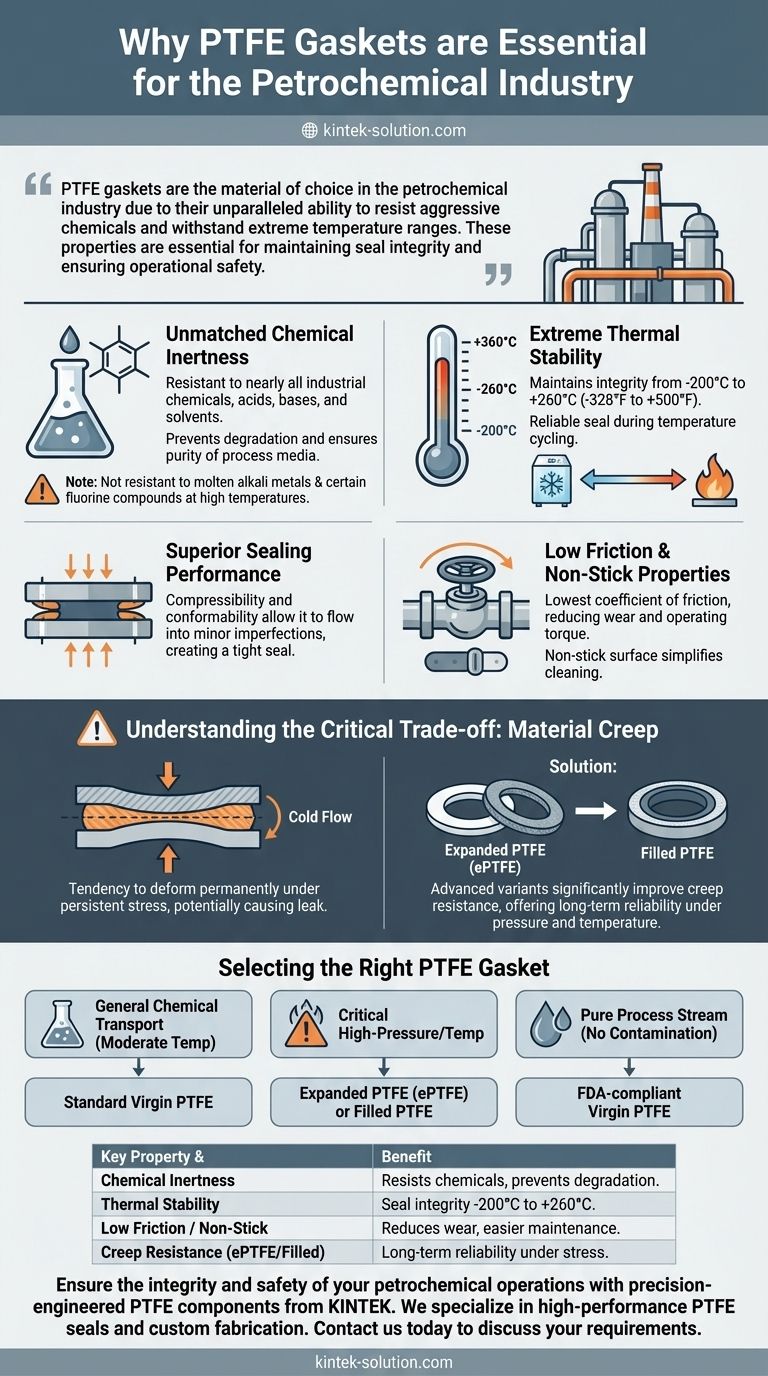
In short, PTFE gaskets are the material of choice in the petrochemical industry due to their unparalleled ability to resist aggressive chemicals and withstand extreme temperature ranges. These properties are essential for maintaining seal integrity and ensuring operational safety in the demanding environments of refineries and processing facilities.
The core challenge in petrochemical applications is finding a sealing material that won't degrade when exposed to corrosive fluids or fail under thermal stress. PTFE's unique molecular structure makes it almost completely inert and thermally stable, providing a reliable and durable seal where most other materials would quickly fail.

Why PTFE is Essential for Petrochemical Sealing
The suitability of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not based on a single characteristic, but on a combination of properties that make it uniquely equipped for the hazards of the petrochemical industry.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, solvents, and hydraulic fluids. This chemical stability prevents the gasket from swelling, dissolving, or degrading over time.
This inertness is critical for preventing leaks and ensuring the purity of the process media. The only notable exceptions are molten alkali metals and certain fluorine compounds at high temperatures.
Extreme Thermal Stability
Petrochemical processes can operate at a wide spectrum of temperatures, from cryogenic lows to high-heat reactions.
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing capability across a vast temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). This stability ensures a reliable seal during temperature cycling and process upsets.
Superior Sealing Performance
A gasket's primary function is to create and maintain a seal between two surfaces. PTFE's properties of compressibility and conformability allow it to flow into the minor imperfections of flange surfaces, creating an exceptionally tight seal.
This ensures that volatile or hazardous fluids are safely contained within pipelines, valves, and vessels.
Low Friction and Non-Stick Properties
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This is highly beneficial in applications with rotating or moving parts, such as certain valve designs, as it reduces wear and operating torque.
Its non-stick surface also prevents process media from adhering to the gasket, which simplifies cleaning and maintenance during shutdowns.
Understanding the Critical Trade-off: Material Creep
While PTFE's benefits are significant, it has one primary limitation that every engineer must account for: a tendency to creep, also known as "cold flow."
The Phenomenon of Cold Flow
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. For a gasket, this means it can slowly be squeezed out from between the flanges over time.
The Risk of Lost Bolt Load
As the gasket material creeps, the pressure it exerts back on the flange faces diminishes. This results in a loss of the initial bolt torque, which can compromise the integrity of the seal and eventually lead to a leak.
Mitigation with Advanced PTFE Variants
To counter this, material science has produced enhanced versions of PTFE. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) and filled PTFE (which incorporates materials like glass, carbon, or silica) are engineered to significantly improve creep resistance.
These advanced gaskets offer the chemical and thermal benefits of virgin PTFE while providing a more stable and reliable long-term seal, especially in high-pressure or high-temperature services.
Selecting the Right PTFE Gasket for Your Application
Choosing the correct gasket type is crucial for maximizing safety and performance. Your selection should be driven by the specific demands of the service.
- If your primary focus is general chemical transport at moderate temperatures: Standard, virgin PTFE offers a reliable and cost-effective sealing solution.
- If your primary focus is sealing critical high-pressure or high-temperature flanges: Prioritize expanded PTFE (ePTFE) or a filled PTFE gasket to minimize the risk of creep and subsequent leaks.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination in a pure process stream: Use FDA-compliant virgin PTFE, as filled variants could potentially leach their filler material.
Ultimately, understanding these distinct material properties is the key to ensuring both the safety and efficiency of critical petrochemical operations.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Petrochemical Industry |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all acids, bases, and solvents, preventing degradation and leaks. |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains seal integrity from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | Reduces wear on moving parts and prevents media adhesion for easier maintenance. |
| Creep Resistance (ePTFE/Filled) | Enhanced variants like ePTFE provide long-term sealing reliability under stress. |
Ensure the integrity and safety of your petrochemical operations with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
We specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, gaskets, liners, and labware for the demanding environments of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a sealing solution tailored to your specific chemical, temperature, and pressure requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE components can enhance the safety and efficiency of your critical processes. Get a Quote & Technical Support
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions



















