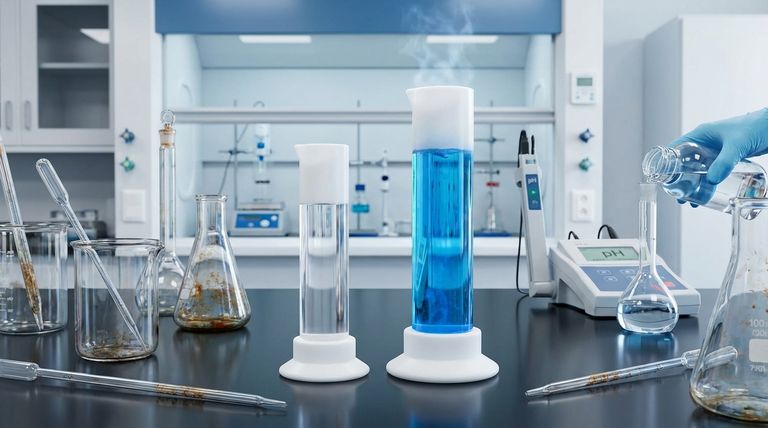

The Molecular Reason for PTFE's Stability
To understand why PTFE is so non-reactive, we must look at its chemical composition. The explanation lies in the unique relationship between carbon and fluorine atoms.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between a carbon atom and a fluorine atom is one of the strongest known single bonds in organic chemistry. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it holds onto its electrons with extreme force. This creates a very short, strong, and stable bond that is difficult for other chemicals to break apart.
The Fluorine Sheath
A PTFE molecule consists of a long chain of carbon atoms, each completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. These tightly packed fluorine atoms form a protective "sheath" around the vulnerable carbon backbone. This sheath is both non-polar and chemically stable, presenting a smooth, impenetrable surface that other molecules cannot easily attack.
A Pure and Simple Structure
The entire polymer is composed of only carbon and fluorine. There are no other, weaker atoms or molecular groups present that could serve as a potential reaction site. This uniform and pure structure leaves no weak points for corrosive acids, aggressive solvents, or reactive alkalis to target.
Practical Implications of Chemical Inertness
This molecular stability translates directly into tangible benefits across many demanding industries, making PTFE a critical material for modern engineering.
Extreme Corrosion Resistance
Because it does not react with most substances, PTFE is highly resistant to corrosion. It is an ideal choice for lining pipes, valves, and vessels that handle aggressive chemicals like strong acids, alkalis, and solvents without degrading over time.
Purity and Non-Contamination
In sensitive applications such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, laboratory work, or food processing, material purity is paramount. PTFE's inertness means it will not leach chemicals or react with the substances it contacts, ensuring the end product remains uncontaminated.
Wide Application Range
This non-reactivity allows PTFE to be used safely with almost any liquid or gas. Its stability, combined with its wide operating temperature range, makes it a reliable choice for everything from chemical processing equipment to high-performance electrical insulation.
Understanding the Exceptions and Limitations
While PTFE is practically inert, it is not absolutely inert under all conceivable conditions. An objective technical assessment requires acknowledging its few limitations.
Reactivity with Alkali Metals
In specific, high-energy environments, PTFE can be attacked by molten or dissolved alkali metals, such as sodium. These highly reactive metals are among the few substances capable of breaking the strong carbon-fluorine bond.
Certain Fluorinating Agents
Under conditions of high temperature and pressure, some rare and potent fluorinating compounds (like chlorine trifluoride) can also react with PTFE. These scenarios are highly specialized and not encountered in common industrial applications.
Physical and Mechanical Weakness
It is crucial to note that chemical inertness does not equate to mechanical strength. PTFE is a relatively soft material with poor resilience. In applications requiring structural integrity, it is often blended with other materials or supported by metal components, such as the springs in a spring-energized seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use PTFE should be based on its unique profile of extreme chemical resistance and its known physical properties.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE is one of the most reliable and non-reactive material choices available for gaskets, seals, and linings.
- If your primary focus is product purity (food, pharma, labs): Its inertness guarantees it will not contaminate the process medium, making it an exceptionally safe choice.
- If your application involves high-energy environments with molten alkali metals: You are operating in one of the few areas where PTFE is unsuitable, and a careful evaluation of alternative materials is necessary.
Understanding the source of PTFE's stability allows you to deploy it with confidence in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Description | Practical Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bond | One of the strongest bonds in organic chemistry. | Exceptional resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents. |
| Protective Fluorine Sheath | Fluorine atoms form a dense, non-reactive barrier. | Prevents chemical attack and ensures product purity. |
| Pure Structure | Contains only carbon and fluorine, with no weak points. | Reliability across a wide temperature and application range. |
Leverage the ultimate chemical resistance of PTFE for your critical applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment is protected from corrosion and contamination, guaranteeing purity and performance.
Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our custom fabrication services deliver the exact solution you require.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE components can solve your most demanding chemical challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications



















