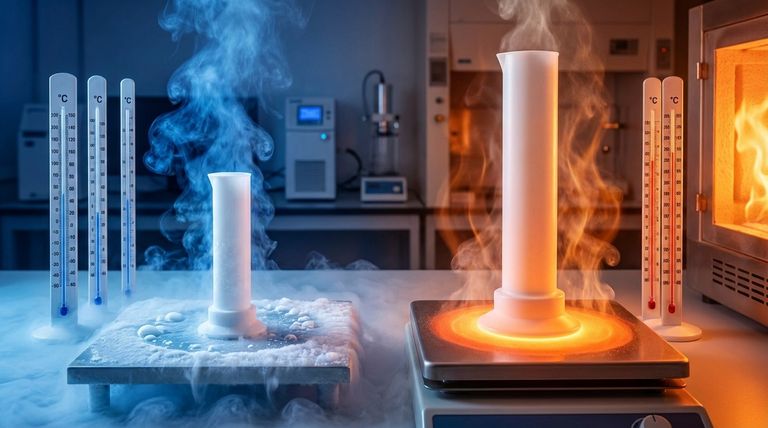
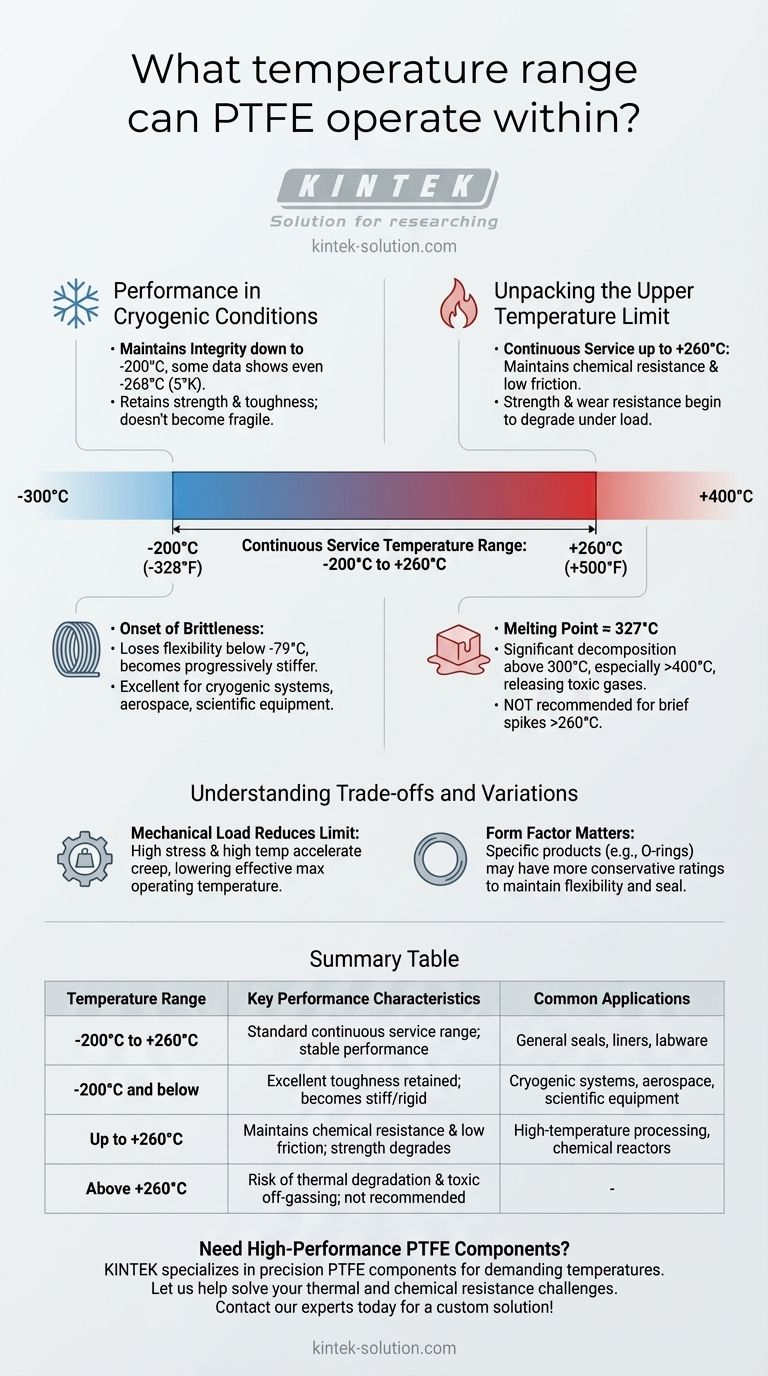
For practical engineering purposes, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a continuous service temperature range of approximately -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). While some sources may cite slightly different numbers, this range represents the widely accepted industry standard for where the material remains stable and performs reliably under most conditions.
The key to successfully using PTFE is understanding that its mechanical properties change significantly at the extremes of its temperature range. The number itself is only the starting point; the real consideration is how the material will behave under the specific stresses of your application.

Unpacking the Upper Temperature Limit
PTFE's performance in high-heat environments is one of its most defining characteristics, but it's essential to understand its behavior as temperatures rise.
The Continuous Service Temperature
The upper limit of +260°C (+500°F) is the maximum temperature at which PTFE can operate continuously without significant decomposition. It maintains most of its unique properties, including extreme chemical resistance and a low coefficient of friction, up to this point.
Approaching the Melting Point
PTFE has a very high melting point for a polymer, approximately 327°C (620°F). However, the material's mechanical strength and wear resistance begin to degrade well before it reaches this temperature. Operating close to the melting point, even for short periods, can compromise the material's structural integrity.
The Risk of Thermal Degradation
Exceeding the service temperature poses a significant safety risk. Above 300°C, and especially above 400°C, PTFE begins to decompose and can release toxic fluorocarbon gases. This makes proper temperature control a critical safety measure in any high-heat PTFE application.
Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
Just as impressive as its heat resistance is PTFE's ability to function in extreme cold. It is a preferred material for many cryogenic applications where other polymers would fail.
Maintaining Integrity at Low Temperatures
PTFE can function effectively down to approximately -200°C (-328°F). Some data shows it retains strength and toughness at even lower temperatures, down to -268°C (5°K). Unlike many plastics, it does not become fragile and fracture easily in extreme cold.
The Onset of Brittleness
While PTFE retains its toughness, it does lose flexibility as it gets colder. It becomes progressively stiffer, which is a critical design consideration for applications requiring movement or sealing at cryogenic temperatures. It maintains good flexibility down to around -79°C (-110°F), but becomes much more rigid below that.
Why It Excels in Cryogenics
The material’s stable molecular structure allows it to maintain useful strength and self-lubricating properties even when frozen. This unique combination makes it invaluable for components in aerospace, space applications, and scientific equipment that operate in deep cold.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
The official temperature range of a material is a guideline, not an absolute law. The real-world performance depends heavily on the specific application and form of the material.
Form Factor Matters
You will often see slightly different temperature ratings for specific PTFE products, such as O-rings. An O-ring listed for -62ºC to 232ºC is likely rated more conservatively because it must remain flexible to maintain a seal under pressure. The core material is the same, but the performance requirement changes the "safe" operating range.
Mechanical Load Reduces the Limit
The published service temperature range assumes minimal mechanical stress. If a PTFE component is under a significant load, its effective maximum operating temperature will be lower. High stress and high temperature combined can accelerate creep and cause the part to fail long before the material itself degrades.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use these principles to determine if PTFE is the correct material for your specific thermal environment.
- If your primary focus is high-heat applications (up to 260°C): PTFE offers exceptional thermal stability, but you must account for the gradual loss of mechanical strength as temperatures rise, especially under load.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic applications (down to -200°C): PTFE is an excellent choice for its retained toughness, but your design must accommodate its significant loss of flexibility in extreme cold.
- If your application involves brief spikes above 260°C: This is generally not recommended. You risk compromising the material's integrity and, more importantly, creating a safety hazard from off-gassing.
Ultimately, choosing the right material means looking beyond a single data point and considering the full context of your application.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Performance Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to +260°C | Standard continuous service range; stable performance | General seals, liners, labware |
| -200°C and below | Excellent toughness retained; becomes stiff/rigid | Cryogenic systems, aerospace, scientific equipment |
| Up to +260°C | Maintains chemical resistance & low friction; strength degrades | High-temperature processing, chemical reactors |
| Above +260°C | Risk of thermal degradation & toxic off-gassing; not recommended | - |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Temperatures?
Understanding the temperature limits is just the first step. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that are engineered to perform reliably within these challenging thermal environments. Whether your application is in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we ensure your parts meet exact specifications, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you solve your thermal and chemical resistance challenges. Contact our experts today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables



















