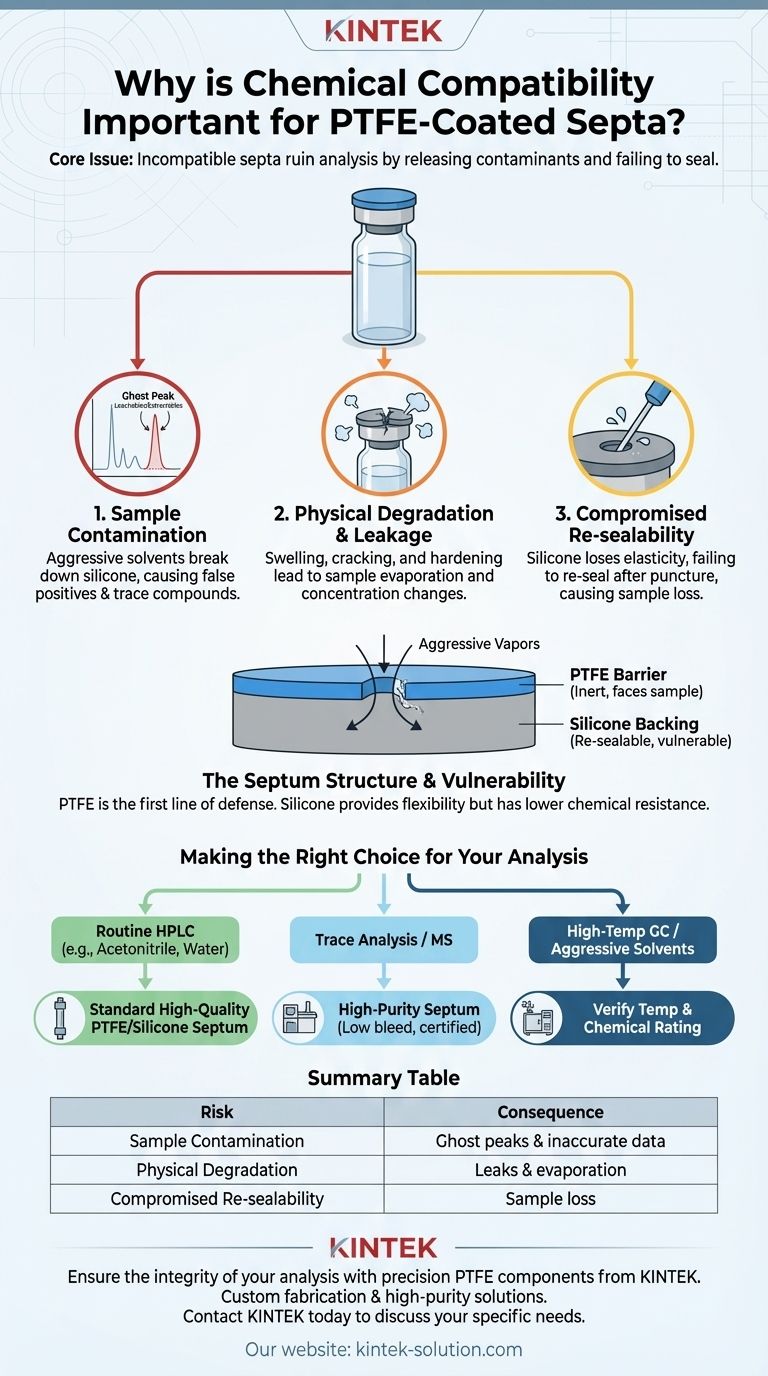
Ultimately, chemical compatibility is crucial because the wrong septum can actively ruin your analysis. An incompatible septum will degrade, release contaminants into your sample, and fail to maintain a proper seal, directly compromising the accuracy, reliability, and reproducibility of your results.
The core issue isn't just about the septum surviving; it's about protecting the integrity of your sample. A chemical mismatch can introduce new substances (extractables and leachables) into your vial, leading to inaccurate data and phantom peaks in your analysis.

The Core Risks of Chemical Incompatibility
Choosing a septum that is not compatible with your sample solvent or matrix introduces three primary risks, each of which can invalidate your work.
Risk 1: Sample Contamination
The most significant risk is the introduction of extractables and leachables. Aggressive solvents can break down the septum's silicone layer, causing trace compounds to leach into your sample.
These contaminants can appear as "ghost peaks" in a chromatogram, co-elute with your analyte of interest, or interfere with detection, leading to false positives or inaccurate quantification.
Risk 2: Physical Degradation and Leakage
A chemical attack can cause the septum to swell, harden, or crack. This compromises the physical integrity of the seal.
A failed seal leads to the evaporation of your solvent and the loss of volatile analytes. This changes the concentration of your sample over time, making accurate and reproducible measurements impossible.
Risk 3: Compromised Re-sealability
The primary function of a septum, particularly in autosamplers, is to re-seal perfectly after being punctured by a needle.
Chemical degradation of the underlying silicone layer destroys its elasticity. This prevents the puncture from closing completely, leading to the same evaporation and sample loss issues seen with a failed primary seal.
Why PTFE is the Standard (But Not Infallible)
A PTFE-coated septum is a two-part system, and understanding both parts is key to making an informed choice.
The Role of the PTFE Barrier
The thin PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) layer is the first line of defense. It is a highly inert material that faces the sample.
This coating provides excellent resistance to a wide range of common laboratory chemicals, including most acids, bases, and organic solvents.
The Vulnerable Silicone Backing
Beneath the PTFE is a much thicker layer of silicone. This material provides the critical physical properties of the septum: its flexibility and ability to re-seal after puncture.
Silicone itself has much lower chemical resistance. If the PTFE barrier is compromised or if aggressive vapors penetrate it over time, the silicone will degrade, leading to the failures described above.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply choosing a "PTFE septum" is not enough. The context of your analysis dictates which specific product is appropriate.
High-Sensitivity vs. General Use
For ultra-sensitive analyses like mass spectrometry, even minuscule levels of leachables can interfere with results. In these cases, you need a high-purity septum specifically certified for low extractables.
For less sensitive applications, a general-purpose PTFE/Silicone septum is often sufficient and more cost-effective.
Temperature Stability is Linked to Chemical Attack
High temperatures, such as those in a gas chromatography (GC) inlet, dramatically accelerate chemical reactions.
A septum must be rated to withstand your instrument's temperature and be compatible with your chemical matrix. High heat can cause an otherwise stable septum to degrade and release contaminants when exposed to certain solvents.
Manufacturer Quality Matters
Reputable manufacturers provide quality assurance and often offer certificates verifying the purity and performance of their septa. Investing in a quality product from a trusted supplier is a critical step in ensuring reliable and reproducible data, preventing the need for costly troubleshooting and re-runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Your analytical goal should always guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is routine HPLC with common solvents (e.g., Acetonitrile, Methanol, Water): A standard, high-quality PTFE/Silicone septum is a reliable and safe choice.
- If your primary focus is trace analysis or mass spectrometry: You must select a high-purity septum specifically bonded and certified for low bleed and minimal extractables.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature GC or work with aggressive solvents (e.g., Chlorinated Solvents): Verify both the temperature rating and chemical compatibility to prevent degradation in the GC inlet.
Ensuring chemical compatibility is a foundational step for generating data you can trust.
Summary Table:
| Risk | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Sample Contamination | Leachables cause ghost peaks & inaccurate data |
| Physical Degradation | Swelling/cracking leads to leaks & evaporation |
| Compromised Re-sealability | Puncture won't close, causing sample loss |
Ensure the integrity of your analysis with precision PTFE components from KINTEK.
Choosing the right septum is critical for reliable results in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-purity PTFE seals, liners, and labware designed for superior chemical compatibility and performance.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get the exact component your process requires. Don't let a faulty septum compromise your data.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and request a quote for PTFE components you can trust.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- In which industries are PTFE lined caps commonly used? Ensure Product Purity & Chemical Resistance
- What are the primary uses of PTFE stirrers? For Chemically Aggressive & High-Purity Mixing
- How does the non-stick surface of PTFE shovels benefit laboratory work? Enhance Accuracy & Efficiency
- Why are PTFE shovels considered cost-effective? Maximize ROI with Superior Durability
- What are the applications of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Ultimate Purity and Chemical Resistance
- What types of solvents and reagents are PTFE vials compatible with? Ensure Purity in Your HPLC/GC Analysis
- What are the advantages of PTFE lids for jacketed and process vessels? Achieve Superior Durability & Chemical Resistance
- Why is consistent performance important in chromatography vials? Ensure Data Integrity and Reproducibility



















