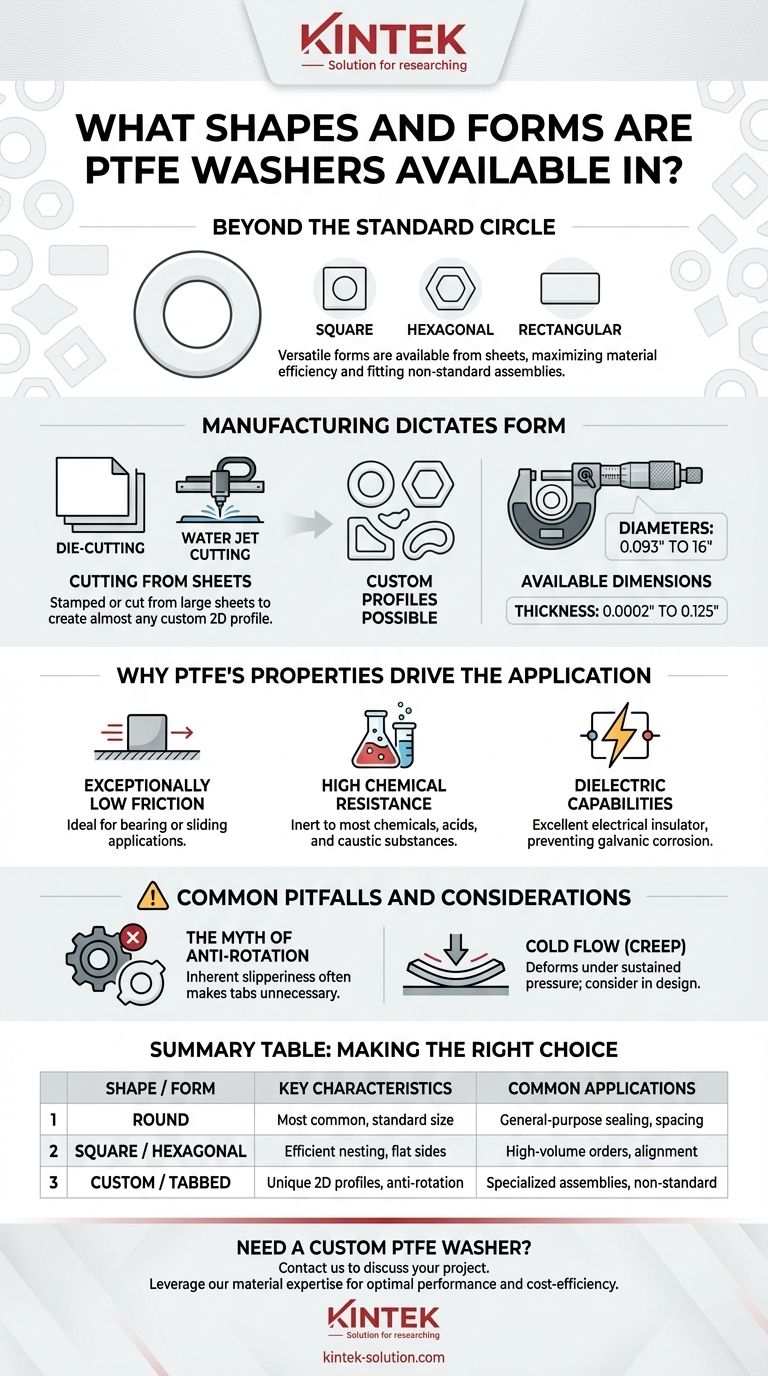
Beyond the standard circle, PTFE washers are available in a wide range of shapes including square, hexagonal, and rectangular forms. Their true versatility comes from manufacturing processes like die-cutting and water jet cutting, which allow them to be produced in nearly any custom two-dimensional profile required by a specific application.
The shape of a PTFE washer is rarely a limitation. While the round washer is most common, the material's easy machinability from sheets means its form can be adapted to solve specific engineering challenges, from maximizing material efficiency to fitting into non-standard assemblies.
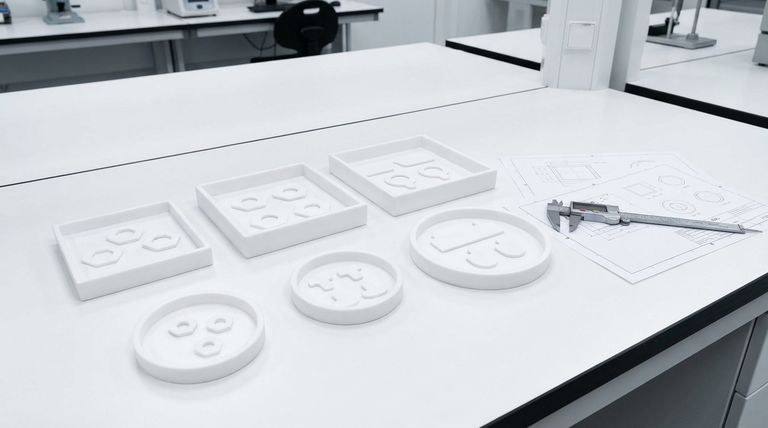

Standard vs. Custom Shapes
The geometry of a PTFE washer is dictated by its intended function and the constraints of the assembly. While a simple circle solves most problems, other shapes offer distinct advantages.
The Ubiquitous Round Washer
This is the most common form, used for general-purpose sealing, spacing, and bearing applications under the head of a bolt or screw.
Square, Rectangular, and Hexagonal
These shapes are often specified for two primary reasons. First, they can be nested more efficiently on a sheet of PTFE material during production, reducing waste and cost on large orders. Second, their flat sides can mate against other components to prevent rotation or align within a specific housing.
Custom and Tabbed Designs
For highly specialized applications, washers can be produced with unique features. Tabs or "ears" can be added to lock into a corresponding slot, providing a mechanical anti-rotation feature. However, PTFE's extremely low coefficient of friction often makes this unnecessary, as the washer is unlikely to bind.
How Manufacturing Dictates Form
The shape possibilities are a direct result of how PTFE washers are made. They are not typically molded but are instead cut from semi-finished sheets or plates.
Cutting from Sheets
Processes like die-cutting, water jet cutting, and flash cutting are used to stamp or cut washer shapes from large sheets of PTFE. This fabrication method is what makes creating custom 2D profiles both possible and economical.
Available Dimensions
This process allows for an enormous range of sizes. Washers are commonly available with diameters from 0.093 to 16 inches and thicknesses from a very thin 0.0002 to 0.125 inches.
Why PTFE's Properties Drive the Application
The choice to use a PTFE washer, regardless of its shape, is driven by the material's unique combination of properties. Understanding these characteristics is key to leveraging the material correctly.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE is one of the most slippery materials known, making it an ideal choice for bearing or sliding applications where you need to reduce friction between two surfaces.
High Chemical Resistance
The material is inert to most chemicals, acids, and caustic substances. This makes PTFE washers essential in highly corrosive environments where metals or other plastics would quickly degrade.
Dielectric Capabilities
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. Washers made from it are used to isolate fasteners from a chassis or to prevent galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While versatile, PTFE has specific behaviors that must be accounted for in any design. Ignoring them can lead to component failure.
The Myth of Anti-Rotation
Adding tabs to a PTFE washer to prevent it from spinning is often a redundant design choice. The material's inherent slipperiness means it is very unlikely to create enough friction to rotate with a fastener as it's being tightened.
Cold Flow (Creep)
A critical characteristic of PTFE is its tendency to "creep" or cold flow under sustained pressure. If you apply too much compressive load, the washer will slowly deform over time, which can lead to a loss of bolt preload and a loose connection. This must be a primary consideration during the design phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select the washer shape and design based on the primary objective of your application.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose spacing or sealing: A standard circular flat washer is the most cost-effective and widely available solution.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost on a high-volume run: Inquire about square or hexagonal shapes that allow for more efficient material nesting during manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is fitting a non-standard assembly: Leverage water jet or flash cutting to create a fully custom profile that perfectly matches your design's geometric constraints.
Ultimately, understanding these options allows you to specify a PTFE component that is perfectly suited to your design's unique demands.
Summary Table:
| Shape/Form | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Round | Most common, standard size | General-purpose sealing, spacing, bearing under bolt/screw |
| Square/Rectangular/Hexagonal | Efficient material nesting, flat sides prevent rotation | High-volume orders, cost-saving, alignment in housings |
| Custom/Tabbed Designs | Unique 2D profiles, anti-rotation features | Specialized assemblies, non-standard geometric constraints |
Need a custom PTFE washer for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get the perfect shape and form to solve your unique engineering challenges in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Contact us today to discuss your project and leverage our material expertise for optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















