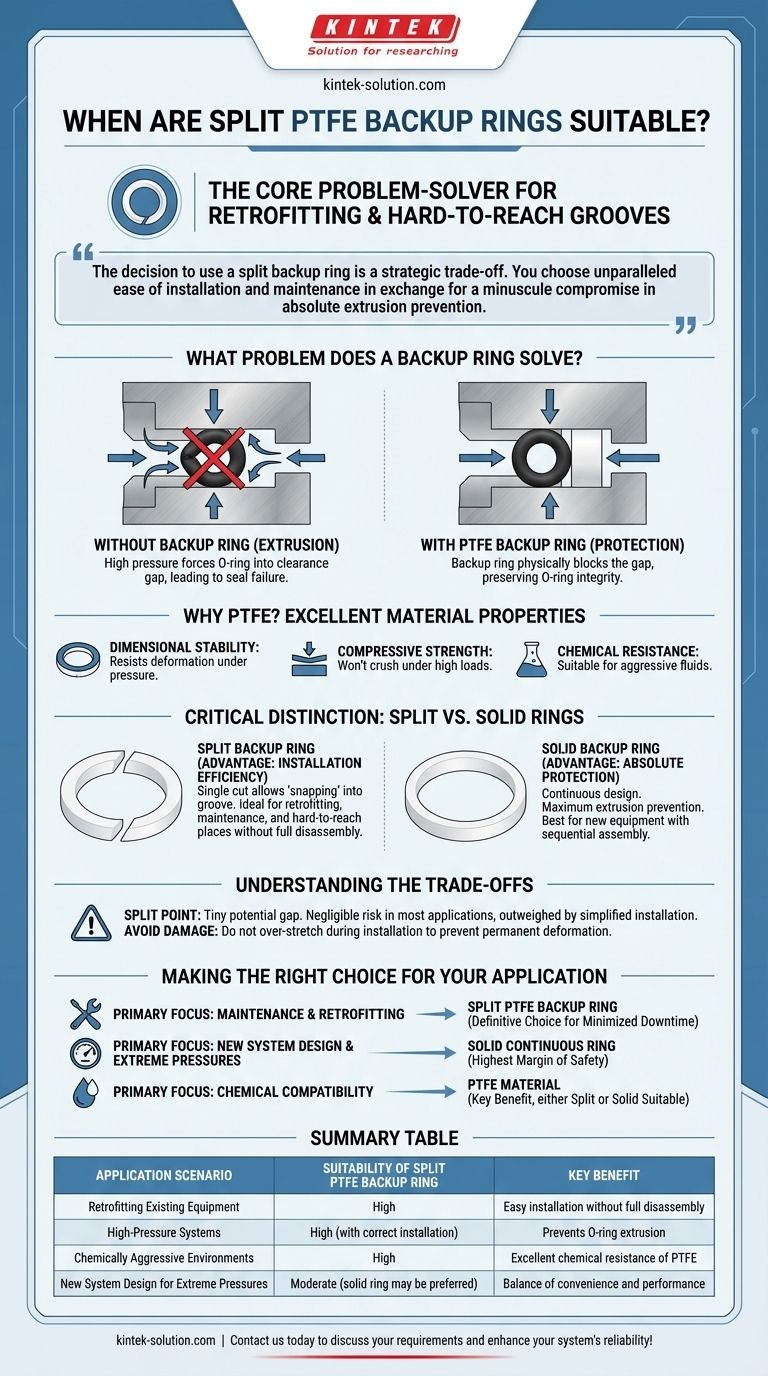
At its core, a split PTFE backup ring is a problem-solver for specific mechanical situations. Its suitability is defined less by the material itself and more by its "split" design, which makes it ideal for retrofitting existing systems or installing in hard-to-reach grooves where a solid ring would be impractical.
The decision to use a split backup ring is a strategic trade-off. You are choosing unparalleled ease of installation and maintenance, especially in existing equipment, in exchange for a minuscule compromise in absolute extrusion prevention compared to a solid ring.

What Problem Does a Backup Ring Solve?
Backup rings are a critical component in high-pressure sealing systems. They serve a single, vital purpose: protecting the primary seal, typically an O-ring, from damage.
Preventing O-Ring Extrusion
Under high pressure, a soft elastomeric O-ring can be forced into the small clearance gap between mating metal parts. This process, known as extrusion, quickly damages the O-ring, leading to seal failure.
A backup ring is a rigid, strong ring installed next to the O-ring. It physically blocks the clearance gap, providing a robust barrier that the O-ring cannot be forced into, thereby preserving its integrity and lifespan.
Why PTFE is an Excellent Material
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a premier material for this task. It is inherently dimensionally stable and possesses excellent compressive strength, meaning it won't deform or crush under the high pressures it's designed to withstand.
Furthermore, its exceptional chemical resistance makes it suitable for use in systems with aggressive fluids or gases, ensuring it doesn't degrade in harsh operational environments.
The Critical Distinction: Split vs. Solid Rings
The primary decision point is not just the material (PTFE), but the physical form of the ring.
The Advantage of Split Rings: Installation Efficiency
A split backup ring has a single cut through its circumference. This simple feature is its greatest strength.
This design allows the ring to be slightly twisted and opened, enabling it to be "snapped" directly into a seal groove. This is invaluable for retrofitting or maintenance, as it eliminates the need to completely disassemble a component to slide a ring down a long shaft.
The Case for Solid Rings
A solid, or continuous, backup ring has no cut. It provides the absolute maximum protection against extrusion because there is no potential gap for the O-ring to find.
However, its installation requires sliding it over the end of a shaft or into a bore, making it best suited for new equipment manufacturing where components are assembled sequentially.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a split ring is an engineering decision that balances convenience against ultimate performance.
Acknowledging the Split Point
The cut in a split ring creates a theoretical point of weakness. In ultra-high-pressure applications, this tiny gap could potentially become a path for O-ring extrusion if not installed correctly.
For the vast majority of applications, this risk is negligible and is far outweighed by the benefits of simplified installation and maintenance.
Avoiding Installation Damage
While easier to install, care must be taken. The ring should be gently expanded just enough to fit over the shaft and into the groove. Over-stretching a split PTFE ring can permanently deform it, compromising its effectiveness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct backup ring is about aligning the component's features with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and retrofitting: A split PTFE backup ring is the definitive choice to minimize system downtime and labor costs.
- If your primary focus is new system design for extreme pressures: A solid, continuous ring offers the highest margin of safety against extrusion and should be your default consideration.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility: The PTFE material itself is the key benefit, making either a split or solid ring a suitable choice based on your assembly and pressure requirements.
Ultimately, understanding the context of your application allows you to select the component that provides the most effective and efficient solution.
Summary Table:
| Application Scenario | Suitability of Split PTFE Backup Ring | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Retrofitting Existing Equipment | High | Easy installation without full disassembly |
| High-Pressure Systems | High (with correct installation) | Prevents O-ring extrusion |
| Chemically Aggressive Environments | High | Excellent chemical resistance of PTFE |
| New System Design for Extreme Pressures | Moderate (solid ring may be preferred) | Balance of convenience and performance |
Need a reliable split PTFE backup ring for your sealing system? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom backup rings, seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, we ensure dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and compressive strength for demanding applications. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your system's reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions



















