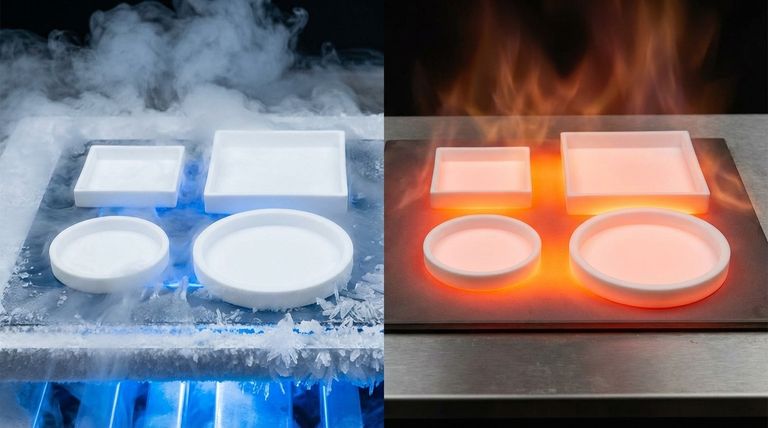
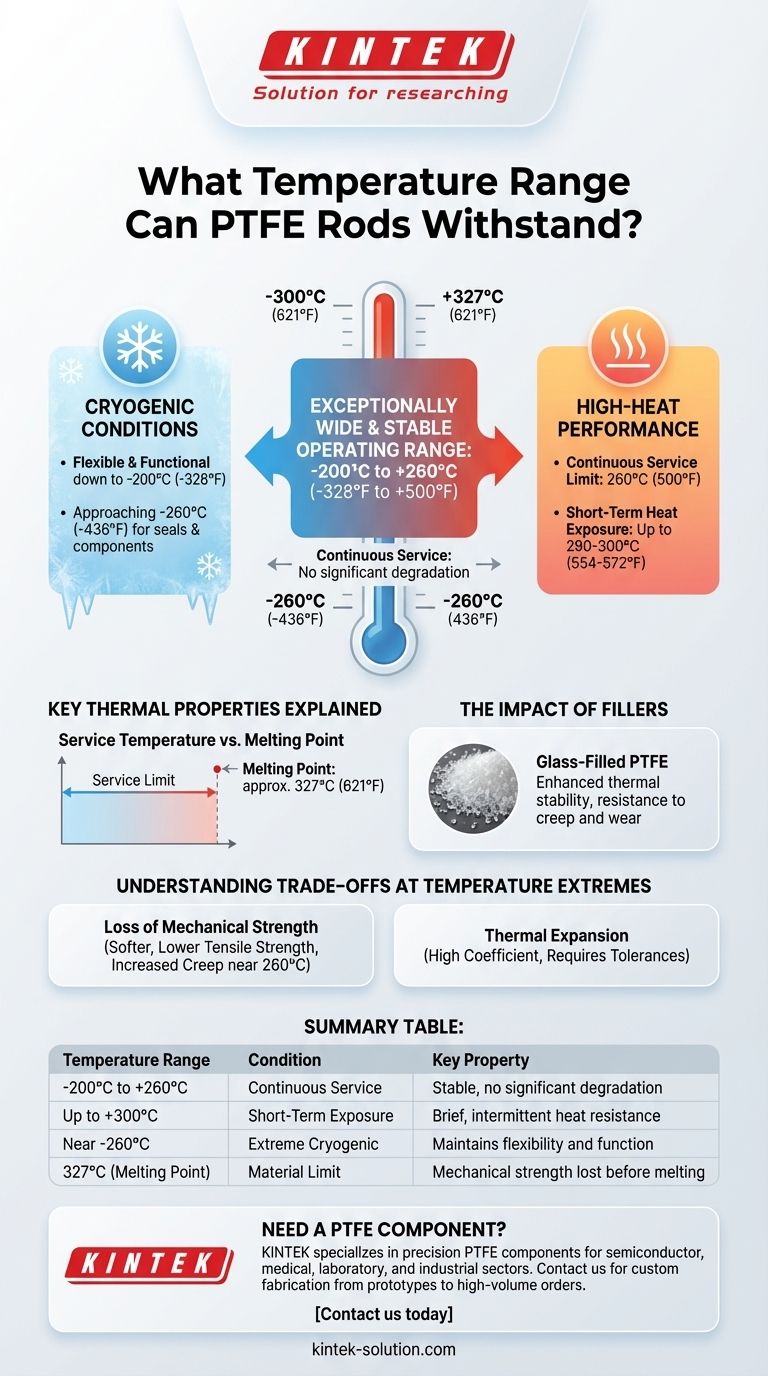
In short, PTFE rods have an exceptionally wide and stable operating temperature range. They can be used continuously in environments from as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to a high of +260°C (500°F) without significant degradation of their core properties.
The true value of PTFE is not just its high-temperature resistance but its remarkable versatility. It maintains its integrity and performance across an enormous thermal spectrum, from deep cryogenic applications to sustained high-heat industrial processes, a range that most other polymers cannot match.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Performance
To properly select a material, it is critical to understand the difference between various temperature ratings. These figures define the practical limits for safe and reliable operation.
The Continuous Service Temperature
The most important figure for any application is the continuous service temperature, which for standard PTFE is 260°C (500°F). This is the maximum temperature at which the material can operate for extended periods without compromising its chemical and mechanical properties.
Short-Term Heat Exposure
For brief, intermittent periods, PTFE can withstand even higher temperatures. Some data suggests it can handle exposure up to 290-300°C (554-572°F), but this should not be considered a normal operating condition.
Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
PTFE's performance at low temperatures is just as impressive. It remains flexible and functional down to -200°C (-328°F), with some sources citing usability at even lower temperatures approaching -260°C (-436°F). This makes it a preferred choice for cryogenic seals and components.
Key Thermal Properties Explained
Beyond a simple temperature range, two other concepts are crucial for understanding how PTFE behaves under thermal stress: its melting point and the effect of reinforcement.
Service Temperature vs. Melting Point
It is vital not to confuse the service temperature with the melting point. PTFE’s melting point is approximately 327°C (621°F). However, the material begins to lose its mechanical strength and stiffness well before it melts. The service temperature of 260°C is the practical limit for maintaining structural integrity under load.
The Impact of Fillers (e.g., Glass)
Standard "virgin" PTFE can be enhanced by adding reinforcing fillers. For example, glass-filled PTFE rods exhibit even higher thermal stability and improved resistance to creep and wear at elevated temperatures. These composites push the performance envelope for more demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs at Temperature Extremes
While PTFE's performance is impressive, engineers must account for how its properties change at the edges of its operating range.
Loss of Mechanical Strength
As PTFE approaches its upper service temperature limit of 260°C, it becomes softer. Its tensile strength and resistance to deformation (creep) decrease, which must be factored into the design of any load-bearing components.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals. This means it will expand and contract significantly with temperature changes. This must be accounted for in assemblies with tight tolerances to avoid binding or stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE is the correct material for your specific thermal requirements.
- If your primary focus is continuous high-heat industrial use: Standard PTFE is an excellent choice for applications that consistently operate at or below 260°C (500°F).
- If your primary focus is cryogenic systems: PTFE's outstanding flexibility and stability at temperatures down to -200°C (-328°F) make it a reliable material for seals and insulators.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat resistance and rigidity: Consider a glass-filled or other reinforced grade of PTFE for improved strength and dimensional stability near the upper temperature limit.
Ultimately, PTFE's predictable performance across its vast temperature range makes it one of the most reliable engineering plastics available.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Condition | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to +260°C | Continuous Service | Stable performance, no significant degradation |
| Up to +300°C | Short-Term Exposure | Brief, intermittent heat resistance |
| Near -260°C | Extreme Cryogenic | Maintains flexibility and function |
| 327°C (Melting Point) | Material Limit | Mechanical strength lost before melting |
Need a PTFE component that performs reliably in extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require standard PTFE for cryogenic applications or glass-filled grades for enhanced high-temperature stability, we deliver custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in PTFE can solve your thermal challenges and ensure the integrity of your critical applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















