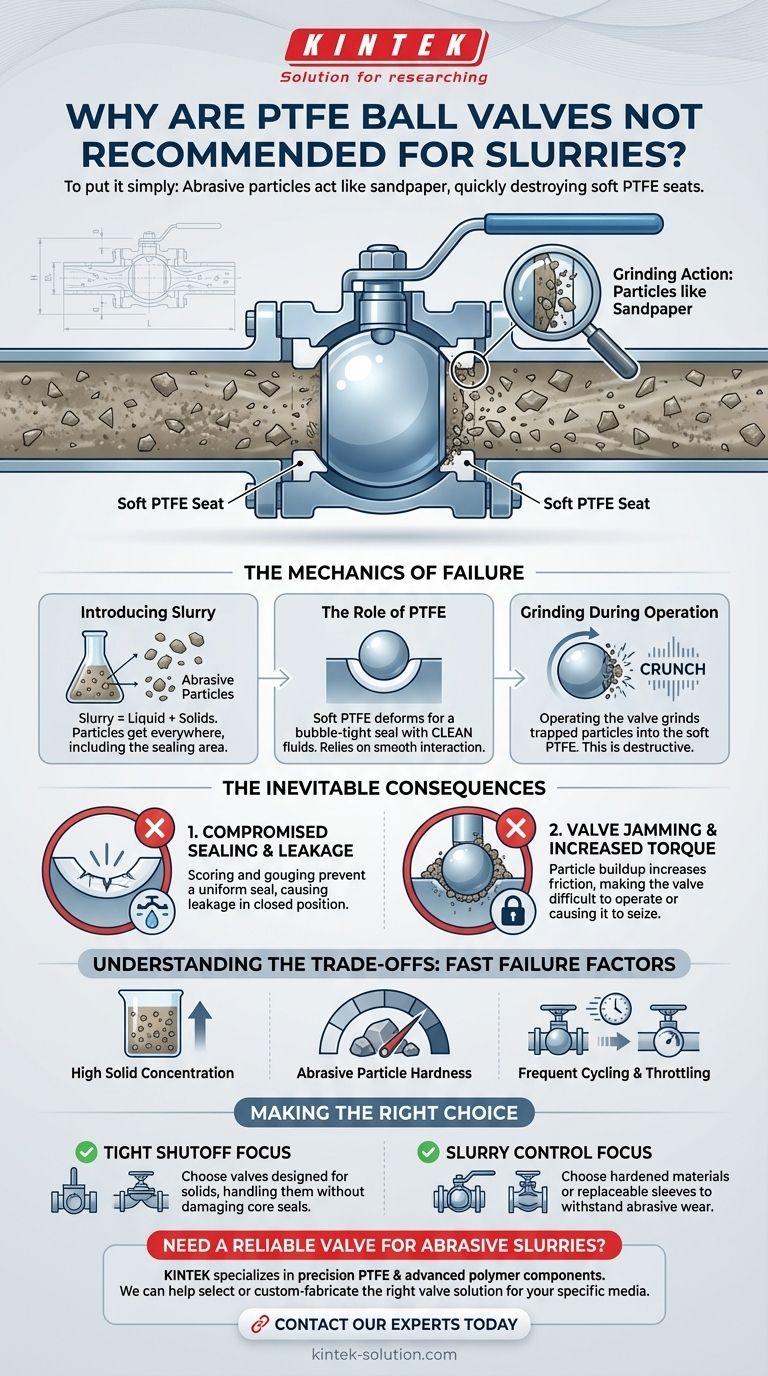
To put it simply, PTFE ball valves are not recommended for slurries because the solid particles within the slurry act like sandpaper against the soft PTFE seats. This abrasive action quickly damages the seals, leading to valve leakage, jamming, and eventual failure.
The core issue is a mismatch of materials and mechanics. A ball valve's greatest strength—creating a perfect seal with a soft seat—becomes its critical weakness when abrasive solids are introduced, grinding away the very component responsible for its performance.
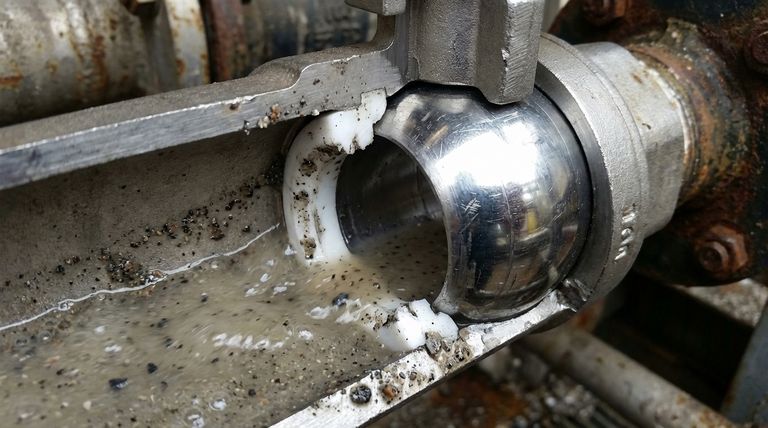

The Mechanics of Failure: Why Slurries Destroy PTFE Seats
A standard ball valve is designed for clean liquids and gases. Its effectiveness hinges on a precise interaction between a smooth, hard ball and two soft, pliable seats, typically made of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This design is what creates a bubble-tight shutoff. The introduction of a slurry fundamentally breaks this system.
The Role of the Soft PTFE Seat
The PTFE seat's job is to deform slightly as the ball rotates into the closed position. This creates a complete, positive seal that prevents fluid from passing through. This design relies on the media being a clean fluid that won't physically damage the seat surface.
Introducing Abrasive Particles
A slurry is a mixture of a liquid and suspended solid particles. These particles can be anything from fine sand and mineral fragments to larger, irregular solids. When this mixture flows through the valve, these particles get everywhere, including the critical sealing area between the ball and the seats.
The Grinding Action During Operation
When you operate the valve (either opening or closing it), the sharp edge of the ball's bore rotates directly across the face of the PTFE seat. If slurry particles are trapped between these two surfaces, they are ground into the soft PTFE. This action is incredibly destructive.
The Inevitable Consequences
The repeated grinding of solids into the PTFE seats does not just cause minor wear; it leads to distinct and predictable failure modes that render the valve useless for its intended purpose.
Compromised Sealing and Leakage
The most immediate result of this abrasive action is scoring and gouging on the surface of the PTFE seat. Once this smooth surface is damaged, it can no longer create a uniform, positive seal against the ball. The valve will begin to leak when in the closed position, failing its primary function.
Valve Jamming and Increased Torque
Solid particles can become embedded in the soft PTFE seats or build up in the tight tolerance areas between the ball and the valve body. This buildup dramatically increases the friction when trying to rotate the ball. The valve becomes difficult to operate, and in severe cases, it will jam or "seize" completely.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Failure is Fastest
Not all slurry applications are equal, but PTFE ball valves are a poor choice for nearly all of them. The speed of failure is directly related to the nature of the slurry and the valve's operation.
High Solid Concentration
A higher concentration of solids in the liquid means more abrasive particles are present to damage the seats with every cycle of the valve.
Abrasive Particle Hardness
Hard, sharp particles like silica sand or metallic fines will destroy a PTFE seat much faster than softer solids, such as in a food-grade slurry. The harder the particle, the more effective it is at grinding away the seat material.
Frequent Cycling or Throttling
A valve that is cycled frequently will fail much faster than one that is rarely operated. Worse yet is using a ball valve to "throttle" (partially open) a slurry flow, as this creates a high-velocity jet that directs particles directly into the sealing area, accelerating erosion catastrophically.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To handle slurries effectively, you must select a valve specifically designed to keep abrasive materials away from its sealing components or one that uses materials robust enough to withstand them.
- If your primary focus is tight shutoff in an abrasive slurry: Choose a valve like a knife gate or a diaphragm valve, which are designed to handle solids without damaging their core sealing mechanisms.
- If your primary focus is slurry control without perfect shutoff: Consider a metal-seated ball valve or a pinch valve, which use hardened materials or replaceable sleeves designed for abrasive wear.
Ultimately, choosing the right valve means matching its fundamental design to the physical reality of the media it will control.
Summary Table:
| Key Issue | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Abrasive Particles in Slurry | Grind and score soft PTFE seats |
| Compromised Seal | Leakage when valve is closed |
| Particle Build-up | Increased torque, potential jamming |
| Frequent Valve Cycling | Accelerated wear and failure |
Need a reliable valve for abrasive slurries? Don't let valve failure disrupt your process. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE and other advanced polymer components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We can help you select or custom-fabricate the right valve solution for your specific abrasive media, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and prevent costly downtime!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- In which industries are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Key Applications & Benefits
- How do the chemical properties of PTFE balls influence their performance? Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments
- How do PTFE balls contribute to reduced maintenance costs? Extend Component Life and Cut Downtime
- What are the key chemical properties of PTFE balls? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What factors determine the different grades of PTFE balls available? Select the Right Grade for Your Application



















