At its core, PTFE liner thrives in challenging environments due to a unique combination of extreme thermal stability and near-universal chemical inertness. Its molecular structure allows it to withstand temperatures that would degrade most plastics while remaining unaffected by nearly all common solvents and corrosive agents.
The suitability of PTFE liner isn't just about surviving harsh conditions; it's about maintaining consistent, reliable performance. Its ability to resist both high heat and chemical attack ensures operational integrity in critical applications where failure is not an option.

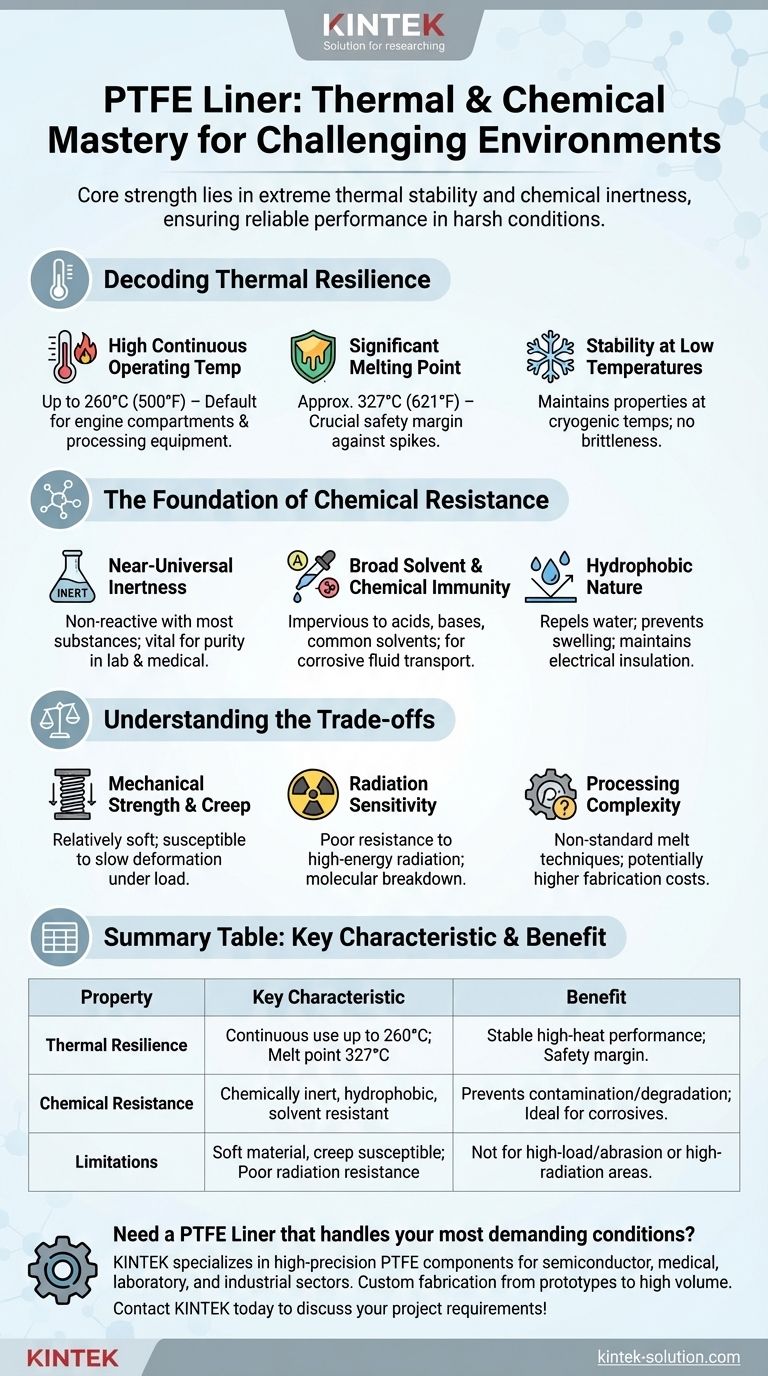
Decoding PTFE's Thermal Resilience
The defining characteristic of PTFE is its ability to perform across an exceptionally wide temperature range without losing its essential properties. This stability is fundamental to its use in demanding thermal environments.
High Continuous Operating Temperature
PTFE can operate continuously at high temperatures, typically up to 260°C (500°F). This makes it a default material for applications inside hot environments like engine compartments or industrial processing equipment.
Significant Melting Point
The material has a very high melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F). This provides a crucial safety margin, ensuring the liner maintains its structural integrity even during unexpected temperature spikes well above its normal operating range.
Stability at Low Temperatures
PTFE's thermal performance extends to extreme cold. It maintains its properties and does not become brittle at cryogenic temperatures, making it a versatile choice for applications that cycle between temperature extremes.
The Foundation of Chemical Resistance
PTFE's reputation for chemical resistance comes from its molecular composition, which features strong carbon-fluorine bonds. This structure makes it one of the most non-reactive materials known.
Near-Universal Inertness
PTFE is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of substances. This property is critical in laboratory settings or medical devices where material purity and non-contamination are paramount.
Broad Solvent and Chemical Immunity
It is impervious to almost all common chemical solvents, acids, and bases. This allows it to be used reliably for transporting or containing highly corrosive fluids in industrial pipelines and chemical processing.
Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not absorb moisture. This prevents swelling or degradation due to moisture exposure and helps maintain its excellent electrical insulating properties over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal and chemical properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the ideal solution for every engineering problem. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Strength and Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is not designed for high-load, high-abrasion applications and can be susceptible to "creep"—a slow deformation under sustained mechanical stress.
Radiation Sensitivity
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, which can cause its molecular structure to break down. It is generally not suitable for applications in high-radiation environments.
Processing Complexity
Unlike many common thermoplastics, standard PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt techniques. This can lead to higher fabrication costs and limitations on the complexity of parts that can be produced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material requires balancing its strengths against the specific demands of the environment.
- If your primary focus is heat and chemical exposure: PTFE is one of the most robust and reliable materials available, offering unmatched performance in corrosive, high-temperature systems.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load or abrasion resistance: You must carefully evaluate whether PTFE's durability is sufficient, or if a reinforced grade or an alternative high-performance polymer is necessary.
- If your primary focus is a balance of cost and performance: PTFE is a premium material; ensure its high-performance characteristics are truly required to justify the investment over other materials.
Ultimately, understanding these core properties empowers you to deploy PTFE with confidence in the applications where it truly excels.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resilience | Continuous use up to 260°C (500°F); Melting point of 327°C (621°F) | Stable performance in high-heat environments; Safety margin against temperature spikes |
| Chemical Resistance | Chemically inert; Resistant to solvents, acids, and bases; Hydrophobic | Prevents contamination and degradation; Ideal for corrosive fluids and lab settings |
| Limitations | Soft material susceptible to creep; Poor radiation resistance | Not for high-load/abrasion applications; Unsuitable for high-radiation environments |
Need a PTFE Liner that can handle your most demanding conditions?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components deliver reliable performance under extreme thermal and chemical stress.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailoring the solution to your specific environmental challenges.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and leverage our material expertise!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















